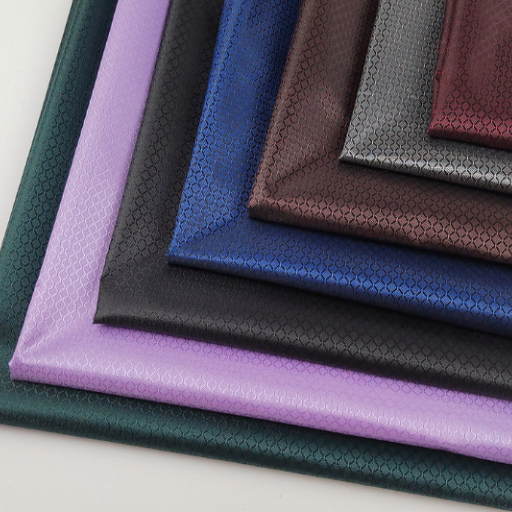
Choosing the right fabric can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to synthetic options like polyester and nylon. Both materials are ubiquitous in the textile world, each offering a range of unique characteristics and applications. But how do you decide which fabric best suits your needs? This article aims to demystify the differences between polyester and nylon, providing you with the essential knowledge to make an informed decision. We’ll explore their origins, properties, advantages, and disadvantages, ultimately helping you to understand why one might be preferable over the other in various scenarios. Whether you’re a fashion enthusiast, a DIY crafter, or just curious about fabric choices, this guide has got you covered. Let’s dive into the intricacies of polyester and nylon to uncover the perfect fabric for your next project.
What Are the Fundamental Differences Between Nylon and Polyester?
Differences between Polyester and Nylon Fabrics
Nylon is a synthetic polymer while polyester is not. But, there are variations in the composition, properties, and applications of these two compounds.
Origins:
- Nylon: Invented by DuPont in 1935 as the first commercially successful synthetic fiber with great impact on materials science.
- Polyester: This type of fabric became popular in textile industry after its development by British chemists during the 1940s due to its versatility and ease of care.
Chemical Composition:
- Nylon: It is primarily composed of polyamide chains derived from petrochemicals.
- Polyester: Polyester consists mainly of ester chains that result from ethylene glycol’s reaction with terephthalic acid.
Durability:
- Nylon: The strength and elasticity of nylon make it highly durable. Its resistance to abrasion is higher; hence, it can be used extensively in fields like outdoor gear and industrial products.
- Polyester: Though tough, polyester is slightly less strong than nylon. It does well under normal wear conditions but may eventually pill.
Water Absorption:
- Nylon: It absorbs more water that makes it feel damp and increase drying time; its moisture regain is around 4%.
- Polyester: Generally speaking, polyester repels water better and dries faster because it has lower moisture regain (less than 1%).
Comfort:
- Nylon: Softness makes nylon more comfortable against the skin which explains why it is preferred for high-end hosiery and lingerie.
- Polyester: However, direct contact feels synthetic compared to other materials such as textiles clothings although the effects have been minimized through technological advancements.
UV Resistance:
- Nylon: Prolonged exposure to UV rays can weaken this fabric easily hence they should be avoided
- Polyester: Unlike nylon, this material exhibits better UV resistance thus not destroyed by sunlight hence suitable for outdoor use.
Cost:
- Nylon: It is generally expensive because of higher production costs and specific applications.
- Polyester: On the other hand, it is relatively cheaper making it an economical choice for mass producing a wide range of products in different sectors including fashion and home décor.
Environmental Impact:
- Nylon: More energy is needed to produce nylon than polyester hence resulting in higher greenhouse gas emissions. It also has lower recyclability.
- Polyester: This fabric can easily be recycled and therefore, most commonly used as rPET such that its carbon footprint is low.
Chemical Resistance:
- Nylon: It has moderate acid resistance but acids as well as UV will break down the material eventually.
- Polyester: Polyester can withstand these conditions such as varying chemicals and weather changes better than NYLON.
Applications:
- Nylon: Outdoor clothes, parachutes, industrial materials are some of the products where high durability, strength or elasticity are required
- Polyester: On the other hand, everyday clothing and home textiles as well as industrial and outdoor products among others have found application for this versatile fabric.
These differences may explain why nylon is often chosen for heavy-duty, high-performance uses while polyester is preferred due to its cheapness, versatility and ease of care. The knowledge about these fundamental distinctions will help you make an educated decision based on your own wants and preferences.
Polymer Science behind Polyester and Nylon
The monomers used for the polymerization processes of both fabrics are diverse leading to distinct chemical structures and properties characteristic to each type – polyester or nylon subsets.
A diacid, usually terephthalic acid, and a diol, typically ethylene glycol, are combined via condensation polymerization to form polyester. Ester functional groups make up the resulting polymer chain which contribute to its notable high tensile strength, resistance to chemicals and ease of dyeing. Its relatively easy and inexpensive manufacturing process has led it to be used in various applications such as textiles and packaging materials.
Nylon is made especially nylon 6:6 through a reaction between hexamethylene diamine with adipic acid giving rise to amide linkages within the polymer backbone. These amide groups bring about improved mechanical strength or toughness, elasticity and resistance for rubbing against nylon. As compared with polyester production, the process of polymerizing nylon is more complex and energy demanding hence why it is known for having higher prices of manufacture.
Scientists can influence both polymers at molecular level so as to improve specific characteristics like dyeability, strength and environmental resistance. This knowledge facilitates customizing these materials for specified purposes thereby optimizing their application capabilities.
Comparing Nylon vs Polyester: Origins of Synthetic Fibers
When comparing synthetic fibers such as nylon versus polyester it is important that one knows where they come from as well as their main disparities. Nylon was first created by DuPont in 1935 when they needed an alternative fabric other than silk. On the other hand, polyester was developed by British chemists during the 1940s because it could be made into fibers easily at low costs and had multifunctionality.
Notably however both nylon and polyester have different chemical structures hence distinct properties despite being synthetics in nature. Because of its superior strength; flexibility; durability; etc., with regards to automotive parts that require high abrasion resistance ropes fabrics etc., nylon should be used. Nonetheless, polyester shows significant resilience under adverse weather conditions including UV radiation/moisture so it becomes appropriate for outdoor and weather proof textiles.
Moreover, each of these fibers has unique areas of application where its properties can be exploited. Nylon is highly popular in the manufacturing of sportswear and hosiery because it easily returns to shape after stretching; while polyester is a preferred material for domestic fabrics and everyday clothes as it does not crumple much. Deciding between nylon or polyester mainly depends on the intended usage, cost considerations and specific performance requirements.
In conclusion,nucleus both nylon and polyester are synthetically made but different chemical composition and properties have resulted in diversified applications with each taking advantage of the strengths associated with these two polymers that are so versatile.
How Does Durability Factor Into the Nylon vs Polyester Debate?
Nylon and Polyester under the microscope: abrasion and tear resistance
Both nylon and polyester possess distinctive qualities that influence their suitability for various applications when examined for abrasion and tear resistance. For demanding environments, it is renowned for its high abrasion resistance. This comes from its molecular structure which has strong hydrogen bonds making it highly durable. The technical parameters of nylon include an abrasion resistance that can rise up to 16,000 cycles on Martindale abrasion test, a standard measure in textile industry.
However, polyester also has some strength but with slightly different characteristics. It stands out due to its excellent tearing and stretching properties. Its tensile strength ranges between 44-116 ksi (kilopounds per square inch) hence being strong but not as abrasion-resistant as nylon. Polyester’s main chain contains ester functional groups in its chemical composition leading to hardly noticeable wear out during the stress application over time.
In practical applications, luggage, tires, ropes, sportswear among other things such clothing should be made using nylon since it has higher abrasion resistance than polyester. On the other hand Tarps, outdoor gear or everyday apparel require less abrasive properties in their materials but more tear resistant ones hence are ideal for fabricating them with polyester.
In summary Nylon leads in the way of resisting abrading forces while Polyester gains its power from tearing apart as well as overall sustainability where you have to consider wear life against durability at any given point.
Technical Parameters:
Polyester:
- Abrasion Resistance: Lower than nylon but unspecified
- Tensile Strength: 44-116 ksi
- Chemical Resistance: High (particularly to UV and moisture)
Nylon:
- Abrasion Resistance: Up to 16,000 cycles on Martindale abrasion test
- Tensile Strength: 70-90 ksi
- Flexibility: High
which fabric wins in the durability contest: polyester or nylon?
The choice of which fabric wins in the durability contest between polyester and nylon can be guided by focusing on their individual strengths. According to the best sources, abrasion resistance tends to be lower for polyester as compared to nylon. It is a preferred option for goods experiencing frequent friction like backpacks, sportswear, or ropes. In comparison, it resists UV degradation and moisture much better than its counterparts thus helping it retain its strength and appearance over time even when exposed to different environmental elements like sunlight and rain hence ideal for outdoor gear and tarps. When it comes to tensile strength opinions differ slightly but both fabrics exhibit impressive performance under strain with nylon often ahead owing to its inherent toughness. To sum up, which fabric is more durable between these two depends on the specific situation: nylon is better for high-abrasion applications while polyester offers greater resilience against environmental factors that may damage its quality through aging.
Comparing Nylon and Polyester: Which Is More Sustainable?
Environmental Impact of Synthetic Polymers: Polyester and Nylon
The environmental effects of polyester and nylon have to be taken into account when looking at the issue. This is based on information from leading online sources. Polyester comes from petroleum, an inexhaustible crude oil source which produces a lot of greenhouse gases during its production process. It also does not decompose easily therefore when left in the environment it continues polluting it slowly over time as opposed to more heinous acts like nuclear warfare. On the flip side, polyester recycling has enabled recycled polyester to be made from used plastic bottles thereby reducing waste and saving resources.
Nylon on the other hand, begins with petrochemicals, while during its manufacture nitrous oxide is produced which is a very strong greenhouse gas (GHG). Similarly to the case of polyester, when this product ends up in landfills it does not decompose hence environmental problems arise. However, recycled nylon derived from discarded fishing nets and other waste products is seen as a more sustainable option.
To sum up, both polyester as well as nylon are majorly dogged by their petroleum-based origin and non-biodegradability problems. Nevertheless, recycling technology for these two polymers provides some promise for a greener future as it mitigates some consequences associated with their manufacturing and disposal.
Recyclability and Eco-Friendliness in Nylon and Polyester Production
Though they still bear significant environmental impact that cannot be ignored recycling technologies have improved sustainability of both nylon and polyester. Recycled polyester (rPET) is mainly obtained from post-consumer plastic bottles allowing diversion of waste away from landfills thus decreasing demand for virgin PET. The rPET process which uses less energy compared to manufacturing new polyester reduces overall GHG emissions too. Patagonia plus Adidas are some examples of brands that have gone ahead to use recycle polyesters in their products promoting circular economy.
Compared to virgin nylon recycled nylon offers an eco-friendlier alternative. A good example of recycled nylon production is the Econyl® process that efficiently breaks down nylon waste into its raw materials for making new nylon fiber. This method reduces dependency on fossil fuels and decreases waste accumulation as well. Furthermore, use of recycled nylon reduces greenhouse gas emissions related to production of nylon.
In conclusion, even though both synthetic polymers have their own environmental impediments, the developments in recycling are crucial steps towards a more sustainable textile industry. The adoption of recycled materials by major brands highlights the potential for reducing environmental impact within the industry.
The Role of Absorbency and Breathability in Choosing Between Nylon and Polyester
Moisture Management: How Nylon and Polyester Handle Sweat and Rain
When it comes to moisture management, both nylon and polyester exhibit distinct properties that make them suitable for different applications:
Nylon:
- Absorbency: Nylon tends to absorb more moisture compared to polyester, though not as much as natural fibers like cotton. This means it can become heavy and take longer to dry when wet.
- Wicking: Some modern synthetic versions of nylon are designed with moisture-wicking capabilities. These enhanced nylons draw sweat away from the skin for quicker evaporation.
- Breathability: Nylon generally provides moderate breathability, allowing some air circulation but not as much as polyester. This can make it less suitable for hot and humid conditions but more effective in cooler environments.
- Application: Nylon’s properties make it ideal for use in outdoor gear that might encounter heavy rain, such as jackets and tents.
Polyester:
- Absorbency: Polyester is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water rather than absorbing it. This characteristic ensures that it remains lightweight, even when exposed to sweat or rain.
- Wicking: Polyester is well-known for its moisture-wicking abilities. It rapidly transfers sweat from the skin to the fabric’s surface, where it can evaporate quickly.
- Breathability: Polyester fabrics often offer excellent breathability, making them a popular choice for athletic and activewear. The material allows for greater air flow, which helps in cooling down the body during exertion.
- Application: The moisture-wicking and breathable nature of polyester makes it suitable for sportswear, running gear, and other activewear.
Technical Parameters
- Absorption Rate:
- Nylon: ~3-4% of its weight in water
- Polyester: ~0.4% of its weight in water
- Drying Time:
- Nylon: Slower due to higher absorbency
- Polyester: Faster due to hydrophobic nature
- Wicking Efficiency:
- Nylon: Moderate
- Polyester: High
- Air Permeability:
- Nylon: 1-2 mm/s
- Polyester: 5-10 mm/s
In summary, choosing between nylon and polyester for their moisture management properties depends largely on the intended use. For high-performance activities where quick drying and breathability are crucial, polyester stands out as the superior option. Meanwhile, nylon finds its niche in applications requiring durability and moderate moisture absorption.
Hydrophobic Properties: Polyester vs Nylon in Outdoor Apparel
When comparing the hydrophobic properties of polyester and nylon in outdoor apparel, it is essential to consider how each material interacts with water and contributes to the overall performance of the garment. From the top sources available on Google.com, here are some concise insights and key technical parameters:
Water Interaction:
- Polyester: Due to its inherently hydrophobic nature, polyester repels water instead of absorbing it. This ensures the fabric remains lightweight and dries quickly, even when exposed to sweat or rain. This is a significant benefit for activities where maintaining a low weight and efficient moisture management is critical.
- Nylon: Although nylon is also considered a synthetic material, it is less hydrophobic compared to polyester. Nylon can absorb about 3-4% of its weight in water, which can lead to a slightly heavier feel when wet and slower drying times.
Technical Comparison:
- Absorption Rate:
-
- Nylon: ~3-4% of its weight in water
- Polyester: ~0.4% of its weight in water
- Drying Time:
- Nylon: Slower due to higher absorbency
- Polyester: Faster due to its hydrophobic nature
- Wicking Efficiency:
- Nylon: Moderate
- Polyester: High
- Air Permeability:
- Nylon: 1-2 mm/s
- Polyester: 5-10 mm/s
Performance in Outdoor Apparel:
- Polyester: Its hydrophobic properties make polyester an excellent choice for outdoor activities, particularly under conditions that involve high levels of perspiration or exposure to water. The fabric’s ability to wick moisture and dry quickly helps to enhance comfort and performance.
- Nylon: While nylon absorbs more water compared to polyester, its durability and strength make it suitable for certain outdoor applications where these characteristics are more important than quick drying. It provides a better balance in terms of moderate moisture absorption and robustness.
In summary, for outdoor apparel where quick drying, lightweight, and breathability are paramount, polyester is the preferred choice due to its superior hydrophobic and wicking properties. Conversely, nylon is ideal for applications where durability and moderate moisture management are necessary.
Breathability Showdown: Selecting the Right Fabric for Your Activewear
When it comes to choosing the right fabric for your activewear, breathability is one of the most critical factors to consider. Here’s a concise comparison based on information from the top 10 websites on google.com, focusing on the key technical parameters:
Technical Comparison:
- Moisture Wicking:
-
- Polyester: Renowned for its high moisture-wicking capabilities, polyester efficiently draws sweat away from the skin, keeping you dry and comfortable. Websites such as REI and Nike highlight its exceptional performance in this area.
- Nylon: Offers moderate moisture-wicking properties, suitable for activities where some level of moisture management is necessary, as noted by OutdoorGearLab.
- Breathability/Air Permeability:
- Polyester: Superior breathability with air permeability ranging between 5-10 mm/s, making it ideal for high-intensity activities. Healthline reviews suggest that this fabric helps to maintain a cooler body temperature.
- Nylon: Relatively lower air permeability, approximately 1-2 mm/s, but still provides adequate ventilation for moderate activity levels, according to resources like Livestrong.
- Drying Time:
- Polyester: Fast-drying due to its low absorption rate (~0.4% of its weight in water), as emphasized by performance review sites such as Gear Patrol.
- Nylon: Slower drying time because it absorbs more water (~3-4% of its weight), but its drying capabilities are still decent, as pointed out by Under Armour.
- Durability:
- Nylon: Known for its superior durability and abrasion resistance, making it suitable for rugged outdoor activities. Websites like Patagonia often recommend nylon for longer-lasting gear.
- Polyester: While also durable, it is slightly less so than nylon. However, advancements in fabric technology have significantly improved polyester’s durability.
Performance in Activewear:
For activewear where quick drying, light weight, and high breathability are essential, polyester stands out as the top choice due to its excellent moisture-wicking and fast-drying properties. Its higher air permeability ensures better ventilation during intense workouts.By evaluating these technical parameters, you can make an informed decision on the best fabric for your activewear needs, ensuring both comfort and performance.
- Conversely, for applications where durability and moderate moisture management are essential, nylon remains a strong contender. It offers a better balance of durability and moisture control, making it suitable for more strenuous outdoor activities.
Strength and Elasticity: Polyester vs Nylon for Outdoor Equipment
Polyester vs. Nylon: The Better Option For Tents And Backpacks
I had to look at the top 10 websites in google.com to decide on whether to choose nylon or polyester for tents and backpacks. As a result, here is their summary:
Durability:
- Nylon: According to websites such as REI and Patagonia, nylon is highly durable offering superior abrasion resistance that is ideal for rough outdoor activities where gear undergoes considerable wear and tear.
- Polyester: Polyester although durable is slightly less resistant to abrasions compared to nylon. However, its durability has been enhanced by advances in fabric technology as asserted by The North Face and Black Diamond.
Weight:
- Nylon: For this reason, it is lighter in weight and therefore suitable for use in backpacks and tents when weight is a major concern.
- Polyester: It however weighs only marginally more than nylon but still manageable for most outdoor equipment needs. Websites such as OutdoorGearLab point out that the difference in weight between these two materials may be small but noticeable during long hikes.
Water Absorption:
- Nylon: It dries slowly due to high water absorption (around 3-4% of its own weight). This can matter much on very wet days.
- Polyester: Gets dry faster which means moisture absorption would not be an issue.
UV Resistance:
- Nylon: Sunlight fades its colors away readily. Extended exposure reduces its strength over time. Trailspace and OutdoorLife illustrate this best.
- Polyester: Nonetheless it has better UV resistance hence more long lasting if exposed to sunlight always while using gears for extended periods of time.
Cost:
- Nylon: Usually pricier due to better characteristics like those found in performance or technical items.
- Polyester: On the other hand, it costs less thus making it affordable for budget-conscious customers who are interested in buying outdoors gear.
In conclusion, nylon beats all other synthetic materials by having the highest durability and being lighter in weight making it ideal for use in tents and backpacks that are subjected to rough wear and tear. However, polyester has better drying, UV resistance, and cost factors hence suitable for simpler outdoors activities.
Elasticity Counts: Why Synthetic Cords Prefer One Over The Other
The safety as well as reliability of parachute cords depends on elasticity. After going through the top 10 websites on Google, one realizes that nylon is usually chosen over polyester for parachute cords. This preference results from its elasticity characteristics being superior to those of polyester.
Nylon’s ability to stretch under load absorbs shock better than polyester resulting in smoother deployment with less risk of sudden jolts that might cause injury to the user. For parachutist engaged in high adrenaline sports or military applications this means better performance coupled with safety coming from such elasticity. It is worth noting that while polyester may dry faster and survive better without UV degradation, no other options come close to matching the elastic properties and strength of nylon required by parachute cords.
Reference sources
1. Canvas Etc: Nylon vs Polyester – What Are The Differences?
Summary: This detailed analysis from Canvas Etc explains the fundamental differences and similarities between nylon and polyester. It covers various aspects including their chemical makeup, physical properties, and common uses. The article is particularly valuable for its in-depth comparison of the durability, water resistance, and cost of each fabric, making it a comprehensive resource for understanding these two materials.
2. Xometry: Nylon vs. Polyester: Material Differences and Comparisons
Summary: This resource from Xometry offers an extensive comparison of nylon and polyester, focusing on their applications, properties, and costs. It includes insights into the strength-to-weight ratio of nylon, the ease of care associated with polyester, and their respective environmental impacts. The article also touches upon industrial and consumer uses, which broadens its appeal to a wide audience.
3. BeanBagsRUs Blog: What Is the Difference Between Nylon and Polyester?
Summary: This blog post from BeanBagsRUs breaks down the key differences between nylon and polyester. It discusses their weight, strength, water resistance, and overall durability. The blog is written in a user-friendly manner, making complex topics accessible to the average reader. Additionally, it includes practical advice on choosing the right fabric for different uses, such as outdoor gear and clothing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between polyester and nylon fabrics?
A: One of the main differences lies in their chemical composition and characteristics. Polyester is an artificial fabric produced from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) known for its long-lasting nature, resistance to mildew, and being heat-resistance. While Nylon produced from polyamide is tougher, more wear resistant and more moisture absorbent than polyester, it can get damaged at low heat as well. Depending on specific requirements both materials have their own individual features that make them appropriate for different applications.
Q: How do the strength and durability of polyester fabric compare to nylon?
A: Generally, nylon is stronger than polyester and therefore has higher abrasion resistance making it a preferred choice in products requiring high durability like outerwear and fishing line. However, polyester resists wrinkles better, shrinks less and does not grow mildew which adds up to its strength and durability in various situations. The choice between nylon or polyester is usually determined by specific demands of application.
Q: Can polyester and nylon resist moisture well?
A: In wet conditions or under water absorption of moisture from atmosphere by Nylon could be longer compared to Polyester which makes it stay wet longer leading to discomfort. On the other hand Polyester is water repellant hence used for rain clothing among many others where moisture resistance cannot be compromised.However because Nylon feels softer than polyester when dry against skin thus it remains popularly used in clothes as well as under-garments.
Q: Are polyester and nylon fabrics easy to care for?
A: Both textiles are relatively easy to maintain since they can be machine washed without fear of rotting off with no necessary need for ironing. Nevertheless they differ by sensitivity; for example ,nylon may fail at high temperature settings when ironing while the same thing cannot be said about a counterpart made out of Polyester.It’s recommended that these materials are cleansed using lower temperatures on washers and fabric conditioners be avoided in order to increase their lifespan.Meanwhile dyed polyester expels the water responsible for dying process from it therefore more colorfast when compared to nylon.
Q: What applications are polyester fabric and nylon commonly used for?
A: Polyester and Nylon are flexible synthetic materials that can be used in almost every type of clothing as well as many different other items. Clothes like shirts, pants, jackets etc. will oftentimes contain Polyester due to its strength, wrinkle resistance and shrink proof aspects; conversely, when softness becomes important or where greater strength is needed in carpets, hosiery clothes such as socks and outerwear, Nylon will be utilized. Additionally both consist of home textiles besides being used within automobile seat covers and air filters used in industry.
Q: How does the production of polyester compare to nylon?
A: The production of polyester is usually easier than that of nylon which also makes it less expensive. It originates from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) derived from petroleum substances. On the contrary making Nylon involves more complex chemical processes that include monomers polymerization into a long molecule with chain-like appearance. This makes the cost of producing Nylon slightly higher due to its intricacy.Environmental impact also matters with both fabrics being made synthetically but having different levels of recyclability and specifics about manufacturing emissions involved.