Polystyrene is a term that surfaces often during discussions about substances found in daily commodities, but some may not know what it exactly means. On its simplest level, polystyrene is one of the many different kinds of plastics utilized in many ways across diverse applications, starting from packaging materials such as foam peanuts to disposable coffee cups and insulating buildings. This article will go into the various forms assumed by polystyrene, describe its characteristics and investigate its uses in different industries. By knowing the diverse kinds of polystyrene we can understand their various functions in modern life.
What Is Polystyrene and How Is It Made?

Image source: https://plasticseurope.org/
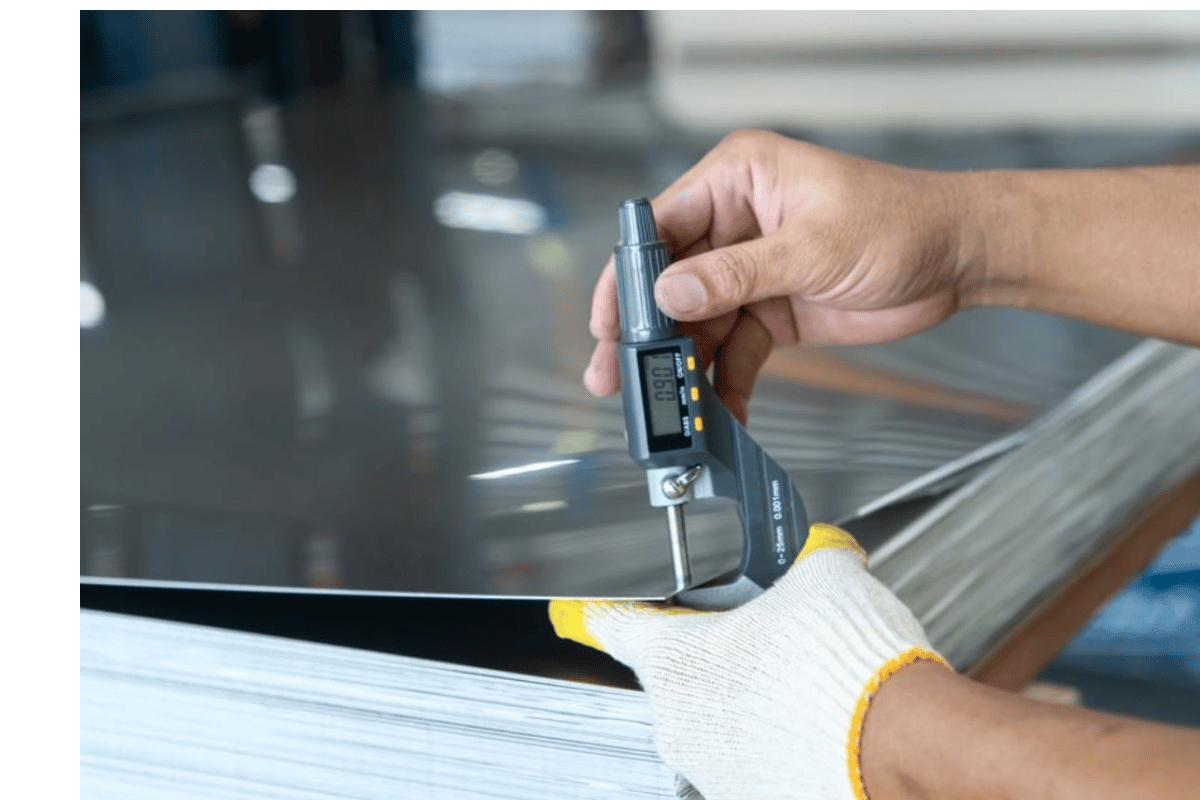
Synthetic aromatic hydrocarbon polymer produced from monomer styrene, a liquid hydrocarbon that is commercially manufactured from petroleum is called polystyrene. Polymerization reaction process of making polystyrene consists of joining together styrene molecules in a pattern which repeats itself resulting into long chains. This leads to the development of light weight, hard and rigid plastic material. Polystyrene can be made in various types such as solid, foam and film that have specific properties for particular uses. It may be molded into many products during its production hence making it vital in several industries with variable items.
What Are the Basic Properties of Polystyrene?
The distinctiveness of polystyrene’s properties has made it an attractive material for use in different aspects. Polystyrene is clear, thereby facilitating the visibility of content inside packaging or bottles. Moreover, polystyrene offers good thermal insulation properties and that is why it is used to insulate homes and buildings. Besides, polystyrene is light but has high ridgidity; this gives it a structural stability without much weight addition. It also features good electrical insulating properties that are useful in electronic devices as well as appliances such as microwaves. However, remember that polystyrene does not bend or flex well and can crack when stressed. Nevertheless, due to its easiness of molding and versatility into various forms like solid, foam and film; polystyrene has become one of the most used plastics in many industries.
How Is Polystyrene Produced?
Polystyrene comes from petroleum; it is synthesized through polymerization of the monomer styrene. Styrene monomers are extracted during chemical reactions involving benzene and ethylene that mark the start of the process. The next phase involves polymerisation, where these styrene monomers interact to form a chain reaction using suspension, solution and/or mass polymerization methods. Mass polymerization is generally used in most cases whereby an initiator heats up the styrene monomer leading to a chain reaction thus forming polystyrene. Once molten, this material can be extruded or moulded into different forms including sheets, beads or foam as per its intended use. This results in expanded polystyrene resins which are then utilized for disposable cutlery and packaging materials and structural insulation materials among other household articles.
What Makes Polystyrene a Unique Polymer?
Polystyrene is an exceptional polymer as a result of its combination of physical and chemical properties. Polystyrene is versatile, found in forms that range from rigid solid plastics to expandable foams. Such flexibility gives it the ability to be used in various applications including food packaging and disposable containers among others such as insulation and electronics. It means that polystyrene resists acids, bases, and other substances; therefore, making the polymer durable than others. Also, it is transparent and can be molded thus ideal for products with clarity or intricate designs. Although brittle with rigidity, its lightweight nature coupled with its good thermal as well as electrical insulating abilities are also some of the reasons why it has become so popular in different industries today.
What Are the Different Types of Polystyrene?
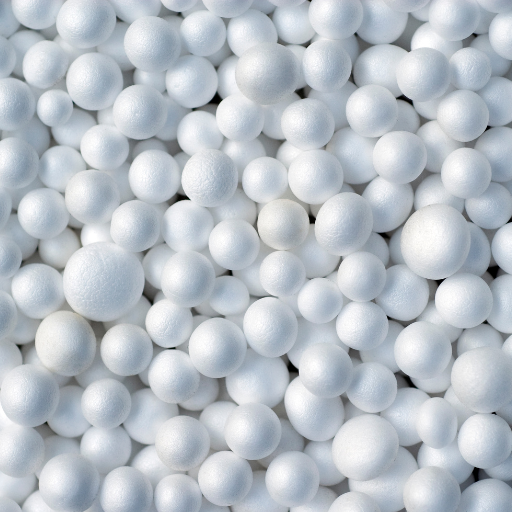

It is found in diverse forms that have different applications. This includes General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS), High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS), Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS).
- General-Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) is clear and rigid plastic which are preferred for making CD cases and laboratory ware.
- High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) is modified with rubber to give it improved resistance to impact, thus it can be used in packaging, toys and appliance housings.
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is the light foam that one can see inside insulations, packages or disposable food containers.
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) on the other hand has a smoother surface and higher density compared to EPS. It is used in the construction industries for thermal insulation panels as well as crafts.
The different types of properties intrinsic to each kind make polystyrene versatile enough to meet various industrial requirements.
What Is Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Foam?
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) foam is a lightweight, rigid, closed-cell insulation material made from expanded polystyrene beads. It is known for its exceptional thermal insulating properties, moisture resistance, and cushioning capabilities. EPS foam is highly versatile and commonly used in various applications, including packaging, building insulation, and as a cushioning material for transporting delicate items. Its structural integrity and flexibility to mold into different shapes make it ideal for both commercial and residential construction projects, where it helps in reducing energy consumption and enhancing overall building efficiency. Additionally, EPS is recyclable and has a relatively low environmental impact compared to other insulation materials.
What Is Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Foam?
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) foam is a rigid insulation material characterized by its closed-cell structure, offering superior moisture resistance and thermal insulating properties. This type of foam is produced through an extrusion process, which results in a uniform and dense material. XPS is commonly used in building and construction applications, especially for thermal insulation in walls, roofs, and foundations. Its high compressive strength and ability to resist water absorption make it a preferred choice for areas exposed to moisture such as below-grade applications. Additionally , XPS foam is noted for its durability with long-term performance which contributes to energy efficiency and overall sustainability of buildings.
What Is High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS)?
HIPS is a highly durable plastic with high strength, which is versatile and unbreakable. It is made by mixing rubber to polystyrene, thus making it stronger and hence suitable for applications requiring greater impact resistance. HIPS can be easily fabricated and processed using different methods like injection molding, thermoforming, extrusion etc. This material has found wide applications in the manufacturing of consumer goods, electrical components as well as packaging due to its processability and cost effectiveness. Besides, HIPS can be printed on, painted or glued which makes it among the most preferred materials for point of purchase displays and signage in many organizations. Its characteristics include good dimensional stability, aesthetic appearance and coping ability with day-to-day tear.
What Is General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS)?
On the other hand General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) is a clear hard thermoplastic known for its excellent transparency and ease of processing. GPPS results from polymerization of styrene monomer and has great stiffness, dimensional stability, optical properties that are very import in some industries that require high transparency and rigidity respectively. Typical examples are disposables such as cutlery cases; food wraps; lab ware; different types of display items at stores among others. The material GPPS has an easy moulding ability, extrusion capability as well as thermoformability enabling inexpensive production processes that are also versatile in nature. Although it does not have the same level of toughness against impact as High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS), its clarity together with ease of fabrication make it widely used in various applications where aesthetics play a part too including visual appeal justification purposes related.
How Is Polystyrene Used in Packaging?

Polystyrene is a big part of packaging because it’s versatile, light, and protects things well. High-Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) and General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) are the usual materials for manufacturing different kinds of packaging. HIPS is frequently thought to be suitable for making strong and shock-resistant materials used for packing goods such as blister packs, trays and clamshell packaging. GPPS possesses high degrees of clarity that makes it useful in clear items like food containers or lids where the product must be visible. In essence, both sorts can be molded, thermoformed & fabricated with ease to suit numerous diverse applications required by packing industries.
What Are the Benefits of Polystyrene Packaging?
Polystyrene packaging has many reasons that contribute to its popularity in a variety of sectors. First, it is an excellent insulator which is very essential when trying to keep food and beverage temperatures stable. This feature makes it ideal for use in food packaging since it retains freshness while still making it safe for consumption. Secondly, it is light but strong meaning that this material can be handled, transported and stored with ease thus reducing shipping costs as well as environmental impact. Furthermore, polystyrene offers cushioning protection to fragile and delicate items thereby preventing their breakage during transit. Finally polystyrene packaging is cheap and versatile; Other than easily assuming various shapes and sizes hence being applicable diversely in different products. These are the advantages of Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) materials used in manufacturing packages through injection moulding technique.
How Are Polystyrene Packaging Materials Made?
Styrene monomers polymerization starts the process of making polystyrene packaging materials. This results in solid polystyrene resin from liquid styrene monomers through this method of polymerization. Polystyrene packaging is produced using diverse methods such as extrusion and molding techniques. In the first one, sheets or other shapes are created by melting polystyrene resin which is later cooled and cut into desired forms after it has been pushed through a die. Conversely, melted polystyrene is poured into molds to create certain packaging structures including clamshells or cups during molding techniques. The foam that is used most frequently for protective packaging purposes is Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), which involves the expansion of polystyrene beads with pentane gas and then fusing them together in a mold. Depending on the properties required for the final product, General Purpose Polystyrene (GPPS) and High Impact Polystyrene (HIPS) both can be applied here.
What Types of Polystyrene Packaging Products Are Commonly Used?
Polystyrene packaging materials are incredibly versatile and widely used across various industries. Common products include:
- Foam Peanuts and Loose Fill: The extensively used commodities in shipping, they cushion wares against breakage during shipment by preventing displacement.
- Foam Sheets and Planks: Pieces of foam that safeguard large fragile things most times have their forms cut to match the outline of the material hence having a very high absorbing effect.
- Clamshell Containers: Frequently used in the food industry, these containers are popular for take-out meals and packaging fresh produce due to their lightweight and insulating properties.
- Disposable Cups and Plates: These are ubiquitous in fast food places as well as casual restaurants because of their handiness and ease on one’s pocket.
- Insulated Shipping Containers: Ideal for transporting temperature-sensitive goods, such as medical supplies or perishable food items, these containers maintain a stable internal temperature during transit.
- Packaging Inserts: Custom-shaped inserts are used to secure products inside a container providing an additional level of safety measure.
These various forms of polystyrene packaging are valued for their ability to combine light weight with durability, making them indispensable in both commercial and consumer applications.
What Are the Environmental Impacts of Polystyrene?
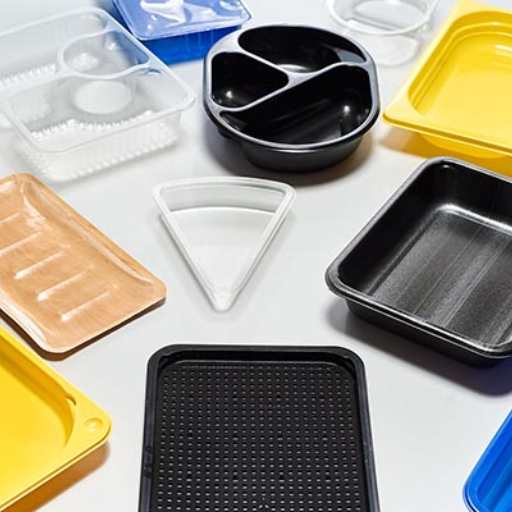

Polystyrene is a material that causes significant environmental impacts majorly because of its non-biodegradability. Inadequate disposal methods and handling can result in its presence in the environment for several centuries thus contributing to landfill congestion and sea pollution. Littering is another common use of polystyrene which not only destroys landscapes but also poses dangers to wildlife who may eat or be caught by these objects. The manufacture of polystyrene involves fossil fuels and hazardous chemical release leading to air pollution and global warming gases that are emitted. Furthermore, recycling this particular material is tough as well as unpopular; therefore there are increased chances that it will be thrown into garbage instead of being put into possible uses again. All this results in a serious concern on the part of the environment over polystyrene.
How Does Polystyrene Pollution Affect the Environment?
The environment is significantly affected by polystyrene pollution. To start with, in marine ecosystems, polystyrene fragments eventually break down into smaller units called microplastics that are eaten up by fish and other sea creatures. Therefore, these animals can suffer from obstructions, malnutrition and even demise as a result of ingestion. Moreover, the release of dangerous chemicals such as benzene and styrene to the environment from polystyrene causes air, water and soil contamination. These chemicals are harmful not only to wildlife but also can pose health challenges to human beings.Lastly, since polystyrene is neither biodegradable nor easily recycled it often gets accumulated in landfills and natural habitats consequently leading to long-term environmental degradation.This calls for better waste management practices as well as enhanced development towards finding alternative sustainable means that would reduce the risk factors associated with polystyrene pollution.
Are There Eco-Friendly Alternatives to Polystyrene?
Polystyrene is getting unpopular due to its environmental un-friendliness. Instead, mushroom-based packaging is proposed as one of the alternative approach that makes use of agricultural waste and mushroom mycelium to yield a compostable material which can be used as an effective replacement for polystyrene. It decomposes naturally and nurtures soil making it sustainable.
Another choice is cornstarch-based packaging made from cornstarch obtained from renewable sources. The material is biodegradable and has similar properties suchlike insulation and cushioning as polystyrene, thus can be applied in various applications such as food containers and packaging materials.
Moreover, PLA (polylactic acid) occurs as a kind of bioplastic generated through the fermentation of plant starch typically got from corn. PLA is compostable, exhibits fewer emissions during production than traditional plastics like PET including their numerous variants, and therefore suitable for making items like disposable cutleries or packages. Apart from reducing the environmental footprint, these substitutes also promote circular economy by using renewable resources and minimizing waste generation.
What Recycling Options Are Available for Polystyrene?
The fact that it is light and bulky makes recycling of polystyrene hard because transporting and processing it is expensive compared to other materials. However, there are a few ways in which this environmental impact can be reduced:
- Drop-off Recycling Centers: Some communities provide specific places for recycling polystyrene. The centers often take in clean foam packaging, food containers, and other polystyrene products which are then sent to specialized facilities for recycling.
- Mail-Back Programs: A number of organizations and companies offer mail-back programs where the public may send their waste polystyrene for recycling. In this regard, it’s more useful when there are no local options as people from such region have an opportunity to participate in reduction of waste.
- Commercial Recycling Services: Companies producing large volumes of polystyrene wastes can contract with commercial entities that recycle such wastes. Such services usually provide collection bins at their premises as well as regular pickups resulting to efficient management and recycling of these kinds of refuses.
By repurposing it into insulation products, picture frames or park benches among others these recycling methods help cut down on the environmental footprints left by expanded polystyrene (EPS). Nevertheless, the success rates for these schemes will hinge upon knowledge amongst the public and involvement thereof thus underscoring the need for continuous learning plus promotion.
What Are the Common Uses of Polystyrene in Everyday Products?

Due to its being light weight, insulative and cushioning quality, polystyrene is a plastic that can be used in many everyday things. Some common applications are outlined below:
- Packaging: Polystyrene is commonly applied as protective packaging materials like foam peanuts and molded inserts used in fragile shipments to ensure the products get to their destination undamaged.
- Food Containers: Many disposable coffee cups, takeout boxes, meat trays and egg cartons are made of polystyrene for thermal insulation purposes as well as providing structural support.
- Insulation: It helps insulate things like foam boards or building insulation which enable energy efficiency in homes as well as commercial buildings.
- Household Items: A number of domestic items such as throwaway cutlery, plastic utensils among others and DVD cases are normally made from polystyrene hence they are long lasting and inexpensive to produce.
- Consumer Electronics: To protect against damage an electronics item has a foam casing surrounding it like the television sets, computers and other delicate accessories usually manufactured from polystyrene.
Significantly, these uses demonstrate how vital this material is in our daily life despite numerous environmental concerns arising from its disposal.
How Is Polystyrene Used in Food Containers?
Polystyrene is highly used for food packaging because of its good insulation characteristics and capacity to maintain hot or cold temperatures when necessary. It goes well with throwaway coffee cups, takeaways among others. In addition, the build quality of the material ensures that such containers are strong enough to keep any edibles safe while being transported from one place to another. Moreover, polystyrene is light and cheap thereby cutting down on costs associated with production stages and transportation. Additionally, it can be molded into different shapes and sizes, making it versatile enough to cater for various solutions in food packaging. Nonetheless, this gives inconveniences as its disposal is not a straightforward matter as well as the fact that it takes long before decomposing thus having an environmental impact.
What Other Products Are Made from Polystyrene?
Apart from the foregoing, there are a variety of other products that make use of polystyrene. For instance, in medicine it is utilized to manufacture items like petri dishes and test tubes because of its clearness and durability. In cars industry, it is used for the production of interior components such as knobs, instrument panels among others including energy-absorbing panels. Besides making toys, model kits and crafts are made from this material as it can be molded easily and is also adaptable in design. These extra applications show how widely polystyrene can be employed across different sectors indicating its flexibility and useful features.
Why Is Polystyrene Popular in Packaging and Disposable Products?
The low cost of polystyrene, its durability and good thermal insulation properties are the main reasons why it is commonly used in packaging and disposable products. Moreover, polystyrene is relatively cheap to manufacture, hence an appealing option for consumers as well as manufacturers. The material has lightweight characteristics which help to mitigate the costs associated with transportation and energy consumption during transit. Besides, polystyrene provides a strong cushioning for goods hence they do not break when handled or shipped. This also means that it has great insulating qualities that ensure both hot and cold foods keep their temperatures while in such vessels as food storage boxes and takeaways. However, despite these merits, there is need to consider the environmental implications of using polystyrene because it cannot be recycled easily and also takes many years before decomposing completely.
What Are the Differences Between Polystyrene and Other Plastics?

Polystyrene is different from some other plastics in many respects. The first one is that, polystyrene has a more rigid and brittle structure that sets it apart from other commonly used plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene which are more flexible and durable. Polystyrene also has excellent optical clarity making it suitable for applications requiring transparency like food containers and laboratory instruments. Furthermore, polystyrene has good insulation property in terms of thermal qualities but a lower melting temperature than the rest of the plastics meaning that it can only be used at low temperature conditions. Also, when compared to PET or HDPE among others, the environmental effect of polystyrene is much greater due to its ineffectiveness in biodegradation and recycling processes. These distinctions underscore the distinct attributes as well as specific uses of polystyrene relative to other kinds of polymers.
How Does Polystyrene Compare to Other Thermoplastics?
Certain areas set polystyrene apart from other thermoplastics. In comparison to polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), polystyrene is more brittle and rigid, which means it’s less ideal when flexibility is required. However, this rigidity gives it some advantages for specific purposes such as protective packaging. Further, polystyrene is of exceptional optical clarity, making it a material of choice for products requiring transparency like certain food containers and laboratory ware. Conversely, both PE and PP offer better chemical resistance and malleability. In respect to thermal properties, PS provides excellent insulation but has low melting point that makes it unsuitable for high temperature applications unlike some other thermoplastics such as PC or PET. Furthermore, from an environmental perspective PS is not easily recyclable and has lower biodegradability compared to other thermoplastics like PET or HDPE which are widely recycled with small environmental footprints.
What Are the Physical and Chemical Differences?
In both physical and chemical terms, Polystyrene (PS) is distinct from other thermoplastics. For instance, PS has got high rigidness and optical clarity, qualities that make it useful in applications where strength and transparency are required such as food packaging and laboratory ware. Conversely, polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP) are more flexible materials than polystyrene but less brittle thus they can handle stress better and last longer.
Chemically, polystyrene has rather simple structure with repetitive aromatic ring units that result in its stiffness. On the other hand, this same structure makes it less chemically resistant than PE or PP because it is prone to UV light degradation to a greater extent while the latter polymers have larger amounts of saturated backbones. Moreover, polystyrene exhibits low melt point (<240°F or 115°C), which restricts its use at high-temperature conditions unlike polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and polycarbonate (PC), which can tolerate higher temperature levels). These dissimilarities highlight when PS is advantageous over other common thermoplastics or not suitable enough in particular instances.
Why Choose Polystyrene Over Other Types of Plastic?
Polystyrene is the ultimate choice among other sorts of plastics for a number of reasons. It has good clarity and stiffness making it an ideal material for packaging where content visibility is vital as in food packing and medical supplies. The costs of producing it are also relatively low, which provides manufacturers with cost savings. On top of that, polystyrene is light weight, thus reducing transportation costs. From design view point, it can be easily shaped to any form allowing for detailed fabrication. In many cases, these advantages make polystyrene the preferred material for applications where cost effectiveness, transparency and rigidity are important.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is polystyrene?
A: Polystyrene is a synthetic polymer made from the monomer styrene. It can be found in various forms, such as polystyrene foam, polystyrene plastic, and polystyrene film.
Q: Is polystyrene a type of plastic?
A: Yes, polystyrene is a type of plastic. It is commonly used in various applications due to its versatility and physical properties.
Q: What are the different types of polystyrene plastic?
A: Types of polystyrene plastic include expanded polystyrene foam (EPS), extruded polystyrene foam (XPS), and oriented polystyrene. Each type has different uses and properties.
Q: Where is polystyrene commonly used?
A: Polystyrene is commonly used in packaging materials, disposable cups and plates, insulation, and various other plastic products. Polystyrene containers and polystyrene foam are popular for their lightweight and insulating properties.
Q: What are the physical properties of polystyrene?
A: The physical properties of polystyrene include being lightweight, rigid, and clear. These properties make it suitable for various applications, from packaging to construction materials.
Q: How is polystyrene foam different from styrofoam?
A: Polystyrene foam and styrofoam are often used interchangeably, but Styrofoam is a trademarked brand of polystyrene foam created by Dow Chemical Company. Both materials exhibit similar properties, such as low density and good insulation.
Q: What are some common products made of polystyrene?
A: Common products made of polystyrene include polystyrene sheets, foam polystyrene, polystyrene containers, plastic cutlery, and insulation materials. Polystyrene is used extensively in the packaging industry.
Q: Is polystyrene environmentally friendly?
A: Polystyrene is generally not considered environmentally friendly because it is not biodegradable and can contribute to environmental pollution. Efforts are being made to recycle polystyrene, but its disposal and environmental impact remain concerns.
Q: How does the strength of polystyrene compare to other plastics?
A: The strength of polystyrene can vary depending on its form. For example, expanded polystyrene foam has low density and is relatively weak, whereas oriented polystyrene and syndiotactic polystyrene offer better strength and rigidity.
Q: Can polystyrene be recycled?
A: Yes, polystyrene can be recycled, although the process can be challenging. Recycling programs are not as widespread for polystyrene as they are for other plastics, but innovative methods are being developed to repurpose polystyrene materials.