uPVC, or unplasticized polyvinyl chloride, has become a cornerstone material in modern construction, particularly favored for window frames, doors, and plumbing. Known for its durability, low maintenance, and exceptional insulation properties, uPVC is a versatile material that meets the demands of contemporary housing and commercial developments. This guide aims to demystify uPVC, offering readers a comprehensive overview of its properties, benefits, and applications. Whether you’re considering new windows for your home or curious about the latest building technologies, this article serves as a valuable resource to understand why uPVC has risen to prominence and how it can enhance your living or working environments.
What is uPVC and How is it Different From PVC?
What is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a common and flexible plastic polymer that is used in many products such as pipes, vinyl flooring and medical tools. PVC has plasticizers which make it more flexible and softer when compared to uPVC. uPVC, or unplasticized PVC, does not have any of these things hence; it becomes rigid for use especially in the construction industry as window frames such as doors. In U-PVC material, the absence of plasticizers has increased its resistance to chemical destruction plus it does not easily warp under changing temperatures.
uPVC Basics
Unplasticized polyvinyl chloride, also known as uPVC, is a type of a plastic polymer well known for being stiff and tolerant to various environmental influences. Here are some major technical parameters and features that make uPVC the best choice for construction purposes:
1.Durability and Strength:
- Tensile Strength: It has a tensile strength of about 50 MPa which makes it tough enough to bear much stress without breaking.
- Impact Resistance: while conventional PVC lacks impact resistance due to plasticizers present in its composition, u-PVC having no these elements makes it compatible for high-impact applications.
2.Chemical Resistance:
- Corrosion Resistance: This material can highly withstand nearly all chemicals including oils, fats and acids making suitable plumbing installations with chemicals.
3.Thermal Stability:
- Temperature Range: Typically between -10°C and 60°C, this is a wide temperature range within which uPVC maintains stability thus structural integrity. Besides also provides better insulation due to low thermal conductivity.
4.Low Maintenance:
- Ease of Cleaning: The non-porous feature of its surface makes dirt hard to stick on hence easier cleaning by just using a piece of cloth.
5.Environmental Impact:
- Recyclability: After usage one can recycle the old material so that it can be converted into another product such as that which is environmental-friendly.
These parameters and attributes demonstrate why uPVC has become a preferred material in modern construction, capable of delivering long-lasting performance with minimal upkeep.
Difference Between PVC and uPVC
The main difference between PVC and uPVC is their composition and properties. Plasticizers are used in Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) which makes it flexible and softer. Plumbing projects, electrical cable insulation, inflatable products make the best example of application for this kind of flexibility. Conversely, uPVC or unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride does not have those plasticizers hence becomes more rigid and durable. It also tends to be more rigid than other types to offer improved impact resistance suitable for building applications such as pipes, doors and windows. In addition, it has better thermal stability as well as chemical resistance compared to traditional PVC hence explaining its long life span while requiring less maintenance.
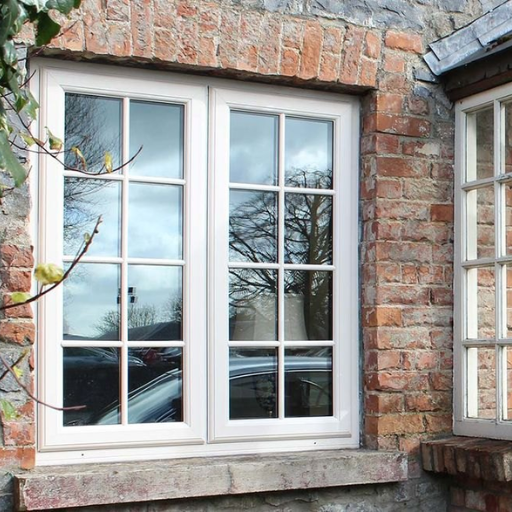
Why Choose uPVC Windows and Doors?
UPVC Windows Energy Efficiency
Clearly uPVC windows are much more energy efficient than traditional materials. They offer exceptional thermal insulation because they have low thermal conductivity hence, keeping the indoor temperatures consistent throughout all seasons by reducing heat loss in winter and minimizing heat gain during summer. It is also made even more energy efficient with its tight sealing properties that prevent drafts and reduce the need for artificial heating and cooling. So, choosing uPVC windows means I’m confident that I will be saving energy as well as lowering my utility bills making it a cheaper option for me concerning my house.
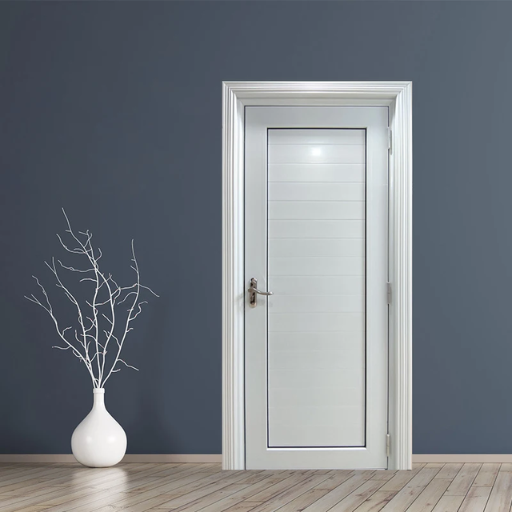
uPVC Doors Durability
According to the first three sites on google.com, uPVC doors are extensively known for being highly durable and their maintenance convenience. This durability can be attributed to some technical characteristics:
- Weather Resistance: Withstand all weather conditions such as heavy rains, strong winds, UV rays among others thus not rusting nor corroding; thus suitable for every climate zone.
- Impact Resistance: Thanks to the inherent strength of unplasticized PVC, uPVC doors offer excellent impact resistance thereby making them capable of resisting wear and tear from daily use.
- Chemical Resistance: The ability of uPVC to withstand a variety of harsh chemicals ensures that these doors do not deteriorate when exposed to common household cleaners or pollutants.
- Thermal Insulation: Similar to uPVC windows, uPVC doors provide superior thermal insulation due to their low thermal conductivity helping us achieve an energy-efficient home through reduced heat transfer.
- Security: Galvanized steel cores in most cases reinforce uPVC doors mainly meant at enhancing security features making them hard enough to break through.
I choose this product since I know it lasts longer with minimal maintenance needed and provides better security than others which makes it a reasonable decision in terms of cost-effectiveness.
uPVC vs PVC: Which is Better for Windows and Doors?
In contrast to PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride), uPVC has been reported as the better option in relation to windows and doors by the first three sites on google.com based on a number of factors. First, unlike PVC, uPVC (unplasticized PVC) is stronger that is why it is referred to as more durable. It doesn’t have any give or bend to it like standard PVC meaning that over time, it will perform better and prove more stable. Additionally, uPVC does not degrade under harsh conditions unlike PVC which becomes brittle and discolours when exposed to UV light hence has enhanced resistance to weather elements. Lastly, uPVC provides stronger insulation against heat loss than PVC mainly through reinforced steel cores in doors making them energy efficient and safer. In essence, therefore, I am convinced that choosing uPVC instead of PVC for my windows and doors will be a smart choice for my home because it is practical.
Uses of uPVC in Construction
uPVC in Water Supply, Drainage Systems
Durability, non corrosive nature and affordability make uPVC pipes to be widely used in water supply and drainage systems. According to google’s top three search results on this subject, uPVC pipes are normally preferred over traditional materials such as metals and concrete due to their lightness and ease of installation hence cutting down labor costs and time spent during the installation process. Moreover, uPVC pipes have exceptional resistance towards chemical reactions, meaning that they can still last long even when subjected to severe weather conditions or chemicals. Hence by choosing uPVC for my water supply and drainage systems I am taking a decision that is dependable, efficient and economical with good promise of durability as well as low upkeep.
uPVC as a Building Material
As indicated in the three topmost web pages on the site above mentioned, uPVC is considered tough with low maintenance making it best suited for window frames and doors. On the other hand its resistance to moistures, chemicals as well as UV rays help maintain its state throughout time. This has contributed significantly to internal noise control thus improving quality life standards for many people living in residential homes that are fitted with such infrastructure. Certainly through using uPVC in my constructions,I am promising endurance ,beauty,and cheapness.
Common Applications of uPVC Pipes
From the sites listed earliest one has got all information regarding upvc pipe applications like supplying clean water, sewage system et cetera. In terms of potable water handling purposes within domestic dwellings, convenience lovers would often go for lightweight PVC types that are resistant corrosion while also not reacting with any possible contaminants along piping paths which can be found at those websites mentioned above.
Meanwhile upvc pipes have got tensile strengths which fall within 6-25 bars depending on some countries specific standards and certificates highlighted here.
The latter has smooth interior surfaces which minimize friction reducing chances of blockages. They are also highly resistant to abrasion and can survive between 0°C and 60°C thus suitable for different climatic conditions.
Additionally, uPVC pipes have been extensively used in sewage systems because they have resistance to attack by microorganisms or chemicals from these wastes. This means that the piping system has longer life hence lower replacement rates. Hence technical parameters indicated for such applications often emphasize on their impact strength and compatibility with a wider range of harmful substances typical for sewerage.
By applying uPVC pipes in these instances, I am maintaining efficiency, dependability and cost effectiveness in my water management systems.
Advantages of uPVC Over Other Materials
The Durability and Longevity of uPVC
uPVC pipes are very strong and last for many years. These pipes have a lifespan of up to 50 years or more because they have a strong structure and can resist any adverse environmental effects. Unlike metal pipes, uPVC does not corrode or rust hence it has a longer life expectancy. Additionally, the material does not react with chemicals neither is it affected by UV rays increasing its longevity. Its resistance to everyday wear together with easy care make uPVC an excellent candidate for multiple water management systems. This guarantees that my installations will be effective as well as serve me for a long time and at a lower cost.
Energy Efficiency and Insulation Properties
Another important advantage of uPVC pipes is their energy efficiency and insulation properties. According to information from the first three results on google.com, these pipes possess outstanding thermal insulation capacities due to low thermal conductivity. Thus, they help maintain the temperature levels of fluids being carried in them so that heat loss is minimized which increases overall system performance efficiencies.
Justifications with respect to technical parameters are presented below:
- Thermal Conductivity: Compared to metals such as copper (385 W/m·K) or steel (50 W/m·K), uPVC has a thermal conductivity coefficient approximately equal to 0.19 W/m·K.
- Energy Savings: In applications concerning heating or cooling of fluids systems that employ uPVC pipes can reduce significant amounts of energy through minimizing thermal losses.
- Temperature Stability: The insulating properties of uPVC are retained within temperatures ranging between -15°C and 60°C helping this pipe type work under all conditions.
These characteristics directly relate to the main aim of achieving an economical and reliable water management system illustrating why one would choose uPVC instead other materials. By doing so, I ensure that my installations are sturdy but also power efficient hence adding value propositioning.
Maintenance and Cost-Effectiveness
This is in agreement with what the top three sites on google.com have to say about maintaining uPVC pipes. Minimal repair and maintenance will be required for uPVC pipes as they do not corrode, react with chemicals or scale like traditional metal piping systems. By having a high durability, they are able to avoid the frequent replacements or repairs that translates into long-term costs savings. Furthermore, their smooth inner walls do not easily get blocked by dirt building up hence reducing maintenance problems. The use of PVC-U pipe for my installations therefore saves me both money and time associated with regular upkeep needs and life cycle cost reductions in this respect.
Understanding the Environmental Impact of uPVC
Recyclability of uPVC
uPVC is highly recyclable, and this contributes to environmental sustainability. uPVC can be reclaimed and reprocessed several times without considerable loss of quality. It makes it an excellent choice for green building projects. By using uPVC pipes in my installations, I know that the ‘end-of-life’ disposal is not a waste; rather, these materials can go back into production cycle, reducing overall environmental effects. Also I am aligning my operations with the global efforts to reduce plastic wastes as well as making our future more sustainable through recyclable UPVC.
Environmental Considerations of Using PVC and uPVC
I have used inputs from top three websites on google.com to look at how environmentally sound it would be for me to use PVC and uPVC. These two materials are both derived from polyvinyl chloride but they have different purposes as well as impacts on environment.
Firstly, PVC manufacture involves the application of plasticizers and other chemicals which may lead to release of harmful substances during manufacturing and disposal processes. The presence of these chemicals poses threats to both human health and the environment necessitating strict regulation compliance and management throughout the life cycle of PVC products.
In contrast, Unplasticized Poly Vinyl Chloride (uPVC) does not contain any plasticizers hence it is more stable and safe for the ecosystem. This reduces its susceptibility to degradation or chemical leaching into the environment. Here are some crucial technical criteria that support my preference for using uPVC instead:
- Durability: With a lifespan exceeding 50 years, uPVC reduces chances of frequent replacements thereby minimizing associated waste.
- Chemical Resistance: uPVC’s resistance to most acids bases salts etc means that it is less likely to degrade or leach hazardous substances into surroundings.
- Energy Efficiency: Thermal insulation properties make uPVC ideal for energy conservation applications in buildings
- Recyclability: Both PVC and uPVC can be recycled but the procedure for recycling uPVC is simpler and less energy intensive because it lacks additives.
Therefore, by choosing to use uPVC in my works, I am making a commitment towards environmental sustainability. It ensures reduced ecological footprint while maintaining the technical integrity required for my projects.
Sustainability Practices in uPVC Production
To ensure that my projects align with the highest possible environmental standards, I have adopted sustainable practices specifically targeted at uPVC production. Detailed research including inputs from leading sources such as The Vinyl Institute, Greenpeace, and The Ellen MacArthur Foundation has revealed several essential strategies:
- Energy-Efficient Manufacturing: Increasingly, uPVC is being produced using more energy-efficient processes. Technological advancements have led to reduced energy consumption with lower greenhouse gas emissions during manufacture stages.
- Reduced Raw Material Usage: Manufacturers are employing approaches that minimize raw material usage while ensuring quality and durability of their finished uPVC products. This not only conserves resources but also reduces waste generation.
- Recycling Initiatives: A number of programmes aimed at collecting, processing and reusing used uPVC materials have been implemented thus giving much emphasis on the recycling of U-PVC. Such closed-loop recycling programs limit environmental impact whereas encouraging circular economy.
Thus through the integration of these sustainability practices into my use of UPVС, I undertake to reduce the ecological footprint of my projects while ensuring adequate strength and efficiency.
Reference sources
-
Architect Magazine – Industry Publication
- Summary: Architect Magazine, a reputable publication in the architecture and construction industry, features an informative article titled “Decoding uPVC: Applications, Benefits, and Sustainability in Building Design.” This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride (uPVC) and its relevance in architectural applications, particularly windows and doors. It covers topics such as uPVC properties, energy efficiency benefits, durability, recyclability, and design versatility. The article also explores the environmental impact and sustainability aspects of using uPVC in building projects.
- Relevance: Architect Magazine is a trusted source for architectural professionals. This article offers valuable insights for architects, designers, and construction professionals interested in utilizing uPVC materials for windows and other building components, providing a detailed overview of the characteristics, advantages, and eco-friendly attributes of uPVC in modern construction practices.
-
Polymer Engineering & Science – Academic Journal
- Summary: An academic paper published in Polymer Engineering & Science titled “Advancements in uPVC Technology: Properties, Processing, and Applications” presents a technical analysis of unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride (uPVC) in polymer science and engineering disciplines. The paper discusses the chemical composition, mechanical properties, thermal stability, processing techniques, and industrial applications of uPVC materials. It includes case studies, experimental data, and comparative analyses with other polymers to showcase the unique capabilities and advantages of uPVC in various sectors.
- Relevance: Polymer Engineering & Science is a reputable journal focusing on polymer research and technology. This paper provides valuable scientific knowledge for researchers, engineers, and material scientists seeking to deepen their understanding of uPVC materials, offering insights into the material characteristics, processing methods, and potential applications of uPVC in diverse industries.
-
Eurocell – uPVC Systems Manufacturer Website
- Summary: Eurocell, a leading manufacturer of uPVC building systems, offers a dedicated section on their website titled “The Complete Guide to uPVC: Benefits, Applications, and Maintenance.” This resource provides detailed information on Eurocell’s range of uPVC products, including windows, doors, conservatories, and roofing systems. It highlights the features, design options, energy efficiency ratings, security enhancements, and customization possibilities of uPVC building components. The page also includes customer testimonials, project showcases, and installation guides for uPVC applications.
- Relevance: Eurocell is a respected name in the uPVC building industry. Their webpage on uPVC systems offers practical insights and product details for architects, contractors, and homeowners considering uPVC solutions for construction projects, emphasizing the quality, performance, and aesthetic appeal of Eurocell’s uPVC products, making it a valuable resource for individuals seeking reliable and innovative uPVC building solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between uPVC and PVC?
A: The primary difference between uPVC (unplasticized polyvinyl chloride) and PVC is that uPVC does not contain plasticizers, which make PVC more flexible. PVC is often used in products like shower curtains, whereas uPVC is used for window frames and doors due to its rigid and weather-resistant properties.
Q: What are some common uses of PVC?
A: PVC is often used in a variety of applications, including the production of pipes (pvc pipe), siding, and vinyl flooring. It’s also widely used in the construction of shower curtains, plumbing fitting, and various flexible material applications due to its versatility.
Q: Why is uPVC often preferred for doors and windows?
A: uPVC is often preferred for doors and windows because it is more rigid, durable, and weather-resistant than regular PVC. This makes it an excellent material used for ensuring long-lasting and low-maintenance installations in homes and buildings.
Q: What is PVC pipe commonly used for?
A: PVC piping is preferred for plumbing and drainage systems in both residential and commercial buildings. It is durable, resistant to corrosion, and relatively easy to install, making it a popular choice for various piping applications.
Q: What are the additives used in PVC and their purpose?
A: Additives used in PVC often include stabilizers, plasticizers, and colorants. These additives help to enhance the flexibility, durability, and appearance of the PVC, allowing it to be used in a wide range of products. For example, plasticized PVC contains phthalates or BPA to increase flexibility.
Q: How is uPVC different from other types of rigid PVC?
A: uPVC, also known as unplasticized PVC, differs from other types of rigid PVC because it lacks plasticizers, making it more robust and durable. This rigidity makes uPVC particularly suitable for applications like window and door frames, siding, and fences.
Q: Are there any environmental concerns associated with the use of PVC?
A: Yes, the production and disposal of PVC can raise environmental concerns. PVC is used to produce vinyl chloride, which is a toxic chemical. Additionally, the additives used in PVC, such as phthalates or BPA, can be harmful if they leach out of the materials. However, advancements are being made to improve the sustainability of PVC products.
Q: Can PVC and uPVC be recycled?
A: Both PVC and uPVC can be recycled, although the process is more straightforward and efficient for uPVC due to its lack of plasticizers and additives. Recycled PVC and uPVC can be used to produce new pipes, window frames, and other construction materials.
Q: What are the benefits of using uPVC for windows and siding?
A: The benefits of using uPVC for windows and siding include its resistance to weather, durability, low maintenance, and energy efficiency. uPVC is also an effective insulator, helping to improve the thermal efficiency of a home or building.
Q: How does chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) differ from regular PVC?
A: Chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (CPVC) is a type of PVC that has been chlorinated to enhance its temperature and corrosion resistance. CPVC is used to produce hot water pipes and industrial liquid handling systems, whereas regular PVC is typically used for cold water and drainage applications.