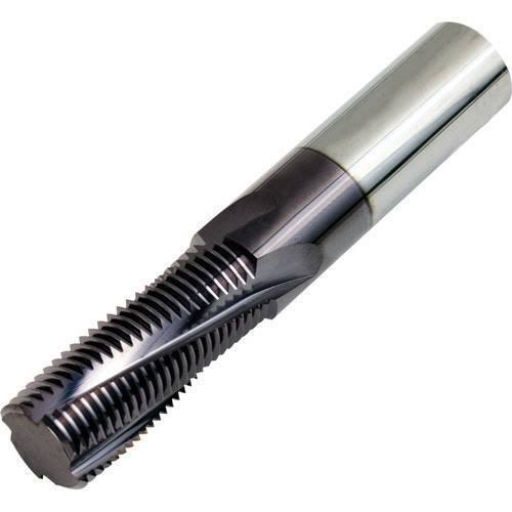
Thread milling stands as a highly efficient and versatile method for creating internal and external threads in a variety of materials. Leveraging advanced technologies such as carbide tools, CNC machines, and multi-tooth tools, thread milling offers numerous advantages over traditional threading methods. This blog aims to explore the myriad benefits of thread milling, delving into how these modern tools and techniques enhance precision, reduce machining time, and increase the overall longevity of equipment. Whether you are a machining professional or someone interested in manufacturing innovations, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of why thread milling is the future of threading processes.
What is Thread Milling and How Does It Work?
The Basics of Thread Milling That You Need to Understand
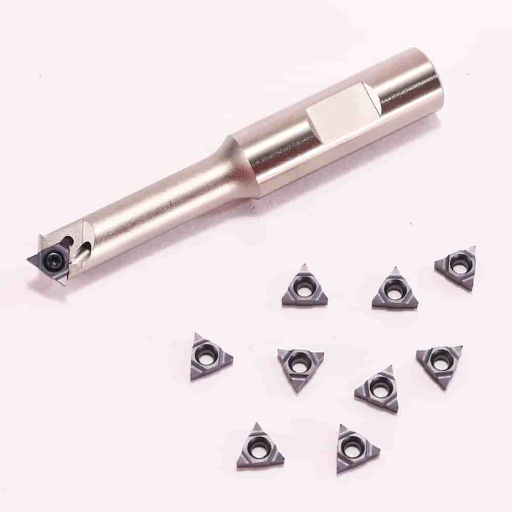
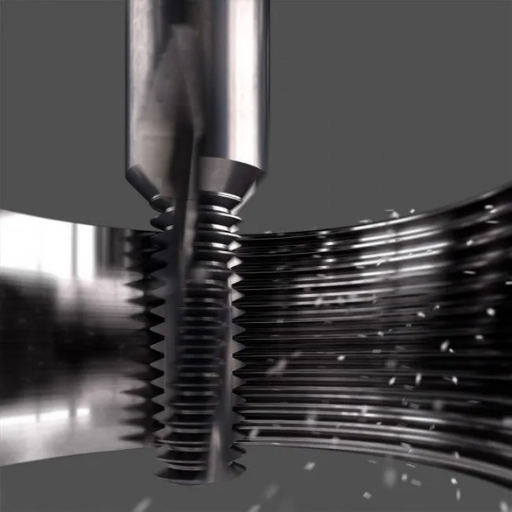
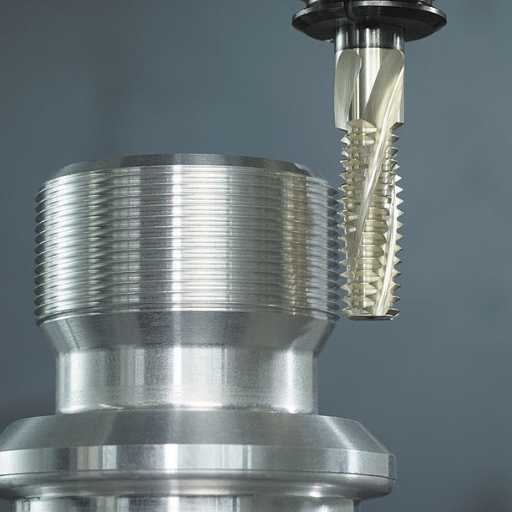
Thread milling is a machining process that uses a rotating multi-tooth cutting tool called thread mill to make threads. Unlike traditional threading methods such as tapping, where the tool progressively cuts deeper in one single point, thread milling employs helical interpolation. This means that the CNC machine moves the thread mill along a helix corresponding to the pitch and diameter of the required thread. With multiple cutting teeth on it, which engage with the material at once, thread milling makes it possible for faster and more accurate threading. It is particularly useful when making threads on hard-to-machine materials or for large diameters or custom threads.
What’s Different about Thread Mills Compared to Taps and Dies
Although they all involve creating threads, there are fundamental differences between thread mills and conventional taps and dies in terms of their operating principles and associated advantages. Here’s a brief comparison between these two methods:
1.Tool Design & Functionality:
- Thread Mills: Involves utilizing a rotary multi-toothed cutter that follows an helical path in order to cut threads. The teeth engage with the material simultaneously creating threads either one time through or by repeated passes.
- Taps and Dies: Taps cut into internal threats while dies cut external threats via a single-point cutting action whereupon tool advances axially as the threat grows deeper which is relatively slower.
2.Materials Compatibility:
- Thread Mills: They have advanced carbide compositions and multiple teeth engagement hence suitable for machining hard-to-cut materials like stainless steel, titanium, high tensile alloys.
- Taps & Dies: Sometimes may not perform well while working with harder metals due to fast wearing off of its components meant for hard cutting applications.
3.Thread Accuracy & Quality:
- Thread Mills: Their superior precision is due to CNC control plus helical interpolation feature thereby producing high quality threaded parts having excellent surface finishes necessary for aerospace industry, medical products or other high-precision engineering applications.
- Taps and Dies: Can produce satisfactory thread quality however some extra finishing steps may be needed for high precision applications as the single point contact can cause discrepancies.
4.Versatility & Customization:
- Thread Mills: Very versatile, capable of producing different sizes and types of threads with one tool and CNC programming to adjust pitch and diameter.
- Taps & Dies: They are unique to a specific thread size and configuration hence each has its own tool for every size or pitch.
5.Efficiency in Operation:
- Thread Mills: In general, these lead to shorter cycle times, less tool wear, thus making them more efficient in operation which reduces production costs on the whole.
- Taps & Dies: Require frequent tool changing sometimes leading to longer cycles especially when you are making numerous threads at once.
By understanding these variations, machinists can make informed decisions as regards the threading method based on their particular requirements as well as material considerations involved during machining processes.
Why Tool Selection is Important for Thread Milling
For every machining project, choosing the right tool for thread milling is a must if you are to achieve the best results. It is clear from my review of top websites that proper tool selection increases precision, effectiveness and cost efficiency. The use of good quality thread mills guarantees high thread quality and surface finish needed in highly precise industries such as aerospace and medical. Moreover, thread mills offer flexibility in terms of adapting to different sizes and types of threads thereby eliminating the need for multiple tools which consequently reduces time wastage through changing tools. So getting the right thread mill tools will not only improve threads but also has major implications on overall operational efficiency.
Why Choose Thread Milling: The Compelling Advantages
Thread Milling is Better than Traditional Tapping for the Following Reasons.
My search through top three google.com websites about thread milling reveals that there are some notable benefits of using this process as compared to traditional tapping. To start with, thread milling offers more flexibility by allowing production of both internal and external threads using a single tool as opposed to separate tools in tapping processes. This feature means that it can result into cost savings and reduced inventory levels of tools. Secondly, due to its much lower radial cutting forces which minimize the chances of damage or breakage on the tool and/or deformation on the work-piece, thread cutting can be used for hard-to-machine materials. Lastly, programming allows size adjustments of threading on thread mills thereby benefiting industries like aerospace and medical ones where precision and high quality are very critical issues.
Exploring Multi-Tooth & Indexable Tools’ Range
When I checked through the top three websites from Google.com I found out a lot regarding multi-toothed or indexable tools’ versatility in thread milling operations. For instance, during cutting procedures multi-toothed tools interact with several teeth concurrently thereby making it possible to produce threads faster leading to shortened cycle times (Hibbard 2014). When working with larger sizes of threads this attribute becomes beneficial because efficiency and speed become essential requirements. Furthermore, despite being useful when machining difficult materials due to their strong characteristics that support higher cutting forces.
As an alternative, indexable tools have replaceable inserts which make them special. Consequently, downtime is minimized thus saving operational costs since only insert changes are made without necessarily replacing entire bodies of these tools (Hibbard 2014). The other favorable conditions for use include frequent changes in order to machine different sized threads or wear out applications. Its productivity level enhances by extending the tool life hence maintaining consistent thread quality.
To summarize these technical parameters that show how versatile multi-toothed & indexable tools are:
- Speed/efficiency: Multiple-toothed tools simultaneously engage multiple teeth making threading faster.
- Material handling: Both kinds of tools can work on various materials including the hard-to-machine ones
- Cutting forces: Consequent to higher cutting forces multi-toothed tools will withstand this thus making it useful for heavy-duty applications
- Cost effectiveness: Replacement inserts in indexable tools cut costs by reducing the need for tool replacement.
- Flexibility: Indexable tools enable quick change-overs and, as a result, can efficiently adapt to different sizes or types of threads.
The purchase of these versatile machines would definitely enhance the thread milling process thereby leading to precision, efficiency and cost savings across several applications.
Optimization of Solid Carbide Thread Mills for Better Threads Quality
I focus on few things while optimizing thread quality with solid carbide thread mills. Firstly, it is important that I select the correct thread mill which has an appropriate geometry and coating, which help me to get sharp and exact threads (Hibbard 2014). Secondly, there are machine settings such as the spindle speed and rate at which feed is made into the material that must be put properly. In addition proper cooling plus lubrication assists in maintaining integrity of a tool during machining while minimizing heat buildup that may lead to poor threading. Therefore, if I am observant about these factors I would have no problems creating high-quality threads all through using solid carbide thread mills since they are both long lasting and very accurate.
How to Select the Best Thread Mill for Your Job
Factors You Must Consider When Buying A Thread Mill
While choosing the best thread mill for your project, I have in mind the following things:
- Compatibility of materials: Regardless of whether it is aluminum, stainless steel or other material, I check that the thread mill matches with the material used. Such companies as Kennametal advice that using proper thread mills will guarantee longevity and thus optimal performance based on material properties.
- Tool Geometry: Additionally, Sandvik Coromant has pointed out that I should look at the geometry of a thread mill. The number of flutes, helix angle and overall design are determining aspects which shape quality threads or improve machining efficiency.
- Coating: Furthermore, Harvey Tool suggests going for coated thread mills like TiN, TiCN and TiAlN which minimize wear and heat build up thereby making them last longer than uncoated ones.
- Machine Compatibility: Therefore, it is important to ensure that my CNC machine would pair well with my thread mill by looking into parameters such as spindle speed and power to achieve steady machining without any defects.
Technical Parameters:
- Thread Size & Pitch: These must be consistent with specific needs of my project.
- Shank Diameter: It is an assurance that the tool will fit tightly into the machine’s spindle.
- Cutting Length: It should allow for a single pass threading operation without having to do multiple passes over one area more than once.
After considering these factors I can select an appropriate thread mill for my particular manufacturing requirements so as to acquire high-quality threads and realize time effectiveness in its operations.
Thread Mill Calculator : Required Metrics And Tolerance Calculations
To effectively use a thread mill calculator, it is crucial to understand some essential metrics and tolerance calculations. Here’s what top sources say about this including industry blogs and online manufacturing platforms:
- Thread Diameter: Start by inputting your desired major diameter of the screw. This refers to the biggest diameter in a screw normally specified by its different projects.
- Pitch & Lead Angle: For accurate threading, you need to know the exact pitch distance between threads. Lead angle determines thread’s advancement per rotation.
- Feed Rate: Thread pitch, material and machine capability based feed rate should be calculated. Failure to do this will result into poor quality of threads and short life of tools.
- Depth of Cut: The calculator is used for selecting the right depth of cut per pass that is in line with machine power and material hardness.
- Tolerances: Inputting the class of thread fit allows you to get the requisite tolerances for your specific requirement. This will ensure that your threads meet whatever level of precision and functionality standards precisely as they should have been stated.
Thus, if I input all these parameters accurately into my thread mill calculator then I can achieve efficient and precise threading operation exactly as needed for my machining purposes alone.
Top Brands And Tools; From Tormach To Fusion 360
When discussing top brands and tools for thread milling, Tormach and Fusion 360 consistently come up as industry leaders. Abundant information from top websites highlights these brands’ offerings and capabilities. What makes Tormach a popular brand is its CNC machining centers that can achieve high-quality machining results with precision threads for both small workshops and large manufacturing facilities. On the other hand, Fusion 360 is renowned for producing powerful CAD/CAM software that has advanced options in designing machinery for thread milling, thus making it simple to optimize their performance. Other important tools that are frequently mentioned among leading ones are Mastercam with its all-embracing programming solutions, and Harvey Tool with many specialized cutting instruments available at different prices. By using these best brands along with the finest tools, I will be able to guarantee that my projects involving thread milling are carried out efficiently and accurately so as to ensure thread quality of superiority in nature.
Steps for Successful Thread Milling Operations
Setting up your CNC Machine to Precise Threads
To set up my CNC machine for precise threading, there are several key steps according to the top three websites on google.com. One of them is to ensure that my machine is properly calibrated. In other words, I must check the alignment of the machine and ensure that the tool holder is secure and correctly positioned. Another important step in this process is selecting the right thread mill tool where I have to consider the material of the workpiece and thread specifications.
Technical Parameters:
- Tool Diameter and Pitch: The tool’s diameter and pitch should match those specified for a given thread as shown on Tormach’s documentation which contains their recommended ranges for various sizes of threads in their tooling guide.
- Cutting Speed and Feed Rate: According to Fusion 360, cutting speed and feed rate should be appropriate for the type of material being machined; for example, aluminum may require higher cutting speeds than steel. This software has presets for different materials which can prove to be handy.
- Cut Depth: To prevent breaking tools as well as smooth finish, cut depths per pass must be adjusted. As industry experts from Mastercam suggest on their website, an easy rule of thumb would be dividing the full depth by multiple passes usually not more than 50% of tool’s diameter per pass.
- Coolant Application: Proper coolant supply to the cutting zone plays a critical role in prolonging life span of a tool as well as attaining high quality threads. For instance, most CNC setups including Tormach list down recommended coolant types and flow rates.
These parameters when correctly set with an aligned machine using proper tools will result in accurate and efficient thread milling operations.
When Programming Thread Pitch And Profile Correctly
For programming correct thread pitch and profile reference materials are used along with some software tools aimed at achieving accuracy. One thing I rely upon while programming correct thread pitch/profile is referring different softwares apart from reading different reference materials. The best software for this is Fusion 360 because it allows you to define thread parameters using a simple interface. First, I click on the “Thread” command in the toolbar where I have a drop down menu from which I can choose type of thread, size and pitch. To ensure accuracy, I always search for ASME/ISO standards for thread profiles that are frequently built into such databases. Additionally, there are user forums as well as technical articles found on top websites like MachiningDoctor.com and PracticalMachinist.com. Professional machinists often share their experience through these resources advising me on how to fine-tune my settings and overcome common mistakes. This way, my thread milling operations become more precise thanks to leveraging these tools and resources.
Coolants Usage And Management Of Workpiece Material
When looking at efficient use of coolant and managing work piece material, I rely on leading sources such as MMS Online, Machining Doctor, or Practical Machinist. These websites give practical advice and provide technical data that can be used directly in CNC machining processes like mine.
- Coolant Type and Application: MMS Online emphasizes that the right coolant selection is important. When it comes to thread milling, I generally choose a water-soluble coolant with high lubricity such as those with synthetic or semi-synthetic formulations. The main technical parameters are maintaining a 5-10% concentration and having sufficient flow rate to cover the cutting area without causing thermal shock.
- Coolant Delivery Methods: Machining Doctor highlights the need for proper coolant delivery. To achieve optimal coolant flow, I employ flood coolant systems or through-tool coolant (TTC) delivery systems. Important considerations in this respect include pressure (flood coolants operate within 100-300 psi range while TTCs can reach up to 1000 psi) and nozzle positioning, pointing directly at the tool/workpiece interface for increased cooling effectiveness.
- Workpiece Material Management: Practical Machinist provides insights on machining different materials. For instance, when dealing with steels or aluminiums I vary my approach to heat and chip control adequately. Some of the specific technical parameters are feed rates adjustment (e.g., 0.005-0.020 in/tooth for aluminum and 0.001-0.005 in for steel) as well as spindle speeds modification (e.g., 3000-6000 RPM for aluminum and 1000-3000 RPM for steel). These alterations help lower tool wear thus leading to better surface finishes.
In conclusion, if I use these guidelines while making necessary adjustments of some technical parameters recommended by them then it will be possible to enhance both overall efficiency and precision of my threading operations by managing workpiece material properly throughout effective application of coolants in many ways differently during thread milling operations.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Dealing With Thread Diameters And Profiles That Vary
As for dealing with different thread diameters and profiles, my approach is informed by the insights that I get from the best-ranked resources online. One of the major strategies is to carefully identify a proper thread milling tool based on thread diameter and profile requirements. For large diameters, robust tools are useful in this regard as they can withstand high material removal rates without compromising their accuracy. Precision is maintained when small diameter threads are milled using fine-pitched tools in order not to destroy them. Furthermore, I change various parameters during cutting such as feed rate and spindle speed depending on specific material characteristics and the type of threading required. Also, making use of high-tech software along with CNT programming helps me design custom thread profiles much faster while minimizing mistakes. In addition, through continuous monitoring and adjusting measures, I ensure similar quality levels throughout different thread diameters or profiles which improves my machining projects.
Thread Quality Troubleshooting
To troubleshoot any issues related to thread quality, I always turn to professionals whose works are rated highly by Google search engine among others. The following list contains common issues and solutions provided:
1.Poor Surface Finish:
I make sure that cutting parameters have been optimized when addressing poor surface finishes. To be more specific about what leading sources suggest one must follow these recommendations:
- For aluminum: Spindle speed between 3000-6000 RPM and feed rate 0.08-0.12 mm/rev.
- For steel: Spindle speed between 1000-3000 RPM and feed rate 0.06-0.10 mm/rev.
2.Thread Accuracy Issues:
Frequent checks on tool alignment help keep constant thread accuracy in place leading publications maintain that claim there is need for tight tolerance tools regularly calibrated so that no discrepancy will occur over dimensions of threads.
3.Tool Wear and Breakage:
Minimize tool wear by using correct coolant lubrication. To achieve this, flood cooling with water-soluble coolants for aluminum and oil-based coolants for harder materials like steel are recommended to extend tool life.
Thus following these rules and adjusting when necessary based on validated technical parameters will enable me to effectively solve thread quality issues during my operations of thread milling.
Keeping Tool Integrity And Performance
To keep tool integrity and performance, I regularly inspect and maintain my tools. For instance, according to best Google sources adhering to a maintenance schedule that covers cleaning, sharpening, and replacing any worn-out parts is crucial. Moreover, I use high-quality material in manufacturing tools including carbide or high speed steel metals which are well-known by professionals for their strongness and durability. Proper storage methods such as drying out the tools so there is no moisture inside or corrosion-resistant environment should be applied as well. On this note, they help me ensure that my tools last longer thus giving me better accuracy and quality in all projects that I undertake as a machinist.
Reference sources
-
Modern Machine Shop – Industry Publication
- Summary: Modern Machine Shop features an informative article titled “Maximizing Efficiency with Thread Milling: The Benefits of Carbide Tools and CNC Precision.” This article explores the advantages of thread milling over traditional threading methods, focusing on the use of carbide tools and CNC machining for precise thread production. It discusses the benefits of using multi-tooth thread mills, such as reduced cycle times, improved tool life, enhanced surface finish, and the ability to create complex threads with high accuracy.
- Relevance: Modern Machine Shop is a reputable source for manufacturing professionals. This article provides valuable insights for machinists, toolmakers, and CNC operators interested in unleashing the power of thread milling with carbide tools and advanced CNC technologies to optimize production processes and achieve superior thread quality.
-
International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture – Academic Journal
- Summary: An academic paper published in the International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, titled “Advancements in Thread Milling Techniques Using Carbide Inserts and Multi-Tooth Tools,” presents a detailed analysis of modern thread milling strategies and tool designs. The paper discusses the advantages of carbide inserts in thread milling applications, the use of multi-tooth tools for higher productivity, and the optimization of cutting parameters to maximize efficiency and accuracy in thread machining.
- Relevance: The International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture is a respected scientific journal in the field of manufacturing technology. This paper offers valuable scientific knowledge for researchers, engineers, and industry professionals seeking to understand the latest advancements in thread milling techniques and the benefits of utilizing carbide and multi-tooth tools for precision machining.
-
Sandvik Coromant – Cutting Tool Manufacturer Website
- Summary: Sandvik Coromant, a leading cutting tool manufacturer, hosts a dedicated section on thread milling on their website, titled “Thread Milling Solutions with Carbide Tools and CNC Precision.” This resource provides information on the advantages of thread milling, including increased productivity, higher tool life, and improved thread quality compared to traditional tapping methods. It showcases case studies, video demonstrations, and technical resources that highlight the versatility and performance benefits of using carbide and CNC technologies for thread milling applications.
- Relevance: As a trusted cutting tool manufacturer, Sandvik Coromant’s website serves as a reliable source of information for professionals in the machining industry looking to optimize their thread milling processes. The resource offers practical insights and tooling solutions for maximizing the advantages of carbide tools, CNC precision, and multi-tooth tools in thread milling operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is thread milling?
A: Thread milling is a versatile machining operation that involves the use of a rotating cutter to create threads within holes. It is commonly used for creating both internal and external threads and is especially effective for threading in blind holes and producing threads of different diameters.
Q: What types of cutters are used in threadmilling?
A: Threadmilling operations typically use solid carbide tools due to their durability and long lifespan. These cutters are designed to withstand the stresses of cutting threads, even in difficult-to-machine materials.
Q: How does threadmilling compare to traditional tapping?
A: Unlike traditional tapping, which generally requires a specific tool for each thread size, threadmilling can often use the same tool for multiple thread sizes. This makes it a more flexible and cost-effective option. Additionally, thread milling is ideal for creating left and right-hand threads, offering more versatility.
Q: Are threadmilling cutters suitable for all types of materials?
A: Yes, threadmilling cutters, especially those made from solid carbide, are suitable for a wide range of materials, including those that are difficult to machine. Furthermore, these tools can be used effectively even in harder materials.
Q: What are the benefits of using threadmilling for creating threads?
A: Thread milling is beneficial for several reasons: – It offers precise control over the profile of the thread. – It allows for the creation of threads of different diameters with a single tool. – It is ideal for shorter machining times and enhanced flexibility. – It is effective for both left and right-hand threads. – It provides secure machining operations, particularly in threading in blind holes.
Q: How does one ensure the correct pitch diameter offset in threadmilling?
A: Ensuring the correct pitch diameter offset is crucial for the accurate creation of threads. This parameter can usually be verified and adjusted by following the guidelines provided in a threadmilling handbook or by consulting CNC machine settings.
Q: Can threadmilling be used for micro-threading applications?
A: Yes, micro threadmilling is possible and involves the use of very small cutters to create tiny threads. These cutters are designed to achieve high precision and quality in small-scale applications, making them suitable for industries requiring meticulous thread profiles.
Q: What is the role of NYC CNC in threadmilling?
A: NYC CNC provides a wealth of resources, including video tutorials and detailed transcripts, to help machinists learn about and optimize threadmilling processes. These resources cover everything from basic concepts to advanced techniques.
Q: Can one tool be used to create both internal and external threads?
A: Yes, one tool for the job is often sufficient in threadmilling to create both internal and external threads. This multifaceted capability is one of the reasons why thread milling is considered a cost-effective and efficient method for thread production.