In the realm of 3D printing, PolyJet technology has emerged as a pivotal innovation, renowned for its ability to produce highly detailed and accurate models. This blog serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding PolyJet technology, shedding light on its functionalities, applications, and the advantages it offers over other 3D printing methods. We will delve into the mechanics of how PolyJet printers work, explore various materials that can be used, and examine real-world examples of PolyJet printing in action. Whether you are a seasoned 3D printing professional or a curious newcomer, this guide aims to provide valuable insights into the high-resolution capabilities and versatility of PolyJet technology. Through this exploration, readers will gain a foundational understanding of PolyJet printing and its potential impact on industries ranging from healthcare to manufacturing.
What is PolyJet 3D Printing?
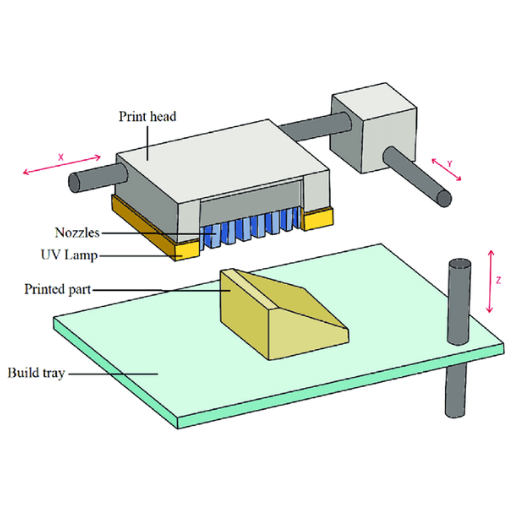
Understanding Objet PolyJet Technology
Objet PolyJet 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that utilizes photopolymer resins to produce super high-resolution and accurate 3D models. It entails spraying layers of liquid photopolymers in the form of droplets onto a tray, where they are then hardened using UV light. The ability to make complex shapes with smooth exteriors such as holes, chamfers etc., is made possible through the system of layer by layer approach for building objects in Objet technology. A wide range of material options can be employed for polyjet right from rigid, flexible and transparent materials to composite materials, which means parts with mechanical properties and aesthetics vary widely. Another feature that distinguishes PolyJet’s technique is its capability of employing various kinds of respective substances at ago making it perfect for applications that necessitate intricate details and high accuracy.
How do PolyJet 3D Printers Work?
PolyJet 3D printers work by jetting out photopolymer droplets on a build tray which are then instantly cured by ultraviolet (UV) light. Starting with the print head moving across the construction area, it deposits tiny droplets of liquid photopolymer in ultra-thin layers as fine as 16microns (0.016mm). As soon as a layer has been deposited it is solidified under a UV light exposure thus enabling a printer to create intricately detailed models characterized by high precision.
Technical Parameters:
- Layer Thickness: 16-30 microns allowing super high resolution printing.
- Accuracy: Finely detailed parts up to 0.1 mm.
- Build Volume: Usually about till model number can vary from machine model but commonly about till1000 x800x500 mm.
- Materials Compatibility: Rigid, flexible, transparent and composite photo polymers available.
This keeps being repeated until the entire model has been built up piece by piece through additive layering process. The capability of PolyJet to use multiple materials simultaneously is achieved by employing several printer heads that enable numerous materials to be printed within a single printout. Each print head is loaded with a specific material during the creation of parts, so they combine seamlessly, resulting in various textures, colors and mechanical properties in one print run. Therefore, PolyJet 3D printing is famous for its ability to produce extremely detailed, precise and versatile prototypes as well as end-use parts.
Applications of PolyJet 3D Printing
PolyJet 3D printing has wide applications across several industries due to its high accuracy, material versatility and ability to create complex geometries. Below are some examples:
Prototyping:
- Technical Parameters: High-resolution printing (layer thickness: 16-30 microns), Accuracy up to 0.1 mm.
- Description: It makes it possible for designers to develop detailed prototypes with fine features and smooth surfaces so that they can test form fit and function before moving into mass production.
Dental and Medical Models:
- Technical Parameters: Accuracy up to 0.1 mm, Material compatibility with biocompatible photopolymers.
- Description: It allows fabrication of precise dental models, surgical guides or custom medical devices used in patient-specific care and treatment planning.
Consumer Products:
- Technical Parameters: Build volume up to 1000 x 800 x 500 mm, Multi-material capability.
- Description: This helps create intricate designs functional prototypes among other consumer goods including those worn such as electronic gadgets; fashion accessories like watches are made this way too while others are just things for home use.
Education and Research:
- Technical Parameters: Versatility in material and color options.
- Description: Thus making it better suited for engineering education providing tangible examples illustrating complex concepts among students attending engineering colleges where doing something hands-on becomes crucially important rather than communicating through abstracts only all the time.
Aerospace and Automotive:
- Technical Parameters: High resolution and accuracy (layer thickness: 16-30 microns, Accuracy up to 0.1 mm).
- Description: Used in the production of prototypes and final consumer goods that must meet specific dimensions and require high-performance materials such as components used in aircraft interior and automotive parts.
Art and Entertainment:
- Technical Parameters: Multi-material capability, Material versatility (rigid, flexible, and composite photopolymers).
- Description: Suitable for movie sets, theatrical hardware, and exhibition artwork involving fine props, costumes, and sculptures.
Generally speaking, PolyJet 3D printing is a valuable tool used in various industries from industrial manufacturing to creative arts because of its ability to produce high-precision parts made of different materials in multiple colors.
How Does PolyJet™ 3D Printing Compare to Other Technologies?
PolyJet vs. SLA 3D Printing
When one looks at PolyJet compared with SLA (Stereolithography) 3D printing, a series of key differences emerges. Photopolymerization is involved in both technologies but the former entails dispersion of multiple layers of liquid photopolymer on a build tray that are then cured with UV light for multi-material and multi-color applications while the latter deploys laser technology to cure liquid resin, layer by layer in a vat, often yielding higher accuracy and smoother surface finishes suitable for small details.
PolyJet is recognized for its flexibility and speed due to it being able to produce different parts with different materials within one print cycle. It is especially good at creating realistic models that have bright colors and diverse textures hence suitable for sectors like healthcare, consumer goods and entertainment. On the other hand, people often choose SLA when they want something really detailed looking or having a better quality finish on the surface such as dental models, jewelry or master patterns for casting.
Both technologies can make excellent parts; however whether PolyJet or SLA will be used depends on project-specific factors such as material properties, color needs, surface finish requirements and size of finished part.
Comparison with Material Jetting Techniques
There are several differences between PolyJet 3D printing and other material jetting techniques. Both PolyJet technology and material jetting methods utilize drops of photopolymers placed layer-by-layer resulting in fabrication of objects; however what makes PolyJet stand out is its ability to use more than one material/color in one print. For example this technique allows production of complex geometries involving many materials like flexible rubber-like parts together with stiff plastics often achieved at once during single build cycle.
Other types of material jetting including Binder Jetting or DOD (Drop on Demand) printing mostly involve single-material printing thus lack multi-material integration capabilities inherent in these methods. In binder jetting, for instance, binding agents are used to join powder particles that need further treatment such as sintering or infiltration before final product is made increasing the steps and time that it takes to produce. On the other hand, DOD printing which is often employed for wax patterns in investment casting is precise but not as versatile in terms of materials since there are few color options available.
To sum up, PolyJet printer and material jetting technology provide the solution for additive manufacturing. However PolyJet can stand out because it has a high-speed production of multi-materials and multi-color models with fine detail which makes it suitable for industries requiring realistic prototypes and diverse material properties.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PolyJet
Advantages:
- Multi-material and Multi-color Printing: What makes PolyJet really unique among 3D printers is its ability to print various materials at once with different colors. This allows not only making realistic prototypes but also achieving different mechanical properties such as stiffness and flexibility in one model.
- High Resolution and Fine Details: In fact, 16 microns layer thicknesses can be achieved on any part printed using polyjet while horizontal resolution could be about 600 dpi thereby enabling the production of parts with intricate details and smooth surfaces.
- Speed and Efficiency: When compared to traditional manufacturing methods, PolyJet technology facilitates faster build speeds coupled with minimal post-processing necessary to deliver good-quality parts within shorter period.
- Versatility: There’s a wide range of photopolymers supported by this technology including elastomers like rubber, polypropylene or ABS plastic-like materials that make it applicable in variety industries.
Disadvantages:
- Material Cost: It is usually the case that photopolymer resins used in PolyJet printing are more costly than those used in other additive manufacturing techniques.
- Mechanical Properties: No matter how impressive PolyJet prints might be to the eyes, the strength and durability of their photopolymers may not match up with those obtained from other processes like SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) or FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling).
- Limited Build Volume: The build volume of PolyJet printers is generally smaller than that of other industrial 3D printing technologies, which could restrict the size at which parts can be manufactured within a single print.
- Post-Processing Requirements: Even though post-processing steps are few, there remains support removal and cleaning of residual material requiring a lot of labor for complex geometries.
In conclusion, although it has issues on material cost, mechanical strength and post-processing requirements; PolyJet 3D printing outstands for its amazing capabilities with regards to material integration and color, resolution and production speed.
What Materials Can Be Used in PolyJet Printing?
PolyJet Material Types
Polyjet 3D printing encompasses a range of materials with each aimed at satisfying specific engineering, design and functional requirements. The main categories are:
- Conventional Plastics: These substances mimic the attributes of common plastics like ABS and polypropylene thus having a combination of strength, flexibility and durability. They are handy in rapid prototyping and manufacturing end products.
- Elastomers: This PolyJet material is designed to simulate rubber-like qualities which provide flexibility as well as toughness that can withstand bending and stretching repeatedly. Gasket, seal and grip applications will benefit from these compounds.
- High Temperature Materials: These materials last longer at high temperatures hence suitable for use in parts that must operate under thermal stress or for high heat applications such as car parts.
- Transparent Materials: There are clear PolyJet materials that allow for making see-through prototypes or objects mainly used in certain industries such as eyewear design, lighting and consumer electronics.
- Medical Biocompatible Materials: These types are specifically formulated for medical/dental device manufacturing because they meet regulatory safety measures along with performance standards. They help produce surgical guides, dental models, prosthetics among others.
- Digital Materials: Combining different resins during printing makes polyjet capable of producing composites with tailored properties. This includes differing levels of hardness or softness, transparency or color etc…
With the wide range of PolyJet materials available it is possible to choose one that has the ideal mix of properties to suit any given application requirement; thus allowing engineers/designers achieve their required outcomes accordingly.
Properties of PolyJet Material
Polyjet materials have a number characteristics which make them useful across various applications. Here are some key properties:
- High Resolution Accuracy: With layer thicknesses as fine as 16 microns (µm), one can appreciate why this technology delivers detailed designs featuring complex shapes unattainable by other methods hence smooth surface finishes.
- Material Versatility: Different mechanical characteristics for various parts such as hardness, flexibility and transparency can be achieved since PolyJet has the capability of using more than one material in the same print. This makes it possible for composite prototypes requiring different properties within a single component.
- Smooth Surface Finish: Parts made with Polyjet technology have very smooth prints that require little post processing work. This is especially important for industries where aesthetics are key.
- Accuracy and Consistency: It also means that the dimensional accuracy of poly jet materials is so high that they can be used for precision engineering applications. The reliable performance of these materials ensures repeatability in production.
- Mechanical Property Range: With tensile/flexural strength, rigidity and elasticity varying, there is enough choice for both flexible and stiff applications which is offered by PolyJet products.
- Color Capability: For producing prototypes or models that need to differentiate colors and look realistic, different colors or shades can be used in a singular polyjet print.
These features demonstrate how durable Polyjet materials are; therefore they are frequently chosen by creative 3D printing users who want their projects done with a quality edge.
Biocompatible and UV Resistant Options
Polyjet technology itself comprises of biocompatible materials as well as those that are resistant to UV light thus making it applicable in medical field or outdoors. Biocompatible PolyJet materials such as MED610 and MED620 meet all regulatory requirements put in place to govern their use on patients hence safe for surgical guidance implants, dental appliances plus many other healthcare products. These substances can withstand sterilization processes performed on them directly as they come into contact with human body organs.
PolyJet also boasts of biocompatibility, and the UV-resistant materials that are suitable for outdoor applications and things exposed to sunlight for a long time. These color-fast, strong and durable UV resistant materials are perfectly matched with outside signs, architectural models and other projects that require them to fight elemental impacts. This interplay of properties makes PolyJet printing useful in numerous industries.
How Do PolyJet™ 3D Printers Achieve High Resolution?
Print Heads Role in PolyJet 3D Printers
In order to achieve high resolution and precision, print heads play an important role in PolyJet 3D printers. These print heads have many nozzles which spurt tiny photopolymer droplets onto the building tray at the same time. These small drops are instantly solidified by ultraviolet (UV) radiation allowing them to be built up one layer at a time for a three-dimensional object. The advanced printers produce material with a thickness of just 16 microns thus ensuring that smooth surfaces, fine details and sharp edges are realized. It is this precise control of droplet sizing and subsequent layering accuracy that allows for highly complex models with more detail than any other type of printer on the market today.
The Importance of Build Platforms
The build platform is vital to producing accurately printed models on a Polyjet 3D printer. There needs to be a stable, precisely calibrated build platform so as to facilitate multiple layers of photopolymer materials. This will ensure that there is minimal movement or misalignment during printing which is very essential for maintaining the high-resolution level and delicate finishing associated with polyjet technology. Moreover, build platforms typically have adhesive properties or supports to secure printed models during output thereby preventing any warping or detachment serious enough to undermine the integrity of final products from occurring. Such combination is important because it assures reliability as well as good quality for these machines’ components when they are used in reality.
UV Light Curing Process
The UV light curing process assists in solidifying polymers used in making accurate detailed scale like objects through PolyJet 3D printers. After being jetted onto the build tray by the print heads, each layer rapidly cures under series of UV lamps. It means that before adding another layer, these rays harden and stabilize builds hence enabling their being built up one thin slice at a time until they form three-dimensional objects. Besides maintaining the fine details and smooth surfaces that are typical of PolyJet 3D printed models, UV light curing is very effective. This means that it is no longer necessary to go through the process of post-processing since the layers become solidified providing a finished product which has already hardened to an extent that it will not require much more time for additional curing or refining.
What are the Key Benefits of Using PolyJet in Product Development?
PolyJet Technology for Efficient Rapid Prototyping
Speed and accuracy are the hallmarks of PolyJet technology in rapid prototyping. I like that PolyJet printers can make intricate designs and details with high resolution so that I can quickly experiment with different versions of my designs. Moreover, this category enables use of multiple materials at one time hence enabling me to produce prototypes which have similarity to final items in property like diverse textures and mechanical attributes. These characteristics often reduce development duration while enhancing product quality thus making PolyJet a valuable tool in my process of developing products.
Creating Prototypes with Multiple Materials and Full-Color
My ability to visualize and test product designs is greatly boosted by creating multi-material and full-color prototypes using PolyJet technology. With Polyjet I can mix various materials together so that prototypes will contain varying textures, strength, flexibility etc all in a single model. The full color feature also helps for producing very real looking prototypes that more accurately demonstrate what the final product will look like and therefore assist better design decisions as well as provide a vision for stakeholders who have more tactile sense about their input during discussions about these objects. Also, by drawing all the resources together into one place, we speed up the developmental process ensuring not only a similar look but also functionality between the models in question and its intended end item.
PolyJet Provides Surface Finishes And Details
As an avid user of PolyJet technology, its outstanding surface finish qualities and incredible precision are game changers. In this light, its smooth surfaces minimize post-processing requirements once printing is over on top of that it allows high resolution levels to be achieved through fine detailing such as texts or complex patterns needed on some prototypes . Additionally, when it comes to detailed functional prototypes or complex design concepts presentation optically thin layers may be produced by said technique even though they were composed from as little material as 16 microns only thereby perfecting even inconspicuousness concerning any minor features. The combination of relatively high detail fidelity and excellent surface finishes leads to a more efficient and accurate product development cycle.
Reference sources
- Stratasys
- Source: PolyJet Technology for 3D Printing
- Stratasys provides an in-depth guide on PolyJet technology, highlighting its precision and versatility, making it suitable for high-resolution 3D printing.
- GoEngineer
- Source: Ultimate Guide to PolyJet: Applications, Advantages, …
- GoEngineer discusses the applications, advantages, and material options of PolyJet technology, emphasizing its capability to produce high-resolution layers.
- Sculpteo
- Source: Ultimate guide to Polyjet 3D Printing
- Sculpteo’s guide covers the versatility of PolyJet technology, including the ability to use various materials to achieve detailed and high-resolution prints.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is PolyJet 3D printing technology?
PolyJet 3D printing technology is an additive manufacturing technology that uses inkjet printing to deposit layers of photopolymer onto a build tray; hence, can create high-resolution, full-color, multi-material prototypes characterized by smooth surfaces and intricacies.
Q: How does PolyJet printing work?
PolyJet prints by curing tiny droplets of photopolymer from multiple print heads through an inkjet on a build tray. Each time these layers are piled up the result is accurate three dimensional printed parts.
Q: What types of materials can be used in PolyJet technology?
PolyJet may be applied to many different materials such as rigid ones, using rubber-like materials or even creating multicolor photopolymers. The mechanical and visual properties of parts made with this kind of technologies vary significantly.
Q: Can PolyJet printers create multi-material prototypes?
Yes, PolyJet printers have the ability to print several colors and materials simultaneously in one build therefore making it possible for the production of multi-material prototypes that emulate a large number of commercially available materials.
Q: What is the resolution of PolyJet 3D printed parts?
It also creates parts with small features, fine finishes and an accuracy down to fourteen microns per layer (Stratasys).
Q: How does support material work in PolyJet 3D printing?
During 3D printing process complex geometries are supported by some material called scaffold. This support material is then eliminated either manually or through water jetting so that what remains is the final printed part.