Sheet metal stamping is a significant manufacturing process that deforms metals into desired shapes and sizes in various industries. The process uses specified methods and tools to cut, bend or shape the metal sheets thus resulting into accurate and robust components. This blog post seeks to provide an ultimate guide for mastering sheet metal design during stamping through giving vital procedures and rules required in producing high quality stamped parts. Whether you are an experienced engineer or starting out as a beginner; this blog will give you new insights which will help broaden your knowledge base as well as sharpening up skills when it comes to sheet metal designs for stamping. We shall cover basic principles of design, talk about material choices among other things that can be done so that production efficiency may be increased while at the same time improving product performance through advanced stamping techniques. Finally, after going through this post one should have strong understanding about different aspects of sheet metal forming thus enabling him/her come up with better designs confidently.
What is Metal Stamping Design?

Image source: https://waykenrm.com/
It is called as metal stamping design to make a plan and specification for the production of stamped metal parts. In other words, it is a way to create definite shape with desired dimensions by using sheet material held in between two dies with pressure applied from top downwards until it gets into required form. The aim of such designs is also reducing mistakes during manufacturing process which may lead to increased costs due to rejection or rework apart from that there are many advantages including saving time since everything has been planned in advance; therefore, workers can concentrate on work rather than thinking what should be done next. Another benefit involves good performance after assembling different components made out of metals where this kind of operation helps eliminate vibrations caused by loose connections among others.
Understanding the Basics of Metal Stamping
Metal stamping refers to the manufacturing process used in converting flat metal sheets into various shapes. It is a complicated method involving many techniques of metal forming such as blanking, bending, coining and punching. This operation employs a stamping press which exerts high pressure on metals to obtain desired forms. Material feeding, cutting or shaping and ejection of the formed part are some key stages in metal stamping. Metal stamping has accuracy and repeatability hence can be used for making large quantities of consistent parts.
Understanding the fundamentals well enables an engineer to design effective and efficient processes of stamping that will have minimum material wastage while delivering high structural integrity in the final product. Moreover, technological improvements have led to integration of precision enhancing systems like computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) within this field.
However, the most important thing is knowing different types of metals used including steel; aluminium; brass; copper among others as well as their properties like malleability or tensile strength since this knowledge is necessary for achieving desirable outcomes during metal stamping projects.
Key Features of a Stamped Metal Part
There are a number of factors that distinguish stamped metal parts and make them highly sought after in many different industries. The first is precision. By using high-tech stamping presses and CAD/CAM technology, it is possible to create pieces with very narrow tolerances, ensuring that they will be uniform and reliable when produced in large quantities. Also important are speed and efficiency because these processes can churn out massive amounts of goods in very little time, thus reducing lead times as well as overall manufacturing costs.
Another crucial aspect is durability. This is because stamped metal parts take advantage of the inherent strength found in such materials as steel or aluminum, which allows them to maintain their structural integrity even under heavy loads. Moreover, versatility deserves special mention; through metal stamping one can fabricate various shapes and sizes ranging from simple brackets to intricate components having complex features.
Finally, cost-effectiveness still remains an important benefit brought about by this process. Metal stamping achieves cheapness for mass production requirements by minimizing wastage of materials and optimizing their use from the raw form onwards. These attributes jointly establish stamped metals as fundamental products across automotive, aerospace, electronics among other sectors of industry dealing with consumer goods production needs at large scales.
Why Choose Sheet Metal Stamping?
The reason why sheet metal stamping is favored in the manufacturing sector is because of its accuracy, speediness and adaptability. This process can produce parts with high quality standards within narrow limits thereby guaranteeing uniformity over large quantities. In terms of time saving, it has been found that lead times are cut down significantly by this method thus making them suitable for mass production runs. Additionally, different types of metals may be used during sheet metal stamping while creating intricate shapes which provides room for creativity in design as well as application areas. Also known as one of the most cost effective methods available today where materials utilization is optimized while waste generation minimized; hence being applicable across various industries such as automotive, aerospace or electronics among others.
How Does the Sheet Metal Stamping Process Work?

Many steps are required for sheet metal stamping to transform flat sheets into finished parts. Firstly, a piece of metal is inserted into the press and held in place by dies that use force to shape it precisely. The process can be divided into stages such as blanking— cutting out the general shape from the sheet—and forming, where this blanked piece is manipulated until necessary contours are achieved. Additionally, piercing, bending or coining can be employed in order to create complex geometries and intricate details on the workpiece. Usually these operations are performed with progressive dies i.e., each performs a separate action as the metal advances through the press. This yields high-quality metalworking results while minimizing material wastage and ensuring repeatability at low costs.
The Role of Stamping Machines
In the sheet metal stamping process, stamping machines are very important because they give the required force and accuracy that turns metal sheets into components of high quality. These tools are fitted with dies and other necessary items for different operations which include blanking, forming, bending and piercing among others in a consecutive manner. In order to have large-scale production with tight tolerances and consistent quality; speed is a factor considered by these machines. Automation is possible due to improved technology in them hence reducing manual work while at the same time increasing output rate as well as minimizing mistakes done during manufacturing process which can be found useful or become necessary in industries like automotive sector where accuracy together with repeatability matter most during production cycle stages such as aerospace industry or electronics field etc.
Exploring Different Stamping Processes
Stamping processes greatly vary, each designed to give different results which depend on the material and desired outcome. The following are some of the most common stamping methods:
- Progressive Die Stamping: This process involves a number of operations in a single die set. When material feeds through the press, it goes through various stages such as punching, bending and coining until it takes the final shape. Progressive die stamping is highly efficient and is used for mass production since it eliminates handling individual parts as well as ensures uniform quality.
- Transfer Die Stamping: In this method, parts are transferred from one station to another where each station performs a different function. It is applicable when dealing with larger sizes or more complex shapes that require substantial changes at every stage. Transfer die stamping provides versatility and is commonly employed during lower volume production runs featuring intricate designs.
- Compound Die Stamping: It allows for many operations to be carried out within one press stroke. Normally such includes cutting and forming actions making it very efficient for producing flat and simple parts with close tolerances. Compound die stamping is especially useful in manufacturing high precision components at once.
These processes of stamping address diverse manufacturing needs so that both simple and complicated pieces can be created accurately and quickly.
The Importance of Precision in Stamping
There are some reasons why precision in stamping is important. One, it guarantees uniformity of products being produced; this is very important for maintaining high levels of quality especially in industries such as automotive or aerospace where slight variations can cause big problems. Secondly, correct tolerances reduce material wastage and costs because accurate measurements result to lesser scraps and reworks. Also, through precision stampings can be made with complicated shapes or patterns that meet particular needs thereby improving their usefulness and dependability as parts within machines or equipment. In general terms, precise stampings streamline production processes which in turn extends the life span of a product while ensuring its compatibility with other assemblies or systems.
What Are the Types of Metal Stamping Techniques?

Among the techniques for metal stamping are blanking, embossing, bending, flanging and coining. Blanketing entails cutting out the desired shape from a piece of metal while embossing creates raised or recessed designs on its surface. Bending is used to change the angle or shape of the material whereas in flanging a lip is added to it; coining involves imprinting intricate details or patterns onto it. These methods have different functions which cater for various manufacturing requirements thereby helping in achieving accurate high-quality components production.
An Overview of Progressive Die Stamping
Progressive stamping is a metalworking process in which a strip of metal is passed through several workstations within one die. Each station carries out an individual function, such as cutting, bending or punching, thereby giving shape to the end product step by step. Such an approach enables continuous and time-saving component production with accuracy being taken into account too. Initially, the coil stock passes into the die from where it moves forward through different phases that increase intricacy of parts.
The major benefit of progressive stamping lies in its ability to manufacture large quantities of items having strict dimensional limits and complex configurations. It reduces material wastage while also cutting down on labor costs thus making it affordable for mass production. Automotive industry as well as electronics or appliance manufacturing use this method frequently because they need many similar pieces with difficult forms that can be made at once using these machines only.
Benefits of Four-Slide Stamping
There are some unique benefits to four-slide stamping that make it useful in metalworking. One of these is its ability to produce parts with many steps and difficult features. Unlike conventional stamping methods, these machines approach work from more than one direction at once, enabling very accurate shapes and designs to be created. This also removes the need for subsequent operations, saving time and money during production.
Another advantage of four-slide stamping is its flexibility when working with different materials and thicknesses. The process can efficiently handle both high and low volume runs, making it applicable in various manufacturing situations. Furthermore, this method can quickly adapt to design changes without requiring extra tooling which enhances its cost effectiveness even more.
Finally, four-slide stamping generates little waste while still holding tight tolerances on parts produced; thus ensuring consistency as well as quality control measures. For these reasons among others such as precision or efficiency offered by four slide technology within automotive industry alone but not limited there: aerospace sector; consumer electronics industry etc., where complex components may need to be made quickly – making four-sliding an ideal choice for such applications.
When to Use Deep Draw Stamping
Deep drawing stamping is useful in making items whose depth is more than or equal to their diameter, like seamless cylindrical parts. The method is best known for creating shapes that are deep and complicated – an impossible feat for any other process of stamping. Therefore, it has become the most used technique when producing fuel tanks, fire extinguishers, kitchen sinks among other items related to the automotive industry. This type of stamping also works well if you want a strong component since it work-hardens materials during its operation and thus makes them tough. Moreover, this method saves money during mass production runs because it produces accurate complex shapes with little wastage at low costs per unit produced when compared against other methods available in the market today.
How to Design for Metal Stamping: Best Practices

To guarantee the efficiency and quality of the final product, there are a few best practices to follow when designing for metal stamping. To start with, you should pick an appropriate material that meets the performance requirements of the part as well as being suitable for stamping. It is also important that the design incorporates generous tolerances so that tearing or wrinkling does not occur due to material flow. Wherever possible make the geometry simpler; this can be achieved through features such as rounded corners and consistent wall thicknesses which in turn reduce tool wear while prolonging tool life. Another thing is that pilot holes can be used to enhance precision during alignment of parts throughout the stamping process. Furthermore, involve closely working with manufacturers of these stamps during design phase since they have more knowledge and experience on them than anyone else would do . This kind of collaboration will help in early detection of potential problems besides optimizing designs for manufacturability based on their advice.
Following Effective Design Guidelines
Guidelines for metal stamping design focus on material choice, part shape, and working with the manufacturer. The first step is to select materials that balance performance needs against ease of use; common choices include aluminum, copper, and stainless steel because they are strong yet malleable. Make sure designs allow for flow by avoiding stress risers like sharp corners or sudden changes in cross-sections.
To minimize defects such as tearing or wrinkling, keep geometries simple while maintaining even wall thicknesses throughout. Also, round off corners wherever possible–this not only promotes longer tool life due to decreased wear-and-tear but also helps align parts more accurately during assembly stage through pilot holes et cetera.
Lastly but most importantly: work closely together with your stamping manufacturer! Getting them involved at an early stage will enable you tap into their wealth of knowledge which can be used in improving manufacturability aspects as well as detecting any potential problems before they become unmanageable thus guaranteeing a more efficient production process that saves money while delivering better quality stamped items.
Choosing the Right Metal Material
Designing a stamp largely depends on selecting the right metal material. Of all metals, aluminum, stainless steel and copper are the most commonly used in stamping.
Aluminum is loved for its high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance and machinability. It is widely applied in the automotive and aerospace industries because of being light which is necessary for weight reduction.
In addition to having good corrosive resistance properties, Stainless Steel also has great strength and durability. It finds extensive use in medical devices as well as food processing equipment among other areas that need high levels of cleanliness together with long service life.
Copper is highly regarded due to its exceptional thermal and electrical conductivity. For this reason, it is mainly utilized as an electrical component material choice; wiring being another common application area while heat exchangers benefit from its conductive abilities too.
If you know what makes each metal unique or advantageous over others then you can select them based on those merits such that performance will not be compromised but still remain within the limits set by manufacturability plus cost-effectiveness for your particular application.
Common Challenges in Metal Stamping Projects
There could be some problems during the process of metal stamping despite its many advantages. Material selection and variability are one of the main challenges. Even if you have chosen the right metal, thickness hardness and quality differences in materials can affect both the stamping process and uniformity of final products.
Another significant hurdle lies within tooling design as well as maintenance. In order to obtain accuracy and repeatability on stampings, it is important that tools are designed properly and maintained regularly tooled breakdowns; misalignments or even wearing out may lead to increased costs in production as well compromised part qualities.
Process control being another common challenge; this entails monitoring every step involved such that none goes uncontrolled hence preventing defects while still maintaining efficiency in terms of output . Forces used during alignment should not vary much otherwise real time adjustments will have to be made since variations at any point between them affects product’s quality adversely that is why press speeds need to be monitored throughout accompanied by necessary corrections where necessary because if forces do not align then parts will not come out good enough thus making it vital for these aspects being kept under watch always during manufacture.
The last challenge is spring back together with residual stresses . After metals have been stamped they often tend to return back towards their initial shapes which in turn leads into errors at the end part. To deal with such inaccuracies material behavior must be known well enough so that appropriate compensations can made through advanced techniques of tool designing capable effectively handling these effects.
What are the Applications of Metal Stamping?

Metal stamping is widely used in many industries because it can make high-precision parts with great efficiency. In the car industry, for example, metal stamping is employed to produce body panels, engine and transmission parts. Enclosures, connectors and heat sinks are among the things made by metal stamping in the electronics industry. Also, aerospace companies use this process heavily when creating strong yet precise structural components or delicate pieces that need high strength. Additionally medical devices need stamped metals due to their durability while consumer appliances and industrial machinery require them for reliability as well as cost effectiveness.
Industries That Utilize Metal Stamping
Metallic punching is an important manufacturing method that is used by different industries due to its effectiveness and capability of producing long-lasting parts with high accuracy. The automobile industry greatly relies on metallic punching in making body panels, engine components, as well as transmission parts. In the electronics industry, without metal stamping it would be impossible to create enclosures or connectors needed for operational devices among other essential elements. When it comes to aerospace engineering both structural and intricate pieces which require superior strength & precision can only be achieved through metals punch press work. Apart from these main sectors, medical devices production also uses this technique alongside consumer appliances manufacturing and industrial machinery construction thus indicating its flexibility together with dependability within various fields.
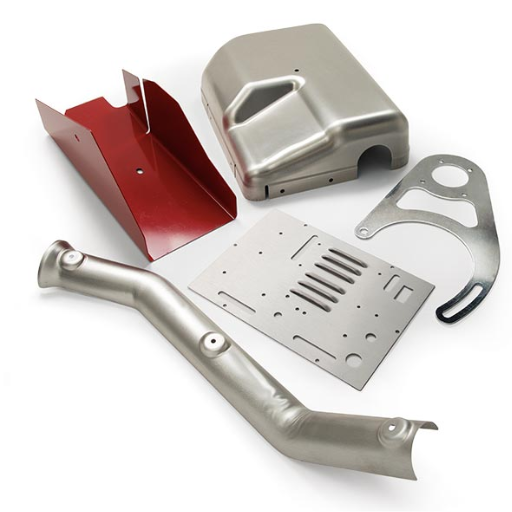
Examples of Stamped Metal Parts
Stamped metal parts are widely used in many industries because they are precise, durable and cost-effective. Some examples of them are as follows:
- Automotive Components: Body panels; engine parts; transmission components; brackets and chassis parts. These require accurate specifications for optimum performance and safety measures.
- Electronic Parts: Enclosures, connectors, heat sinks and shielding components. These protect electronic devices while ensuring their functionality at the same time.
- Aerospace Components: Structural supports; wing spars; aircraft cabin sections etc., all having intricate shapes which can withstand high stress under harsh conditions where such things happen frequently.
Other than these sectors Stamped Metal Parts find their application also in manufacturing Medical Device Components, Consumer Appliances such as Washing Machines or Refrigerators among others where Industrial Machinery uses them too due to their versatility combined with precision together with strength that cannot be matched elsewhere across this field.
Advantages of Custom Metal Stamping Services
Benefits of Custom Metal Stamping Services:
- Accuracy and Precision: The accuracy and precision levels in custom metal stamping are exceedingly high, ensuring that all the parts meet the exact specifications and tolerances required. This is very important especially in industries such as automotive or aerospace where a slight deviation can affect performance as well as safety.
- Cost Efficiency and Time Saving: It is a highly efficient process which can produce large quantities of components within short periods consistently. Therefore, this speeds up time thereby saving costs making it economical for manufacturing complex parts.
- Design Flexibility: There are various designs possible with custom metal stamping ranging from basic design to highly advanced intricate ones. Manufacturers have the ability to come up with any shape they want thus creating products according to their specific needs be it delicate electronic devices or heavy duty automobile components.
- Material Options: Stamping can be done on different materials like steel, aluminium, copper among others including special alloys so as to choose what works best for each application.
- Increased Toughness and Longevity: These types of fabricated elements possess robustness features since during fabrication there occurs some physical transformation that toughens them against wear tear making such materials more applicable under harsh conditions.
-
Uniformity plus Quality Assurance: Through personalized metal stampings, equality can be realized across all produced parts. This is achieved through automation together advanced equipment which help maintain strict standards of quality control leading into consistent outputs.
These benefits position customer stamps as the perfect solution for various industries that need versatile manufacturing options which are both economical and capable of delivering high quality results.
How to Optimize the Stamping Process for Better Quality?

To make the process of stamping more efficient in terms of quality, these are some strategies that should be taken into consideration:
- Precision Tooling: It involves making sure that tooling is designed and maintained with accuracy. For one to produce precise and consistent parts during stamping, high-quality dies must be used at all times; this also applies when maintenance is done on a regular basis.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials should be based on specific requirements of an application. The durability as well performance levels achieved through stamping largely depends on quality hence it is necessary to use best materials available.
- Process Control: During stampingsystems need to such monitor devices are employed which can always check various parameters like temperature, pressure and alignment on a continuous basis. This will enable real-time detection & correction of deviations from set conditions.
- Training and Expertise: Operators together with technicians running these machines must receive proper training so that they become conversant with different aspects relating to management as well troubleshooting skills associated with them.
- Regular Maintenance: Machines plus other related equipment ought to undergo regular servicing in order not only prevent unexpected breakdowns but also keep them working at optimum levels throughout their lifetime.
- Quality Inspections: From the time raw materials are received up until final products get tested; there should be strict measures put place regarding quality control checks. Such steps help identify defects early thereby correcting them before too late thus saving both time and money required for reworks or replacement items.
Manufacturers can improve their product’s quality by following these guidelines which will ensure that they meet customer needs and also comply with industry standards.
Factors Affecting Metal Stamping Quality
To make high-quality stamped products, manufacturers must pay attention to several determinants of metal stamping quality:
- Quality of the Tools: The final product quality is largely affected by the quality and precision of dies used in the stamping process. They should be maintained regularly and made from good materials so as to prevent wear that can lead to inconsistent results.
- Properties of Materials: Tensile strength, thickness, and ductility are some of the properties exhibited by metals which are being stamped. It’s important therefore for one to choose a material whose characteristics match with what is required lest there be problems like cracking or excessive wearing out.
- Machine Settings: Stamping machines need correct calibration including pressure levels applied; speed at which they operate among others such as alignment features. With advanced systems for monitoring this can be done easily thereby ensuring that there is no variation from perfect condition throughout production period which will maintain uniformity in terms of item qualities.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature prevailing in a given area together with humidity content available within it may also have impact on both materials used and machinery involved during manufacture process. Thus controlling these conditions could assist a lot in ensuring constant production standards are met.
- Operator Competence: Having skilled operators who are well conversant with various aspects related to running this operation is very important if efficient output realization has to be attained. These individuals should receive proper training followed by continuous acquisition of new skills which would minimize errors thus enhancing the value delivered through their workmanship.
By addressing all these considerations, industry players can ensure excellence in metal stamping while meeting customer needs and surpassing set benchmarks.
Implementing Precision Stamping Techniques
Precision metal products are the main focus of precision stamping methods. Here are some commonly used methods in this industry:
- Computer-Aided Design and Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) Software: Using advanced CAD/CAM software can help achieve accuracy in die design and tool path planning. It minimizes mistakes and optimizes the production process.
- Highly Accurate Machinery: It is important to invest in state-of-the-art stamping machines that offer high precision and repeatability rates. These machines should have real-time monitoring systems with feedback for adjustments that enable the production of consistent quality products.
- Automated Quality Control: Automated inspection systems like vision systems and sensors detect defects or inconsistencies immediately they occur. This prompts instant corrective action which reduces scrap rates hence increasing overall efficiency.
- Material Utilization Techniques: Advanced techniques such as progressive die stamping aid material utilization besides ensuring accurate cuts and forms. Consequently, these methods minimize wastage thereby improving the precision of stamped components.
- Lean Manufacturing Practices: Lean manufacturing principles including Six Sigma methodologies as well as continuous improvement (Kaizen) allow organizations to streamline their operations thus reducing downtime while improving product quality.
Manufacturers can use higher standards, better efficiency achievement, lower costs realization through more close integration with current industry knowledge-based practices and technological advancements by adopting these techniques into their work processes.
Inspection and Testing of Stamped Parts
To achieve quality and dependable produced components, it is important to effectively inspect and test stamped parts. In the industry, the following are some of the commonly used methods:
- Visual Inspection: This means that a person checks for visible faults like scratches or deformations on the surface of an object. Automated vision systems can also be used here because they provide faster speed as well as higher accuracy during inspections.
- Dimensional Inspection: Calipers, micrometers and coordinate measuring machines (CMM) are some precision measurement tools which are utilized to ensure that specified tolerances about dimensions have been met by these components; thereby making sure they fit in place and work as required.
- Dye penetrant testing and magnetic particle inspection: These nondestructive tests help in identification surface cracks or subsurface voids among other things. In dye-penetrant examination, a colored liquid is applied onto the sample’s surface so as to show any defect areas while magnetic fields may be used for this purpose during magnetism testing once again revealing such flaws within them.
- Hardness Test: The resistance offered by materials towards deformation can be measured using such technique where their mechanical strength is determined alongside durability considerations based on Rockwell; Brinell and Vickers hardness test methods respectively.
- Functional Testing: This aims at ensuring that given items operate properly when subjected unto real working conditions. Stress tests may therefore need to be done so as to gauge performance levels under different operational situations followed by load tests which check how objects respond after being exposed either heavy loads or other forces finally fatigue experimentation where parts are repeatedly loaded until failure occurs hence determining their endurance limits against fatigue failures.
It is through adopting these approaches of examination plus verification that makers can uphold higher standards while striving towards reliability improvement; not only do they facilitate early detection of defects but also enhance overall performance reliability associated with stamping operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different types of sheet metal stamping?
A: Types of sheet metal stamping, for example, include transfer die stamping, compound die stamping, progressive stamping and deep drawing. Flat sheet metal is shaped into a finished piece or component by these processes using various dies and tools.
Q: Which materials are commonly used in metal stamping?
A: Steel, aluminum, copper, brass and other diverse metals are commonly used materials in metal stamping. The material to be selected depends on the final properties required for the application in question of the stamped sheet metal part.
Q: What is a stamping die and how does it function?
A: A stamping die is a specialized tool used in manufacturing during the process of making a product by cutting it out from strips or blanks made of metal; this could also involve shaping them into specific designs. To ensure accuracy while creating parts punched out of sheets metal there are different elements like punches dies guides etc., contained within the die itself.
Q: How does metal stamping provide precision in the manufacturing process?
A: Metal pressing guarantees precision by the application of precise stamping tools and dies, coupled with controlled pressure on the metallic workpiece which is responsible for this. This leads to uniformity as well as correctness of manufacture of narrow-tolerance metal parts.
Q: What is the forming process in metal stamping?
A: In metal stamping, the flat sheet metals or even strips can be shaped into particular configurations by use of machines that are equipped with dies. These may involve folding over, drawing outwards towards one direction only (unidirectional drawing), stretching etcetera so as to achieve desired metal components.
Q: What are some common metal stamping applications?
A: Automotive components account for some applications in common with electronic items like circuit boards; home appliances such as oven ranges where everything needs heat supply but also cooling down afterwards plus medical equipment like X-ray machines among others which usually have very complex designs requiring multiple operations during their realization through production.
Q: What is progressive stamping and when is it used?
A: A lot of stamping operations are performed in sequential stages using a progressive die! This is known as progressive stamping, which is a high-speed metal forming process. It can be used for mass production of small to medium-sized metal parts because of its efficiency and ability to produce intricate designs with precision.
Q: Why is blank design important in metal stamping?
A: The sheet metal blank or flat sheet metal that is used in the forming process usually has initial dimensions and shape determined by the blank design which makes it very important. Minimal material wastage will be ensured by well-designed blanks while optimizing metal forming processes so as to produce high-quality metal stamped parts.
Q: How do metal stamping machines vary based on the type of stamping?
A: Different types of stamping processes call for different designs and functionalities when it comes to machines used in metal stamping. Continuous strips of metals should be handled by machines designed specifically for progressive stamping; on the other hand, deep drawing machines should exert more pressure than any other machine during the formation of deep and complex shapes from blanks made out of metals.
Q: What are the benefits of using metal stamping manufacturing processes?
A: One can enjoy several advantages if they decide to use manufacturing methods like these ones that involve working with metallic materials – speediness at work, cost-effectiveness, uniformity in quality among others such as being able to come up with complicated pieces precisely. There is little doubt about cold-forming being one heck of a process since it allows much reiteration along with fewer wastes on materials used up!