PolyJet 3D printing has become a game changer in the way we view contemporary manufacturing and design. In terms of its accuracy, rapidity, and ability to create complex, multi-material items, PolyJet technology is on top of the additive manufacturing industry. This article aims at exploring the basic things about PolyJet 3D printing so as to give readers a complete overview of its features, uses, and how widely it is transforming industries worldwide. For those who are already well established players in this field or just starting out with this concept of 3D printing technology, this manual provides valuable insights into why PolyJet printers represent critical tools for innovation and creativity.
What is a Polyjet 3D Printer?
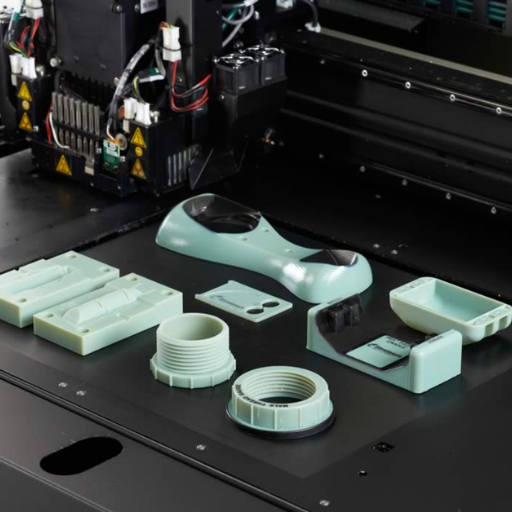
Image source: https://inodus.co.uk/
A polyjet 3d printer is an advanced AM machine that deposits layers of photopolymers onto a build tray and then cures them using ultraviolet (UV) light. This technology allows for high accuracy that permits complex geometries with smooth surfaces and intricate details to be formed. With PolyJet printers it’s possible to print several materials simultaneously including rigid, flexible as well as transparent substances; hence they offer great flexibility that makes them suitable for generating lifelike prototypes, intricate models or assemblies made up from different materials with unique mechanical properties.
How does Polyjet 3D Printing work?
PolyJet 3D printing is an additive manufacturing technology that uses head jets to spray tiny droplets of liquid photopolymer materials onto a build platform as it moves vertically. These layers, usually between 16 and 32 microns thick, are cured immediately by ultraviolet (UV) light. The process is repeated layer by layer until the entire object is created and then each time the build platform lowers slightly. Other than this, gel-like materials are also used to print support structures for overhangs and other complex geometries that may be subsequently removed via water jetting or manual peeling. Thus, PolyJet technology can create multi-material parts with varying mechanical properties and aesthetic qualities in one single build operation.
What are the key components of a Polyjet 3D Printer?
In addition to the cartridges containing these resins, other key components of any PolyJet 3D printer include print heads, UV light sources as well as a build platform. Print heads which have multiple nozzles release hundreds of small droplets of photopolymer material exactly on the location intended on the given surface. Consequently, such droplets solidify upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light source in a form of consecutive layers leading to final creation of a three dimensional product desired. The printed object is supported by a build platform which moves up incrementally allowing for additional layers repeatedly added on top of each other at every cycle. This means that material cartridges contain photopolymer resins including rigid, flexible and transparent substances among others thus allowing different types of 3D printing with high resolution within a broader range of applications. Finally, post-printing removal requires complex structures made out from support material.
What makes Polyjet different from other 3D Printing Technologies?
Notably, PolyJet 3D printing is unique among other 3D printing technologies because it can produce very detailed and precise parts with smooth surfaces. Unlike FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) where filament is pushed through a hot nozzle or SLA (Stereolithography) that uses a laser to cure the resin, PolyJet has several print heads that spray tiny droplets of photopolymer material which are instantly solidified by UV light. Thus, this technology allows for simultaneous printing of various materials and colors within one build, hence enabling complex structures with mixed materials and different colours. The technology also has a lot of latitude for customization as far as materials such as stiffness, flexibility and clarity are concerned making it perfect for intricate models in medicine, prototypes and tailor-made consumer goods. Additionally, compared to most techniques, PolyJet has finer layer resolution thereby offering better details and finish.
What Materials Can be Used in Polyjet 3D Printing?

In order to meet different applications, a wide array of photopolymer materials may be employed in PolyJet 3D printing. This can range from rigid resins which are used for making sturdy and tough parts, flexible resins that are employed for items which require elasticity and transparent resins meant for clear components. Furthermore, blending various resins results in digital materials with differing properties including hardness, flexibility and color among others. This makes PolyJet an ideal choice for delicate prototypes, medical models as well as customized consumer products providing unrivaled detail and surface finish.
What types of photopolymers are available?
PolyJet 3D printing uses different sorts of photopolymers for varied application needs. They include:
- Rigid Photopolymers: These materials are built for strength and toughness making them suitable for making sturdy parts that demand a single structure.
- Flexible Photopolymers: These can be bent and stretched without breaking thus used to produce elastic articles like rubber parts.
- Transparent Photopolymers: For example, these can be lens materials, or covers; they are perfect for applications that entail components with clearness.
- High-Temperature Photopolymers: Designed to withstand high temperatures, these polymers are perfect for assessing the thermal performance of prototypes or components.
- Bio-Compatible Photopolymers: These are intended for medical and dental purposes hence must be biocompatible in order to avoid any harm to human body through direct contact.
- Digital Photopolymers: Digital materials have custom properties as they can combine two or more base resins during printing process hence having specific colors, mechanical characteristics and rigidity levels.
Can Polyjet 3D Printers use multiple materials?
PolyJet 3D printers can simultaneously use multiple materials in a single print job. This feature helps to build complex models with different properties by combining tough and flexible parts, achieving variable transparency or producing multicoloured items. Blending different photopolymers during the printing process allows for highly detailed and functionally varying prototypes and end-use parts which make PolyJet technology a versatile and powerful tool applicable in many areas.
Are there biocompatible materials for Polyjet Printing?
There are biocompatible materials available for PolyJet printing, designed specifically for medical and dental applications. It is worth mentioning that these biocompatible photopolymers meet the strict regulatory requirements set forth for safe use in long lasting skin contact, short term mucosal contact as well as implants of not more than 30 days duration (Stratasys Inc n.p.). According to Stratasys, one of the top providers of PolyJet technology, this list includes the likes of MED610 and MED625FLX that satisfy the biocompatibility criteria thereby making them appropriate for designing dental models, surgical guides and other medical devices meant to interface safely with human body tissues.
What are the Advantages of Polyjet 3D Printing?
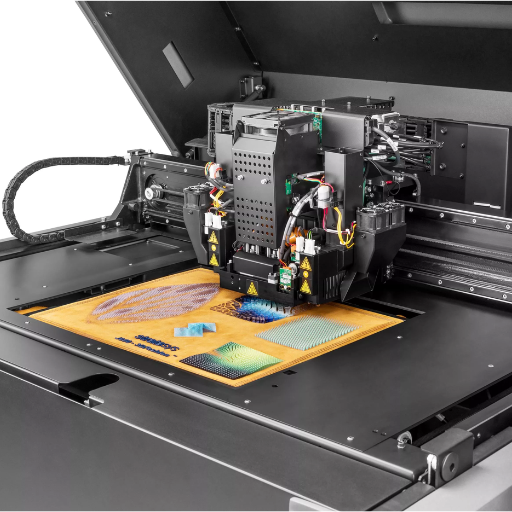

PolyJet 3D printing offers various industrial sectors some distinct benefits that make it a valuable technology. To begin with, it allows for high-resolution printing with intricate details and smooth surface finishes, improving the aesthetics and functionality of prototypes as well as end-use parts. Moreover, it can print using several materials together, producing complicated models that have different mechanical properties, colors and transparencies within one single job. In addition to this , PolyJet printers can create flexible, rigid or biocompatible components which widens its application range especially in the medical and dental fields.Lastly , this technology enables fast production of prototypes leading to shorter development cycles and reduced costs.
Why choose Polyjet for producing full-color 3D models?
To point out why PolyJet is the best option for creating 3D colored models made of a variety of materials, there are several reasons. First is its unmatched ability to print with numerous colors while capturing even the finest details leading to vivid and very accurate models. Stratasys among other companies states that PolyJet has an ability to provide over 500k color combinations which is necessary for applications like medical models or product prototypes requiring detailed visualization.Additionally,multi-material prints are supported by Polyjet on a single run that incorporates different textures along with transparencies increasing further the functionality plus attractiveness of these model designs.Moreover,the technology has high resolution hence making every tiniest complex patterns represented precisely hence being good for complicated designs and unique purposes.Finally,PolyJet’s easy-to-execute printing process makes it possible to have quick turnarounds at minimal cost making it applicable across industries.
How does Polyjet offer high accuracy and smooth surfaces?
PolyJet technology uses a bunch of microscopic nozzles that discharge many layers of liquid photopolymer which are applied at the same time to the build platform in order to achieve high accuracy and smooth surfaces. For instance, this kind of layer by layer precise material deposition usually achieves delicate details as well as smooth finishes with thinnesses sometimes less than 16 microns thick. The UV light cures these layers immediately thus ensuring dimensional stability and retention of all details. Moreover, after printing, the support materials can be removed easily without causing any destruction to the fragile features hence helping in achieving a good finish. Computer software algorithms running the print process have been designed for sophisticated paths optimization and evenness resulting in models with excellent surface smoothness and precision.
What makes Polyjet ideal for creating realistic prototypes?
The ability of PolyJet technology to produce high-resolution models makes it ideal for creating realistic prototypes because of its unmatched precision. With this technology, it is possible to stack them up as thin as 16 micron ensuring that all minute intricacies can be accurately copied at all times. This feature enhances realism by allowing for combination of various textures, transparencies, or colours within one print in PolyJet’s multi-material capabilities. Consequently, fast curing system with removable supports brings about fine details and polished surfaces that will make it hard to tell whether products created via PolyJet process are prototypes or finished goods. That is why Polyjet stands out among other similar technologies as an excellent choice for making real-like prototype models due to its high resolution capability, use of multiple materials; such as when prototyping translucent objects made from different colors; and speedy post-processing steps too according to M4D’s statement.The above guidelines should always be complied with when preparing outputs for this exercise.
How Does the Polyjet 3D Printing Process Work?
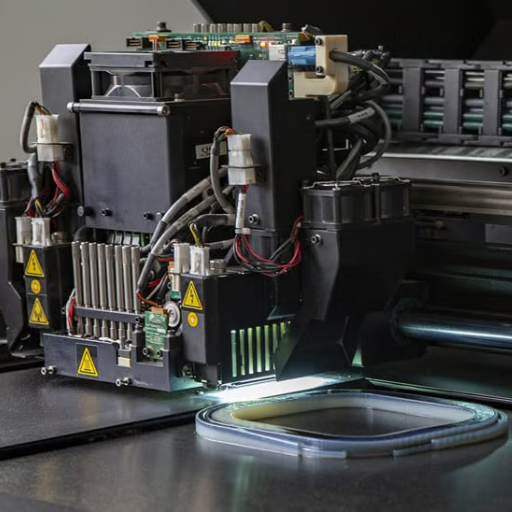
A variety of steps are involved in the PolyJet 3D printing process that results in high resolution models. To begin with, a CAD model is fed into the printer’s software and sliced into ultra-thin layers. This then will be followed by jetting photopolymer droplets onto the build platform as per specific patterns which are cured by UV light at the same time. This jetting and curing process occurs layer by layer until an object is completed. Other substances that are used to support complex shapes are subsequently withdrawn during post-processing. As a result, it can be observed that this leads to a highly accurate model that has an excellent level of detail as well as several material properties.
What is the role of the print head?
The print head is very important in PolyJet 3D printers for achieving accuracy and precision when making models. It deposits tiny photopolymer droplets on the build plate under tight control. Each of these droplets gets cured immediately upon exposure to ultraviolet rays making it harden fast after deposition. The ability of the print head to move nimbly across various axes enables it to create intricate details and complicated geometries with great precision. Moreover, it functions along with support material deposition so as to back up overhangs’ structure and eventually they are scrapped off leaving behind a product acquired through this mechanical means. Henceforth, one may deduce that all these processes lead to an extremely detailed, smooth surfaced model having outstanding resolution.
How are support structures used in Polyjet Printing?
For PolyJet printers to create their complex shapes and features, they rely on support structures which provide a basis for overhangs or intricate details during the printing process. These structures are fabricated concurrently with the model by using a jelly-like material that is simply removed after the completion of printing. The support material supports components that would otherwise buckle or distort under gravity or pressures applied during printing. After it has been completed, the support material can be rinsed off by water or peeled away, so that residual marks and damage do not prevent an ideal physical representation of the final model. This allows for highly detailed parts that are as accurate as possible irrespective of how intricate they might be in design.
How is UV light used in the curing process?
The role of UV light in this PolyJet printing process is to cure the photopolymer deposited while building. As soon as the print-head releases tiny drops of liquid photopolymer on to the build tray, these droplets solidify almost instantly due to UV light exposure forming layers. Through this prompt curing, even fine details and complex geometries can be precisely built up. Before adding another layer, each one is hardened accurately by UV lights preventing structural distortion and maintaining a high resolution appearance at all stages between layers. It ensures a smooth surface finish and captures finest details without much need for any post-processing operation at all since there are no further processes involved.
Comparing Polyjet and Other 3D Printing Technologies
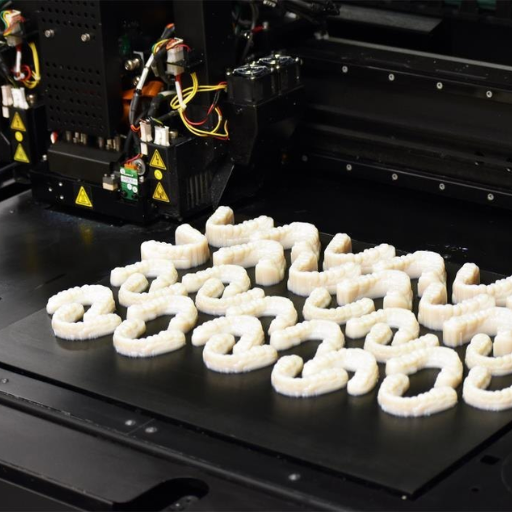

PolyJet 3D printing is different from other technologies in that it can produce very detailed and smooth parts with superb precision. While Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) works by extruding melted material and often produces visible layers, PolyJet has a better surface quality and more intricate features enabled by its fine photopolymer droplets and UV curing process. As compared to Stereolithography (SLA), which also uses a photopolymer resin cured by UV light, PolyJet allows for faster print times and simultaneous multi-material, multi-color printing capabilities. Moreover, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses laser to fuse powders together making it great for robust parts but does not provide the same sleekness of surface or the fine details that PolyJet can achieve. Thus, for high resolution/multi-material prints/complex geometries there are no alternatives to PolyJet.
How does Polyjet compare to FDM?
This means that you have to consider the applications they were originally developed for when selecting between them. The technology of Poly-Jet presents higher definition as well as finer detail because it jets photopolymer droplets which are almost instantly solidified by ultraviolet light so as to create smoother finishes on surfaces and more complicated aspects. Conversely, FDM involves constructing objects through laying down melted thermoplastic layer after layer resulting in detectable seams running along the printed object’s length and an irregular surface texture. A single polyjet print job can use several materials simultaneously; thus making it ideal for creating complex parts with aesthetic requirements. On the contrary, FDM is usually cheaper and has a wide variety of strong engineering-grade thermoplastics making it suitable for functional prototypes or end-use parts. As such choosing between either Poly-Jet or FDM depends largely on what is needed in terms of project specifics whereby: Poly-Jet favors detail & finish while FDM goes for strength/durability/cost efficiency.
What are the differences between Polyjet and SLA 3D Printing?
PolyJet and Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing technologies are both capable of generating high resolution with smooth surface finishes, but there are differences between the two. PolyJet operates by jetting layers of liquid photopolymer onto a build platform which are then cured using UV light. As such, this could allow for multiple materials and colours within one print. On the other hand, SLA uses laser to solidify liquid resin in a vat layer by layer towards forming precise and detailed parts. More often than not, SLA offers slightly higher accuracy and smoother surfaces compared to PolyJet however, PolyJet is known for its agility as well as speed in making multi-colored prints. In addition, SLA may involve more post-processing steps including washing and curing while PolyJet parts can be used right after printing. Finally, the decision between Polyjet and SLA is largely driven by how much detail is needed in the print, material properties required along with application.
How does Polyjet integrate with other additive manufacturing processes?
Polijet technology easily fits into other additive manufacturing processes thus helping enhance production capacities while optimizing end-use parts. Commonly Polijet is used together with Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) to take advantage of both technology’s strengths – FDM’s robustness and cost efficiency combined with Polijet’s high resolution multi-material capabilities. Furthermore, coupling Polijet with Stereolithography (SLA) will give way to creation of highly detailed master patterns for silicone molding or casting processes. When teamed up with Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) or Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), complex jigs that comprise fixtures or assembly tools having mechanical properties that complement those of SLS or DMLS produced parts can be developed using Polijet technology. By integrating Polijet into other additive manufacturing technologies at their disposal manufacturers can strike a balance between design specifics functional requirements as well as cost considerations associated with these requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is Polyjet 3D printing technology?
A: Polyjet 3D printing technology is a type of resin 3d printing that uses curable liquid photopolymers jetted onto a build tray to create high-resolution, detailed prototypes and models. This technology was developed to provide precision and versatility in 3D printing.
Q: What are the benefits of Polyjet 3D printing technology?
A: The benefits of Polyjet 3D printing technology include high resolution and accuracy, the ability to print multi-material prototypes, and the capability for full-color 3D printing. It offers an excellent surface finish and can produce complex geometries with fine details.
Q: What materials can be used with Polyjet 3D printers?
A: Polyjet 3D printers work with a wide range of materials, including rigid and flexible polyjet materials, transparent resins, and even full color materials. This variety allows for a broad spectrum of applications, including anatomical models and industrial 3d printing parts.
Q: How does the Polyjet process work?
A: The Polyjet process involves jetting layers of curable liquid photopolymers onto a build tray using inkjet printing heads. Once a layer is applied, it is instantly cured with UV light. The process repeats layer by layer until the 3d printed parts are built up to completion.
Q: What are some common applications of Polyjet 3D printing?
A: Common applications include creating multi-material prototypes, anatomical models, and complex mechanical parts. Polyjet 3d printing service is particularly popular in industries that require high precision and full-color 3D printing, such as medical, dental, and consumer products.
Q: Can Polyjet 3D printers produce full-color models?
A: Yes, Polyjet 3D printers are capable of full-color 3D printing by combining different inks to achieve a wide range of colors, offering realistic prototypes in vibrant hues.
Q: What is the difference between Polyjet and other resin 3D printing technologies?
A: Unlike other resin 3D printing technologies that may use a single material type, Polyjet 3D printing utilizes material jetting which allows for the combination of multiple materials and colors in a single print. This results in highly detailed and versatile 3d printed parts.
Q: How does using Polyjet 3D printers benefit product development?
A: Using Polyjet 3D printers accelerates product development by enabling rapid prototyping, refining and testing designs quickly, and producing accurate, high-quality models. This helps in shortening the design cycle and reducing time-to-market for new products.
Q: What should one consider when choosing Polyjet 3D printing materials?
A: When choosing Polyjet 3D printing materials, consider the mechanical properties, finish, transparency, flexibility, and color needs of your application. With a wide range of materials available, it’s possible to select those that best meet the specific requirements of your project.
Q: How do Polyjet 3D printers handle support material?
A: Polyjet printers build with support material that is a gel-like substance easily removed after the printing process. This support material allows for the construction of complex geometries and fine details without compromising the integrity of the final model.






