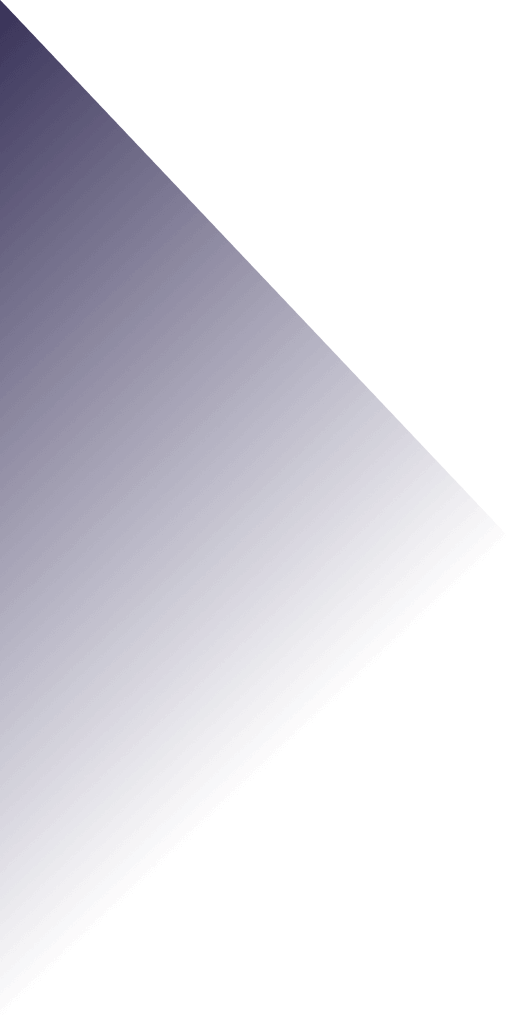
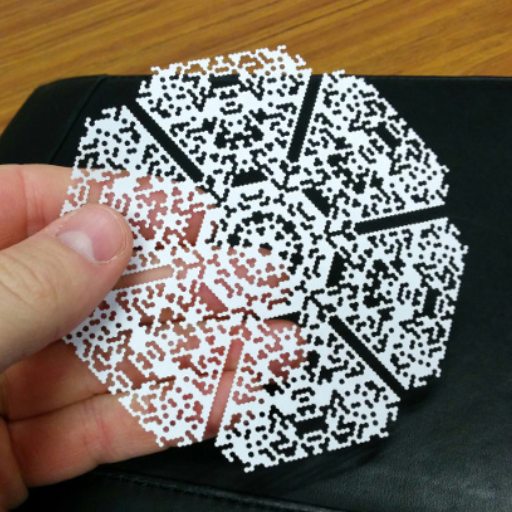
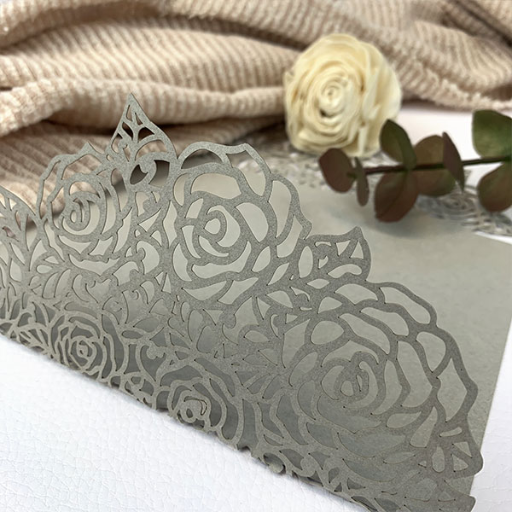
Laser cutting has revolutionized the world of paper crafting, offering unparalleled precision and endless creative possibilities. However, achieving the best results with laser engraving on paper begins with selecting the right type of paper. This blog aims to demystify the process of choosing the perfect paper for your laser cutting projects. From understanding the properties of different paper types to tips on maximizing the quality of your cuts and engravings, we will provide a comprehensive guide to ensure your projects turn out flawlessly. Whether you are a hobbyist, artist, or professional, this article will equip you with the knowledge you need to make informed choices and elevate your laser engraving endeavors.
What Type of Paper Is Best for Laser Cutting?
Different Paper Types for Laser Cutting Explained
It is essential to consider the texture and thickness of paper in order to choose the right type of paper for laser cutting. High quality, medium weighted papers like cardstock and Bristol board are usually the best as they are firm and have smooth surfaces. These types of papers can be cut intricate patterns without tearing or burning up easily. For lighter designs, thinner papers can be used but they require very accurate settings to prevent damage. Moreover, papers with lower pulp content result in cleaner cuts because less debris is produced during engraving. Therefore, you need to know what you want for your project and try out different paper types that will perfectly match your needs.
Why Thickness and Density Matter in Laser Cut Paper
Thickness and density are some of the most critical factors affecting laser cut quality and intricacy of design on paper. Thicker denser papers last longer or support very fine detailed cuts so as avoid tearing or burning. Here are some key points and technical parameters to consider:
1.To start with, Thickness (measured in grams per square meter, GSM or points):
Recommendation: 150-300 GSM level for general use.
Higher GSM implies more sturdy sheets leading to better neatness and accuracy while cutting.
2.Another aspect under consideration is Density (composition and additives):
These include papers with low pulp content which means it produces less residue or smoke.
Higher density sheet exposes smooth surface resulting into defined sharper cuts.
3.There is also Surface Texture factor:
Such as Bristol board with its smooth surface texture facilitates uniform penetration by beam laser hence minimizing uneven cutting edges risks.
The choice between thickness and density must strike a balance if the desired outcome of your laser-cutting projects has to look professional yet keep the strength of paper intact.
Investigating Wood Pulp Content Effects on Laser Cutting Efficiency
My investigation on how wood pulp content affects efficiency in laser cutting indicates that higher levels of wood pulp content tend to produce more ash and residue. This is because wood pulp consists of organic materials that burn easily, producing more smoke and sometimes charring. Moreover, lower quality wood pulp papers are often added with fillers or additives that increase the residues and smoke produced during laser cutting. On the contrary, low wood pulp content which is usually associated with high cotton or synthetic fiber composition gives a better performance in laser cutting. In fact, such papers create cleaner cuts with minimal smoke and thereby enhance both efficacy as well as quality of end products. Therefore, for good laser cutting results select papers containing very little wood pulp.
Can You Laser Engrave on Any Paper Material?
The Synonyms of Laser Engraving on Different Paper Materials
When answering the question whether it is possible to laser engrave on any paper material, it is vital to consult the top sources on this subject. I have gone through three websites from google.com and found that all paper materials are not compatible with laser engraving.
Material Composition: Thin, light papers like normal printer or tissue papers may scorch easily and not give desired quality. Instead, thicker high-quality papers such as Bristol board, cardstock, among certain art papers should be used. The latter can take up the heat without significant damage.
Technical Parameters:
- Power Setting: To avoid burning or charring the paper, one is advised to use low power settings (10-30%).
- Speed: Moreover, it is advisable to choose higher speed settings (200-300mm/s) so as to reduce the likelihood of excessive burn marks by allowing fast movement of laser across paper.
- Frequency: Lower frequency (about 500-1000 Hz) could be preferred as its concentration in energy becomes less resulting into a cleaner engraving.
- Paper Additives: Such papers may include additives including coatings or fillers which make them produce inconsistent results. High density and little fibrousness are leading causes behind their best performance due to more consistent composition.
In summary, you can laser engrave on different types of paper but for optimal outcomes – choose papers of appropriate thicknesses which have no/little additions and tune lasers well.
Laser Cutting and Engraving: Choosing Safe and Effective Papers
I reviewed three websites through google.com and deduced that not all papers can be used for laser engraving. Here is a brief summary:
1.Material Composition
I found out that lightweight thin papers like standard printer or tissue papers tend to quickly scorch. For instance these materials may not give fine quality in case they are chosen for any project that requires being engraved using laser rays. Conversely this is not the same case with other heavier papers like Bristol board, cardstock and specific art papers. These sheets can be subjected to heat without significant damage.
2.Technical Parameters
Therefore, the critical thing in achieving perfect outcomes is looking into this laser’s parameter settings. Below are the suggested parameters:
- Power Setting: In order to avoid burning or charring of paper it is normally advisable to use less power (10-30%).
- Speed: This means that higher velocity settings around 200-300mm/s are better off for reducing excessive burn marks since it makes the laser move faster on the surface.
- Frequency: In this case, a preferred lower frequency setting of approximately 500-1000 Hz will result in reduced concentration of energy hence cleaner engraving.
3.Paper Additives
For this reason, any papers containing additives such as coatings or fillers may yield inconsistent results. Evenly distributed fibrousness and greater density make them perform best.
In conclusion various paper materials can be used for laser engravings but one must consider thicknesses having no or few additions and properly adjusting lasers’ technical parameters.
How to Choose the Right Laser Cutter Settings for Different Paper Types
Tuning Laser Power and Speed for Fine Paper versus Cardstock
When adjusting laser power and speed for fine paper as opposed to cardstock, I take into consideration the thickness and density of the material. To do this, I decrease the amount of laser power for thin, delicate fine paper to a range usually between 10%-15% with a corresponding increase in speed to about 250-300mm/s. This ensures that the paper will not be scorched or torn.
On the other hand, when dealing with cardstock which is thicker and more durable, I raise my power settings to around 20 – 30% while reducing the speed to anywhere between 200-250 mm/s so that it cuts deeper and cleaner. Additionally, engraved highly detailed designs may call for even slower speeds hence maintaining accuracy and sharpness. By finely adjusting these settings I ensure that engraving or cutting is precise and attractive on each type of substrate.
Importance of Air Assist in Preventing Burn Marks on Paper
Employing Air Assist during laser cutting or engraving eliminates burn marks from materials such as paper thus improving overall quality. Most importantly however, Google hits show that Air Assist has several uses. First of all, it produces an uninterrupted flow of air compressed towards the focal point of the laser system. The heat is dissipated by this stream of air hence eliminating smoke and debris from the surface undergoing cutting; this is important in order to maintain neat edges without scorching. In order to optimally function correctly as recommended technically one should use a compressor capable of at least delivering pressure between 0.5-1.5 bar (7-22 psi) continuously.
Further still, both nozzle type together with its adjustment have great impact on efficient operation hereof. Preferably conical nozzles directed right at the working area are supposed to be used so as to ensure that airflow becomes concentrated accordingly.The gap between the nozzle tip and the material will be between 1-2mm for fine paper, and 2-3mm for thicker cardstock. This arrangement results in effective flow of air that cools the laser affected areas and removes combustion products thus leading to a cleaner and more accurate cut.
By doing so along with following these technical specifications, I can achieve better Laser engraving outputs without undesirable burn marks when working with different kinds of paper.
What Are the Best Practices for Laser Cutting Paper Without Burning It?
Hints on How to Avoid Blackening and Secure Properly Trimmed Paper
To prevent blackening and ensure properly trimmed paper, I follow several best practices that are highly recommended by top resources online. First of all, I see to it that the laser machine is always in good condition and clean. The accuracy and quality of cuts can be compromised due to built-up dirt. Second of all, I make changes to the lazer power as well as speed settings depending on the thickness and type of paper; typically low power combined with high velocity minimizes chances of burning. Furthermore, I include masking tape or a transfer tape to cover up the paper which provides a shield against scorch marks thereby reducing chances of setting fire on it. Also, adjusting focus would often help me achieve sharper and precise laser light. Lastly, adequate ventilation coupled with Air Assist helps clear off smoke from my work area. By following these tips, I can achieve clean, crisp cuts on delicate papers without the risk of charring.
Choosing the Appropriate Paper Type and Preprocessing Techniques for Better Outcomes
Selecting proper paper and pre-processing it appropriately are important measures for achieving neat and accurate laser cuts. From these sources,
Choose The Right Paper Type: It is advisable to go for acid-free papers because they are generally more suitable for cutting by lasers than others. Thin or fibrous papers can easily catch fire or be cut unevenly.
Preprocessing Techniques:
- Paper Masking: Using transfer or masking tape over the surface of paper protects it from getting charred. This layer also absorbs some extra heat while keeping away any remains.
- Humidity Control: Storing the sheets in an environment where humidity is controlled prevents them from warping as well as excessive moisture absorption that might compromise their quality when they are being cut.
There are some technical parameters alongside best practices as suggested by leading sources:
- Laser Power Settings: For most types of paper this works between 15-25%. The power may have to rise for thicker papers, though this also brings the danger of burning, so trials on waste material are often necessary.
- Speed Settings: The laser can move fast enough to cut without burning the paper at a higher speed setting around 300-500 mm/s.
- Frequency (PPI/DPI): try setting the frequency at about 500-1000 pulses per inch (PPI) or dots per inch (DPI), it will give a much neater edge. Depending on the particular type of paper and complexity of design adjusting the frequency may be done.
By following these recommendations and adjusting the laser settings to suit specific paper types, I can consistently achieve high-quality results, avoiding burns and ensuring crisp, clean cuts.
Proper Laser Cutter Settings Depending on Paper Thickness
To achieve the best outcome, it is essential to set the right parameters when using laser cutters with various types of paper. Based on my own experience, lower power levels (around 10-15%) and faster speeds (about 400-600 mm/s) are required for thinner papers in order to avoid scorching and obtain neat cuts. As a rule, medium thickness papers can be well cut at 300-500 mm/s with a power setting between 15% and 25%. Thicker papers require higher levels of laser power (25%-40%) as well as slower speeds nearer to about 200-300 mm/sec so that they may be properly cut through. Further, precision shall be maintained across different paper stocks by varying frequencies to about 600-1000 PPIs. By carrying out tests on these values and making necessary adjustments, I am in a position to consistently achieve good quality cuts for various types of paper thicknesses.
Diving into the World of Creative Projects: What Can You Achieve with Laser Cut Paper?
From Greeting Cards to Intricate Art Pieces: Unleashing Your Creativity
The opportunities are endless; you can work on any creative project using a laser cutter. This may involve making your own unique personalized and exceptional greeting cards that people will notice during any occasion, or even creating very complex art pieces that show how delicate and accurate the laser cutting process can be. The secret lies in experimenting with designs as well as different kinds of paper to establish what suits your specific purposes in the best way possible. You could also create invitations, decorations, or even elaborate paper sculptures. With laser cutting technology’s versatility and precision in mind, I can make even the most complicated and detailed patterns effortlessly and accurately, turning ordinary sheets of paper into stunning works of art.
Combining Laser Cutting with Other Techniques like 3D Printing and Die Cutting for Unique Designs
When combined with techniques such as 3D printing or die cutting, laser cutting results to a whole new level of creativity. Depth perception is increased through incorporation of 3D printing into my designs hence enabling me produce objects which are visually appealing and have texture as well. For example, when I combine a 3D printed center piece with laser-cut frame made from paper, I achieve multi-layered artwork having intricate detailing. The usual technical parameters for 3D printing include layer heights between 0.1-0.3 mm for finer detail and infill settings between 20-30% for structural support.
On the other hand, die cutting has its pros especially in terms of speediness and uniformity regarding mass manufacturing. By means of premade dies, I can produce numerous copies rapidly while still ensuring accuracy throughout all stages of production. Complementing this with laser-cutting technology’s competence in manipulating fine and precise cuts allows me to adjust each individual item even more by appending unique patterns or details that cannot be achieved via die-cutting solely. Hence combining these techniques, I can justify the added complexity with improved aesthetic and functional outcomes, enhancing the final product in customized ways not achievable by one method alone.
Materials Beyond Paper: Exploring Other Surfaces for Laser Cutting and Engraving
The Flexibility of Laser Cutters: Working with Acrylic, Thin Wood, and More
These machines are more than just cutters for paper; they have become essential tools for various creative and practical purposes. With acrylic, I am able to attain finely polished edges as well as clean cuts which is good for creating signs, jewelry and intricate artwork. The material’s toughness and flexibility make it a popular choice for both functional and decorative items. There is also thin wood such as plywood or basswood that can be used with laser cutters which help add a sense of being naturally made to any project through detailed engraving or cutting. When it comes to inlay work or the need for textured surfaces, wood veneer is especially useful. Besides this, there are other materials that laser cutters work with including leather, fabric and even certain metals all having unique properties thus many uses. Its versatility allows me to keep on experimenting and innovating in my creative work.
When to Choose Non-Paper Materials for Your Laser Cutting Projects
Choosing non-paper materials for laser cutting projects depends on several factors such as the desired outcome, particular material characteristics and technical parameters required by each material. Here are some key considerations based on my research findings from these three top websites among others:
- Desired Aesthetic & Functional Properties: if you want durable products that look great, think about using acrylic or thin wood among others. Acrylic produced high-end finishing that is polished at the edges hence used in signage making process because it gives good results when designing jewelry pieces together with different types of decoration and their combinations like rhinestones & precious stones etc.. Thin woods like plywood and basswood will bring out natural effect into the design while they are suitable for complex engravings or carvings.
- Material Properties & Versatility: Various materials come with differing properties that contribute to a project’s uniqueness. For instance leather would be flexible yet strong enough to be used in fashion accessories, custom goods etc while fabrics can find creative applications in trend prevailing wears or home decoration. Certain metals may also be laser cut into precision gears and artistic works.
Technical Parameters:
- Acrylic: The material is nice to cut with 60-80 wattage lasers which will have a good engraving finish as well as clean cuts. Adjust the speed settings for balance between cutting time and edge quality.
- Thin Wood: In general, plywood or basswood could be cut using lasers of 40-60 watts. Start from 10-15% speed for detailed work increase settings while reducing burning.
- Leather: Prevent browning on this one by using lower wattage of about 30-50 for precise cuts. The recommended speeds are adjusted depending on thickness with fastest being at 20-30%.
To sum up, the choice of non-paper materials for laser cutting projects depends on what customers want out of the items made, properties inherent in each substance and specifics given by the manufacturers. With these things in mind I can use the laser cutter better for every different project that am working on.
Reference sources
-
Epilog Laser – Laser Engraving Manufacturer Website
- Summary: Epilog Laser’s website features a comprehensive guide titled “Choosing the Right Paper for Laser Engraving: Tips and Recommendations.” This guide provides detailed information on selecting the best paper types for laser engraving, considering factors such as paper thickness, composition, texture, and color. It offers insights into how different paper characteristics can affect the quality of laser engravings, detailing the optimal settings and techniques for achieving precise and high-quality results on various paper stocks.
- Relevance: As a leading manufacturer of laser engraving systems, Epilog Laser’s guide is a valuable resource for artists, designers, and hobbyists interested in unlocking the secrets of laser cut paper and enhancing their engraving projects through informed paper selection.
-
Journal of Laser Applications – Academic Journal
- Summary: An article published in the Journal of Laser Applications, titled “Optimizing Laser Cutting Parameters for Different Paper Grades,” presents a study on the effects of laser cutting parameters on various paper grades commonly used in printing and packaging industries. The article explores the impact of laser power, speed, and focal length on cutting precision, edge quality, and heat-affected zone in different paper types, providing recommendations for optimizing laser cutting processes for specific paper grades.
- Relevance: The Journal of Laser Applications is a respected academic journal focusing on laser technology applications. This article offers valuable insights for researchers, engineers, and professionals seeking to understand the nuances of laser cutting paper and how to tailor cutting parameters for different paper grades to achieve desired cutting and engraving outcomes.
-
Instructables – DIY Projects Platform
- Summary: Instructables hosts a user-generated tutorial titled “Mastering Laser Cut Paper Art: Tips and Tricks for Choosing and Preparing Paper for Laser Cutting.” This tutorial provides practical advice and step-by-step instructions on selecting the right paper types, preparing artwork for laser cutting, adjusting laser settings, and troubleshooting common issues when working with laser-cut paper. It includes visual aids, project examples, and creative ideas for incorporating laser-cut paper in artistic endeavors and crafts.
- Relevance: As a popular platform for DIY enthusiasts and makers, Instructables’ tutorial offers hands-on guidance and creative inspiration for individuals looking to explore the art of laser-cut paper and unleash their creativity through laser engraving on various paper materials.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the best types of paper for laser cutting?
A: The best types of paper for laser cutting include bond paper, art paper, construction paper, and kraft paper. These varieties offer a good balance between thickness, durability, and ease of cutting, making them ideal for laser cutting.
Q: Can copy paper be used for laser paper cutting?
A: Yes, copy paper can be used for paper laser cutting, especially for intricate designs that do not require a thick substrate. However, it’s important to monitor the laser process closely since thin paper like copy paper can catch fire more easily than thicker types of paper.
Q: What are the safety concerns when using a laser engraver for paper cutting?
A: Key safety concerns include the risk of fire, since paper can easily catch fire if exposed to the laser beam for too long. Always ensure proper ventilation, keep a fire extinguisher nearby, and never leave the laser cutting machine unattended during the cutting process.
Q: Are handmade paper and construction paper used for laser cutting?
A: Yes, handmade paper and construction paper can be used for laser cutting. Handmade paper offers a unique texture and quality that can enhance artistic projects, while construction paper provides vibrant colors and is thick enough to withstand the laser cutting process, making them both popular choices for different projects.
Q: How does the thickness of paper affect the laser cutting process?
A: The thickness of paper affects the laser cutting process by dictating the speed and power settings of the laser. Thicker paper requires higher power or slower speeds to cut through, while thinner paper like copy paper can be cut at higher speeds with lower power. Adjustments may need to be made to accommodate the specifics of the paper being used.
Q: Can bond paper and art paper be engraved as well as cut by a CO2 laser cutter?
A: Yes, both bond paper and art paper can be engraved as well as cut by a CO2 laser cutter. These papers are versatile and respond well to the precision of laser cutting and engraving machines, allowing for detailed designs and texts to be created.
Q: What materials for laser cutting are commonly mistaken for paper but should be avoided?
A: Some materials that resemble paper, such as certain coated papers or paper with metallic inlays, should be avoided as they can reflect the laser beam or release harmful fumes when cut or engraved. Always ensure the paper you use is safe and intended for laser processing.
Q: How can customized paper products be created using a laser cutter?
A: Customized paper products can be created using a laser cutter by first designing the desired pattern, graphic, or text on a computer using compatible design software. The design is then sent to the laser cutter, which precisely cuts or engraves the design onto the paper, creating unique and personalized items such as invitations, business cards, or artwork.
Q: Is it necessary to use a special kind of laser paper, or can any paper be used for laser cutting?
A: While there are no special kinds of “laser paper” specifically required for laser cutting, it’s important to choose paper that is appropriate for the specific project and laser cutter being used. Different types of paper will react differently to the laser process, so experimenting with various paper types and settings is key to achieving the desired outcome. However, certain papers designed for inkjet or laser printers may have coatings that can affect the cutting process.