Prescription pills for losing weight have emerged as an effective alternative to helping those encountering difficulty in achieving their weight loss goals simply through diet and exercise. People who struggle to manage their weight can significantly benefit from medications designed to intervene in specific biological pathways associated with appetite, metabolism, and fat tissue accumulation. This is new because previously, losing weight was a dietary goal achieved solely using self-discipline, with no advanced medical supervision. Certain prescription pills have already established markets in 2025 for emerging drugs with novel mechanisms of action and different and advertised efficacy rates. The best and most potent weight loss prescription pills are the subject of this article. We highlight their effectiveness, safety, and applicability for different categories of people. This guide is constructed to help a ‘first-time’ seeker of medical options and does not presume prior knowledge. Make informed decisions is the goal of your weight loss efforts, and this direction aims to help you achieve it.
What are the most effective prescription weight loss medications available?
Looking deeper into statutorily approved drugs for weight loss
Medications that have been sanctioned by the FDA are targeted towards people suffering from obesity or have other health conditions regarding weight and work by suppressing appetite, inhibiting fat absorption, or increasing energy output. Among these medications, several have emerged as widely recognized and prescribed options, such as:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): This medication, which works on the mechanisms of a type 2 diabetes drug, boasts of functioning as a GLP-1 receptor activator that controls appetite and leads to satiety. Clinical weight loss studies have recorded significant results when coupled with additional diet and exercise.
- Phentermine-Topiramate (Qsymia): A combination drug, Qsymia, has as an integral part an anti-obesity drug known to suppress appetite and a medication prescribed to treat epilepsy and is renowned for inducing satiety. Patients have succeeded with this emerging therapeutic drug for chronic weight management when combined with the recommended lifestyle changes, regardless of their sustained weight loss goals.
- Naltrexone-bupropion (Contrave): This combination targets the reward pathway and regulates appetite, helping patients eat less over time and further counteracting cravings.
These medications have particular indications, contraindications, and side effects, which require consultation with a qualified professional to tailor the treatment to the patient’s health profile.
Analyzing the effectiveness of select weight loss medicines
Depending on the compounds in the medication, patients lose weight with drugs for weight loss, the patient’s will to adhere to treatment, and other health factors. Considering some commonly prescribed medications:
- Semaglutide (Wegovy): Clinical trials show that with a combination of diet and exercise, patients can lose 15% of their original weight within 68 weeks, the best option.
- Phentermine-topiramate (Qsymia): Research has shown that after one year of treatment, the average weight loss is between 5% and 10% of total body weight. Thus, it is a good option for most people who need moderate weight loss results.
- Naltrexone Bupropion (Contrave): This drug usually results in a 5-8% decrease in body weight with regular doses for 56 weeks and while helping to control cravings and other behavioral aspects.
The differences in values of mechanisms, side effects, and clinical results warrant that each patient is put under a particular regimen to ensure maximum weight loss effectiveness.
How much medications work towards the promotion of weight loss
These medications promote weight loss through several methods. Semaglutide (Wegovy) works by imitating the action of the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) hormone, which signals satiety and adds to food intake by preventing gastric emptying, thus lowering energy intake. Phentermine-Topiramate (Qsymia) combines an appetite-suppressing stimulant with a medication that increases satiety and decreases energy expenditure. Naltrexone-Bupropion (Contrave) modulates the reward system in the brain that focuses on hunger and appetite, allowing for better control over behavioral eating urges. Every method deals with the overweight condition’s most important physiological and neurological determinants, enabling more significant weight loss and lifestyle changes, i.e., dieting and exercising.
How does Phentermine stack up against other weight loss prescriptions?
Phentermine Weight Loss Mechanisms of Action
Phentermine works by suppressing appetite, which is one of the necessary methods to lose weight. This symptom can be achieved by acting on the sympathetic nervous system. In addition, Phentermine triggers the release of norepinephrine in the hypothalamus, where the hunger centers are situated. This release of norepinephrine blunts appetite and increases the feeling of fullness, thereby causing reduced food intake. In addition, phentermine may also stimulate the secretion of neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin, which are also known to reduce food intake. Its efficiency stands out when coupled with low-calorie diets and exercise. Because of the likelihood of side effects and dependency, Phentermine is recommended only for short periods.
Probable Side Effects and Their Notable Effects
Different side effects come with the use of phentermine, and these may vary in terms of severity. While taking phentermine, typical side effects experienced include dry mouth, insomnia, constipation, and a faster heart rate. There can be additional severe adverse effects, such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or high blood pressure, which will most likely require a doctor’s attention. People with prior heart issues, hyperthyroidism, thyroid illness,s and glaucoma also need to be careful with their medication. Moreover, the medication is known to be addictive, which is also another reason why it can only be used under close medical supervision and for short periods. Constant monitoring and follow-up visits are greatly encouraged to minimize the risks that may arise when using it.
Typical Results in Weight Reduction with Phentermine
Patients utilizing Phentermine for weight management, exercise, and strict diets report a loss of 5% to 10% of their body weight within a 12-week time frame. Studies and reports from clinicians indicate that these results are not uniform and can be affected by compliance, lifestyle changes, metabolism, and even the amount of medication taken. It is critical to note that these results are generally obtained with Phentermine’s short-term prescription because it is not ideal for long-term supervision for weight control.
What are the newest injectable weight loss medications on the market?
Researching Wegovy and Ozempic for Weight Loss
Aspects of Wegovy (semaglutide) and Ozempic (semaglutide) have been attracting much interest lately as they claim to assist with weight loss. These medications fall under the GLP (Glycosylated Hemoglobin) category and work approximately by replicating the Glucagon-Like Peptide, which suppresses feeding, regulates blood sugar and induces satiety. Although Ozempic was primarily approved to manage type 2 diabetes, its weight loss effects are gaining popularity. On the other hand, Wegovy is explicitly approved for controlling weight in obese or overweight adults who also suffer from other related medical problems.
Clinical trials have shown that Wegovy can reduce body weight by an average of 15% when combined with proper diet and exercise. Users of Ozempic also reportedly lose a considerable amount of weight, and the average weight with this medication tends to be slightly lower than that of Wegovy. Both drugs are self-administered as a subcutaneous injection once a week and must be complemented by active lifestyle changes. Unfortunately, both drugs have side effects, including nausea and gastrointestinal distress. Patients are advised to speak to their doctors regarding their specific needs.
Comparative Effectiveness of Injectable and Oral Weight Loss Prescriptions
The effectiveness of the two models of weight loss, injectable and oral prescriptions, varies depending on individual cases as well as factors like the mechanism of action of the drugs. Injectable options, like GLP -1 receptor agonists Wegovy and Ozempic, tend to be more effective in clinical trials as patients often seem to lose more significant percentages of body weight than those using oral medications. This is mainly attributed to their ability to control hunger and increase satiety much better than oral medications. On the other hand, while oral medication for weight loss does not perform as well, some patients may find it more practical than other alternatives. Both approaches, however, will necessitate adherence to more structured diets and lifestyle adjustments to maximize success. It is necessary to decide whether injectable or oral medications are more favorable to patients based on their dislikes and health issues. It is essential to determine the most effective methods in managing the condition, which is why discussions with healthcare providers are necessary.
Who qualifies for these innovative treatments?
As with most revolutionary treatments, eligibility is based on specific criteria such as underlying health status, body mass index (BMI), and previous weight loss interventions. As a rule of thumb, most patients with a BMI of 30 or more, along with a BMI of 27 or more with an obesity-associated disease such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, or sleep apnea, usually qualify. In some instances, documented failed attempts to modify one’s lifestyle are also mandatory. Like all other treatments, careful screening by the treating physician is essential to evaluate individual risks, rewards, and appropriateness of these therapies.
How do prescription weight loss pills work alongside diet and exercise?

Medications coupled with a lifestyle change: a blend of life-changing proportions
The synergism achieved when prescription weight loss medications are administered alongside physical exercises and a nutritious diet is remarkable. The prescribed medications typically work by curbing a patient’s appetite, enhancing their fullness, or inhibiting fat absorption. This complements the controlled intake of calories. Combining the medications with exercise results in higher energy expenditure and aids metabolism. The research shows that lifestyle modifications are still central, while medication serves a supportive role designed to target critical biological components that obstruct weight loss. With such an integrative approach, weight can be managed more efficiently by simultaneously addressing the immediate issue and long-term success.
Significance of employing a cautious approach while dieting
A balanced dieting approach is significant, considering optimum health and achieving long-term results. Current studies suggest an appropriate weight reduction strategy encompasses a careful combination of nutrition, regular exercise, and, if necessary, medical or medication-based support. Reductions in calorie spending often or extreme dieting can bring about nutrient deficiencies, which can result in muscle wasting and disruption in the body’s metabolism. Instead, focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, along with regular physical activity, allows for a healthy metabolism and reduced weight regain. Balance pertains to mental health too since ensuring stress relief and having ample sleep is additionally critical for hormonal balance and appetite control. People seeking to enhance their life quality without adverse health impacts can attain a healthier body weight by considering these interconnected factors.
Strategies for preventing weight regain in the long term
Concentrating on changing behaviors instead of short-term dieting is necessary to minimize the likelihood of regaining weight after losing it. Engaging in regular exercise is perhaps the most crucial strategy, with recommendations including at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise a week. Enhancing physical activity levels must be accompanied by consuming a nutrient-dense diet high in fiber and protein, which tend to suppress appetite and prevent overeating. Additionally, regular self-monitoring, like weighing oneself and counting calories, can help to take action before unhealthy behaviors become too ingrained. Using supportive and corrective feedback in setting reasonably achievable goals, managing stress and getting enough sleep, is vital for long-term weight control because all these factors work together to support a healthy lifestyle.
What should patients ask their pharmacist about weight loss prescriptions?

Essential considerations for assessing possible interactions.
While discussing weight loss medication with patients, it would be wise to prompt the pharmacist with the questions above to take the necessary precautions.
- What weight loss medications can interfere with other prescriptions or dietary supplements?: This question is central to determining whether the weight loss medication gets absorbed with other medicines a patient is already on or counteracts any prescription vitamins, supplements, or drugs.
- Are there particular foods, drinks, or activities I must avoid while taking this medication?: Any weight loss prescription medicines may come with certain do-not-eat lists or particular instructions to reduce adverse effects or ineffective results.
- What do you consider to be the most common side effects, and how can they be minimized in case they do occur? : Side effects can broadly differ in this multifactorial approach, but pharmacists know best the dos and don’ts to work around them.
- What is this medication’s relation to my particular health issues?: Patients need to make sure in advance that their medical history or chronic ailments, like hypertension or diabetes, will not be densely compromised with the weight loss intervention.
- How should I take this medication, and what is the recommended duration for its use?: It ensures the patient takes the medicine appropriately and safely as it clarifies the dosage, timing, and duration of therapy.
Such inquiries can help patients understand better the weight loss remedies prescribed to them so that they are appropriately managed, and their outcomes are maximized.
Understanding accurate dosage and administration
To achieve therapeutic benefits while mitigating risks and adverse effects, following the prescribed dosage and the administration order is key to achieving the desired outcomes. Weightloss medications are mostly ingested, alongside other restrictions about the period of use and whether food is taken. The factors determining tolerable dosage, such as body weight, age, and overall health condition, also determine the amount prescribed. Most primary medications are constructed for short-term use spanning weeks or months, as prolonged use can induce moderate to severe undesired effects. The Patient is only allowed to self administer set regimens after thorough consultations to ensure compliance and guidance while determining if they have set dosage limits for the medications. Failure to follow administrational protocols directly affects efficacy and safety.
Modification of treatment plans and tracking progress
The safety and efficacy of clinical measures rests on consistent follow-ups and monitoring. Healthcare providers often track progress through structured follow up clinical appointments to evaluate the patient’s symptoms, laboratory test findings, and general status to a prescribed medication. Changes to the treatment plan may involve modifying the medication taking, switching medications, or adding other management modalities. Reports from patients capturing adverse effects or any improvements in their life circumstances are also crucial in making a clinical decision. There should be consistent contact between the patient and caregiver to achieve the best results and to handle any problems that arise without delay.
Are there any breakthrough weight loss medications expected in 2025?
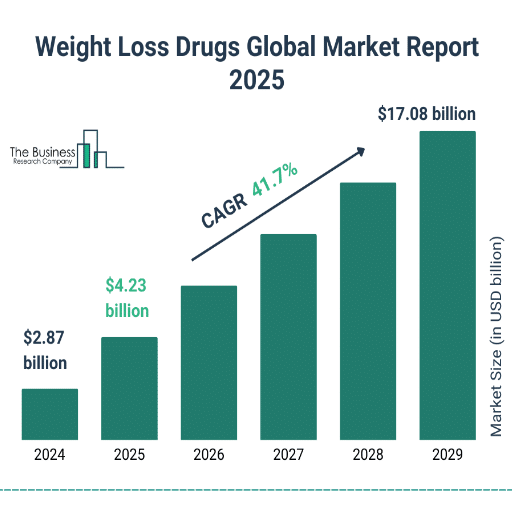
Developing directions in therapy weight loss drugs
New prescription medications will come to market, along with different forms of GLP-1 receptor agonists and metabolic targeted combination therapies in 2025, based on pharmacological innovations. New medications like semaglutide and tripeptide that offer considerable weight loss will be further developed. In addition, researchers are trying out GIP and amylin pathways, which increase corseting and decrease calories in novel ways. Firms are also trying to shift the focus of weight loss to genetic and metabolic treatment modalities to improve compliance and effectiveness in weight control maintenance. Everything points towards a new paradigm in the understanding of the evolution and treatment of obesity as a chronic condition, which is a multi-factorial and multi-treatment modality capable of being managed with numerous drugs.
Future advancements that may radically alter the industry
The most modern weight reduction therapies under development feature novel mechanisms with enhanced possibilities. Among the leading candidates in the 2025 pipeline is retatrutide, a new combination of three GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptor agonists, which in early studies proved to exceed previous weight loss expectations. Cagrilintide is another key contender. It is an amylin analog that promotes sitsiety and appetite suppression when used with GLP-1 agonists. Oral formulations of semaglutide are also being prepared to make the patient’s experience more user-friendly and effective without engaging in injections. These solutions mark an enormous advancement in pharmacological treatments of obesity and, quite possibly, treatment paradigms.
How forthcoming drugs could change the handling of obesity
New treatments seek to change how weight is controlled, retaking the approach to encompass the deeper-rooted biological causes of obesity. These medications enhance metabolic rates and combat insulin sensitivity through high-level, hormone-related techniques and appetite control. Innovations, such as cagrilintide and retatrutide, are pioneering new frontiers of efficacy by providing treatments that enable over 20 % weight loss consistently in their clinical trials. This goal has never been achievable with conventional therapies. In addition, improving oral doses, such as semaglutide pills,73 increases access and compliance and eliminates the obstables of injections. These developments combined could change the perception of managing obesity from an immediate and reactive approach, to one that is preventive and medically sophisticated, minimizing health complications and improving the quality of life.
Reference sources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

Q: What are the strongest prescription weight loss pills available in 2025?
A: As of 2025, some of the strongest prescription weight-loss drugs include Semaglutide (brand name Wegovy), Tirzepatide (brand name Mounjaro), and Phentermine-topiramate (brand name Qsymia). These medications have shown significant efficacy in clinical trials for helping people lose weight when combined with a healthy diet and exercise regimen.
Q: How much weight can I expect to lose with prescription weight-loss pills?
A: The amount of weight loss varies depending on the medication and individual factors. On average, people taking the strongest prescription weight loss pills may lose 5-15% of their body weight over a year. For example, Semaglutide has shown to help people lose up to 15% of their body weight in clinical trials.
Q: Are injectable prescription weight loss medications more effective than pills?
A: In many cases, injectable prescription weight loss medications like Semaglutide and Tirzepatide have shown to be more effective than oral pills. These injectables work by mimicking hormones that regulate appetite and blood sugar, potentially leading to greater weight loss compared to traditional oral medications.
Q: How do I know if prescription weight-loss drugs are right for me?
A: Prescription weight-loss drugs are typically recommended for individuals with a BMI of 30 or higher (obese), or those with a BMI of 27 or higher (overweight) who have weight-related health issues like high blood pressure or type 2 diabetes. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if these medications are appropriate for your specific situation.
Q: What are the potential side effects of taking weight loss pills?
A: Side effects can vary depending on the specific medication. Common side effects may include nausea, constipation, diarrhea, headache, and dry mouth. Some stronger medications may have more serious side effects. It’s crucial to discuss potential side effects with your doctor and carefully follow the prescribed dosage.
Q: Can I regain lost weight after stopping prescription weight-loss drugs?
A: Yes, there is a possibility of regaining lost weight after discontinuing weight loss medications. To maintain weight loss, it’s essential to continue following a healthy diet and exercise routine. Some medications may require long-term use to sustain weight loss benefits.
Q: How long does it take for prescription weight-loss pills to work?
A: The time frame for seeing results can vary. Some people may notice weight loss within a few weeks, while others may take a couple of months to see significant changes. Consistency in taking the medication as prescribed, along with lifestyle modifications, is key to achieving the best results.
Q: Are prescription weight-loss drugs a magic pill for weight loss?
A: No, prescription weight-loss drugs are not a magic pill. They work best when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise. These medications are designed to help with weight loss by suppressing appetite, increasing feelings of fullness, or altering how the body processes fat. However, lifestyle changes are crucial for long-term success in weight management.
Q: How do I get a prescription for weight loss pills?
A: To obtain a prescription for weight loss pills, you need to consult with a healthcare provider. They will assess your overall health, BMI, weight-related conditions, and previous weight loss attempts. If appropriate, they may prescribe a weight loss medication and guide its use. It’s important to have regular follow-ups to monitor progress and any potential side effects.






