What is anodize titanium and How Does It Work?
Understanding the anodizing process for titanium
The thickening of the oxide layer as voltage increases causes different colours to occur through shifted interference patterns in light waves (HOLLYWOOD). At this point, rinsing occurs before drying ready for utilization in various applications when desired colour has been acquired in one’s piece of work. This electrochemical procedure not only contributes significantly towards improving corrosion resistance and hardness on its surfaces but also improves aesthetic appearance on titanium making it suitable for use as anode material in both industrial and decorative sectors.
The role of voltage in creating different colors
Benefits and applications of titanium anodization
How is the titanium anodizing process Carried Out?

Steps in the titanium anodizing process
- Cleaning and Preparation: The titanium surface must be properly and carefully cleaned to get rid of any greasy substances, oil and other forms of dirt. This is primarily done using a solvent that removes grease before applying a chemical solution in order to have clean surfaces.
- Electrolyte Bath: After cleaning the titanium piece, it should then be immersed into an acidic based electrolyte solution. Sulfuric acid or phosphoric acid are commonly used acids in the solution that help in anodizing process.
- Applying Electrical Current: Titanium serves as anode under which electrical current is applied. The voltage is adjusted accordingly for thickness control and colour formation of oxide layer on the surface of the titanium.
- Rinsing: The anodized titanium is rinsed to remove any remaining acids or electrolytes after attaining the desired oxide layer.
- Sealing: In most cases, anodized titanium that protects its oxide film from corrosion may be sealed. Besides, this stage ensures that the bright colors achieved during anodizing are retained.
Required anodizing equipment and materials
Some essential equipment and materials required to conduct titanium anodizing includes:
- Degreasing Agent: Utilized for the elimination of dirt and grease from the surface of the titanium during the cleaning as well as preparation process.
- Acid Etch Solution: Generally it is a composition of strong acids like nitric acid or hydrofluoric acid that ensures a clean metallic surface.
- Electrolyte Solution: It has such acids like sulfuric or phosphoric acid, which allow for easy passage of electric current through them in order to facilitate anodizing.
- Power Supply Unit: It avails the electrical current to be regulated. This is usually adjustable so that one can control voltage hence color and thickness of oxide layer.
- Anodizing Tank/Bath: The electrolyte solution must be contained and also the titanium piece inside it throughout the anodizing process. It should not be corrosive due to its acidic nature.
- Titanium Anodes: A pure titanium serves as anode in this circuit thus enabling oxide formation.
- Rinsing Station: These are normally used water baths in rinsing off after remaining electrolytes and acids following anodization.
- Sealing Solution: Mostly, it involves hot water or chemical sealing solutions that seal pores within the anodic layer increasing corrosion resistance and maintaining colors.
Common challenges in color anodizing
Coloring titanium through anodization is a powerful technique but also has its own challenges that are well known to many experts. It has been difficult to have uniform color across the entire titanium surface. This is due to variations in electrolyte composition, temperature fluctuations and electrical current inconsistencies resulting into uneven oxide layer hence variation in colors.
- Consistent Coloring:
Thorough cleaning and preparation should be done on the surface of titanium. Any residual grease, oils or other forms of contaminants will prevent even oxide layer from forming hence leading to defects on the anodized finish.
- Surface Preparation:
Achieving certain color depends on precise voltage control. Slight changes may lead to significant differences in thicknesses of the oxide layers thus affecting their final colors as well. Maintaining stable voltages throughout this process can be quite challenging but it must be done to ensure consistency.
- Voltage Control:
Precise control of voltage is important for achieving specific colours. A slight deviation may result into significant difference in thicknesses of oxide layers therefore affecting the ultimate hue they will have at last . However, maintaining steady voltage throughout this process can be challenging but is necessary for consistency.
What Colors Can You Achieve with Titanium Anodizing?
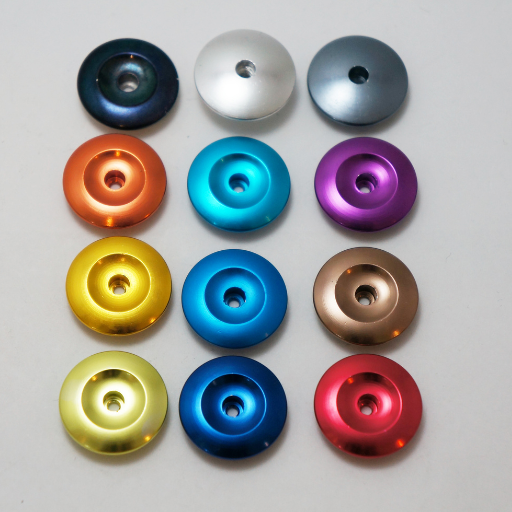

Exploring the anodized titanium color chart
The colors that can be achieved in anodized titanium by precise voltage control is a very amazing spectrum that unveils when the color chart is explored. The starting point of this spectrum on the chart is a bright gold at about 12 volts, which leads to vibrant purples and blues as one goes up in voltage, finally reaching rich greens and deeper shades at high voltages.
- Gold (12-20V): At lower voltages, different bronze and bright gold hues are developed by anodizing.
- Purple (20-30V): Increasing the voltage introduces rich purples and some blue hues.
- Blue (30-40V): Various bright blues appear as the process moves higher, making it more dramatic and lively too.
- Green (40-50V): Raising higher voltages produces different shades of green which gives another dimension to color palette.
- Pink/Red (50-80V): Pinks and reds are possible at highest voltages but these colors are harder to achieve consistently.
Factors affecting titanium color outcomes
- Surface Preparation: To obtain uniform coloration, it is important to prepare well the surface of titanium. Cleaning and finishing procedures such as complete de-greasing and mechanical polishing are used to remove impurities and irregularities hence this ensures Anodization that is even.
- Electrolyte Composition: The final color of the anodic film depends on the composition of the electrolytic solution that is used in anodizing. These solutions include phosphoric acid or sulphuric acid which can affect hues as well as consistency. The concentration and purity of the electrolyte are also decisive in obtaining fruitful results.
- Voltage Precision: In order for one to achieve accurate color representation, strict control over voltage application during anodization process is required. Voltage differences lead to inconsistencies in the visible appearance of colors necessitating maintenance of a stable voltage level within each desired hue range from a color chart. Consistently achieving same results across various parts calls for reliable sources and/or monitoring systems for power supply among other factors.
Comparing titanium anodizing color with aluminum anodizing
Aesthetic value and surface properties are two features that can be enhanced by titanium and aluminum anodizing processes, although with significant variations in their characteristics and outputs.
Color Range and Brightness: Aluminum results in duller, less conspicuous colors as compared to the broader range of more vibrant colors provided by Titanium. Although aluminum typically produces muted metallic shades, titanium can result in vivid rainbow hues from light waves interferences with the oxide film.
Durability: The anodized layer on titanium is highly durable making it resistant to corrosion and wear. In comparison, aluminum anodizing forms a more porous oxide layer that requires sealing to enhance its durability and corrosion resistance.
Process Specifics: During titanium anodizing, higher voltages may be used or different electrolytes may be employed as opposed to aluminium anodizing. Aluminium anodizing normally employs sulfuric acid baths instead of lower voltages. On the other hand, obtaining specific colours requires precise voltage control during titanium’s process.
Applications: While both methods are widely used across various industries, it is particularly common for there to be a use of titanium anodizing in colorful applications requiring high durability such as jewelry artifacts ,medical instruments,pieces made for aerospace unit among others. Alternatively , aluminum anodizing is frequently applied to produce building materials such as automotive parts or consumer electronics.
What Are the Applications of Color Titanium Anodizing?

Utilizing titanium parts in medical devices
Use of anodized titanium in aerospace and automotive industries
Anodized titanium is used for similar purposes in automotive industry too. For instance, it is employed in high-performance applications like exhausts systems, fasteners or suspensions where its durability and ability to resist corrosion contribute to longer life expectancy and dependability of vehicles. Finally, the cosmetic versatility provided by the use of anodized titanium allows customization resulting in superior finishes which are highly appreciated by car manufacturers.
Decorative applications and wear resistance
Anodizing titanium, which is a decorative use of important metal, is therefore highly valued due to its beauty and uses in multiple things. In this case, one just needs to alter the oxide layer’s thickness on the titanium surface resulting in different refractive and reflective abilities towards light. It should be noted that anodized titanium can be used for numerous purposes such as jewelry, watches or art pieces since the color can be varied while preserving original metallic luster.
Increased wear resistance makes anodized titanium superior because of its enhanced surface hardness. As a result of anodization process, this material becomes capable of resisting scratches and wears or it may even stop corrosion. That means that anodized titanium is both attractive and long-lasting, hence suitable for applications that require durability blended with good looks. This is why one will find that it can be easily used as wall panels, ceilings among other many uses due to its robustness against scratching or any form of accelerated wear and tear. Therefore, such factors make anodized titanium remain a top preference in both decorative and practical aspects.
Types of Titanium and Their Anodizing Potential

Commercially Pure Titanium
Grade 1 through Grade 4 are the commercially pure (CP) titanium grades that are notable for their exceptional corrosion resistance and ductility. These types of grades anodize well, producing a wide range of vibrant colors that make them suitable for use in decorations.
Titanium Alloys
The high strength to weight ratio and superior mechanical properties of titanium alloys such as Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) have endeared them to many users. Although they can also be anodized, one may expect slightly less vibrant colors than those obtained on commercially pure titanium. Nevertheless, these materials still greatly benefit from the increased wear resistance and corrosion protection offered by anodization.
Beta Titanium Alloys
Understanding titanium alloys and their characteristics
Their outstanding strength, lightness and resistance to corrosion make titanium alloys highly regarded. Here is a brief summary of these materials based on the latest information from industry professionals.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Titanium alloys, particularly Ti-6Al-4V, have excellent specific strengths that make them ideal for aerospace, medical device and high-performance engineering applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: All grades of titanium including Grade 2 possess excellent corrosion resistance even at very aggressive environments such as seawater and acidic conditions.
- Biocompatibility: Titanium is biocompatible i.e. it is not toxic and can be tolerated in human body that makes it great for biomedical implants as well as surgical instruments.
- Anodizing Potential: Through anodization method, titanium alloys can be made in different colors for aesthetic reasons as well as decorative and industrial cases where both utilities are enhanced through this process.
- Temperature Performance: Mechanical properties of titanium alloys remain virtually unchanged over a wide temperature range – from cryogenic sub-zero temperatures up to over 600°C — making them capable of withstanding severe operating conditions typical for space or deep-sea applications.
How different types of titanium respond to anodization
Anodizing titanium is an electrochemical method that creates an oxide layer on its surface, thus making it more resistant and providing a wide range of physical properties. The response to anodization of the various grades of titanium alloys depends on their chemical composition and inherent characteristics.
- Commercially Pure Titanium (Grades 1-4): These are highly responsive to the process and have the ability to achieve several different colors of the spectrum. Such a uniform oxide layer, which is formed due to high material purity ensures that one can predict the outcome in terms of color. Comparatively softer than Grades 3 and 4, Grades 1 and 2 have better ductility hence more even anodized surfaces.
- Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5): Ti-6Al-4V being among the most common titanium alloy types also exhibits good behavior under anodizing conditions, although its color spectrum might slightly be affected by presence of impurities such as aluminum or vanadium for example. This perfectly conforms to our expectations since this alloy possesses higher strength endurance than others; hence its choice both for functional and decorative reasons is not surprising.
- Beta Titanium Alloys: For instance, there are aluminides like Ti3Al8V6Cr4Mo4Zr, which offer excellent mechanical properties combined with flexibility. However, beta alloys may vary in their color during oxidation because they often contain several intermetallic phases. Adjustment of parameters during anodization should ensure specific surface finish.
The importance of the underlying titanium in color formation
Reference sources
1. Online Article: “Titanium Anodizing Color Guide” by Siren Body Jewelry
- Link: Siren Body Jewelry
- Summary:
Siren Body Jewelry’s article offers a detailed Titanium Anodizing Color Guide, presenting 12 distinct titanium anodized colors. The guide explains the process behind titanium anodizing and showcases high-quality images of the different colors achievable, including a high polish (silver) finish. With a focus on both aesthetics and practical application, the article serves as a visual reference for individuals interested in understanding and selecting titanium anodizing colors. - Relevance:
This source is valuable for those seeking a comprehensive overview of various titanium anodizing colors, complete with visual representations. Siren Body Jewelry’s expertise in body jewelry ensures credibility and relevance for individuals looking to explore color options in titanium products.
2. Manufacturer Website: “Anodized Titanium Color Chart” by Monster Bolts
- Link: Monster Bolts – Anodized Titanium Color Chart
- Summary:
Monster Bolts’ color chart provides a detailed overview of anodized titanium colors, showcasing options such as Bronze, Purple, Blue, Light Blue, Gold, Rose, Magenta, Teal, and Green. The chart explains how these colors are achieved through the anodization process and highlights the wide range of color variations possible. It also touches on the limitations of certain colors due to the nature of anodizing. - Relevance:
This resource is relevant for those looking for a visual representation of titanium anodizing colors and an understanding of the achievable color spectrum. Monster Bolts’ specialization in fasteners and hardware products lends credibility to the information provided.
3. Blog Post: “Anodized Titanium: Ultimate Guide 2023” by Tuofa CNC Machining
- Link: Tuofa CNC Machining Blog
- Summary:
Tuofa CNC Machining’s blog post serves as the ultimate guide to anodized titanium, focusing on the various colors that can be achieved through voltage variation during the anodization process. The post discusses how higher voltages result in gold and pink colors, while lower voltages produce different hues. It provides practical insights into manipulating voltage settings to achieve desired color outcomes on titanium surfaces. - Relevance:
For readers interested in the technical aspects of titanium anodizing and color manipulation, this blog post offers valuable information on voltage control and its impact on color variation. Tuofa CNC Machining’s expertise in CNC machining enhances the credibility and relevance of the content for those seeking in-depth knowledge on anodized titanium colors.
These sources collectively offer a mix of practical guidance, visual references, and technical insights into titanium anodizing colors, catering to a diverse audience interested in exploring the colorful possibilities of titanium surfaces.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is titanium anodizing?
A: Titanium anodizing is a technique in which a layer of oxide is formed on the surface of titanium by means of electro-chemical process. A variety of colors can be obtained by varying the thicknesses of this layer.
Q: Why is titanium anodizing popular?
A: Titaniums have been the preferred materials for many years because it renders them to be multi-colored, while maintaining their inherent strength and resistance to corrosion.
Q: How does the anodizing process produce the color on titanium?
A: The colors are caused when light interferes with its passage through the layer of titanium oxide. The color depends on the thickness of this oxide during anodic oxidation.
Q: What are the available colors in the anodized titanium color chart?
A: In fact, almost all colors from blue, purple, green, orange to yellow can be found in a color chart containing different forms of oxidized titanium. The choice rests on voltage applied during oxidation.
Q: What voltages correspond to specific colors when anodizing titanium?
A: Specific voltages as seen in the colour chart tell us what colour will result at specified voltage values. For instance, gold or bronze colours might be obtained using lower voltages whereas blues and purples can come about from higher ones.
Q: Can anodized titanium parts be used in medical applications?
A: Yes, these are commonly used in medicine since they are bio compatible, non-reactive and resistant to wear due to being treated with Anodic Oxidation.
Q: What should be avoided to prevent a splotchy color during anodizing?
A: For example; insufficient cleaning prior to ANODIZING (and any surface contaminant) can cause blotching and other defects. Maintaining uniform voltage levels throughout and ensuring that appropriate steps have been taken before applying power are vital.
Q: How does titanium anodizing differ from anodized aluminum?
A: However, while titanium anodizing has to do with the thickness of the layer of oxide on this metal, anodized aluminum makes use of dyes to achieve color.








