Polychloroprene, commonly known as Neoprene, is a versatile synthetic rubber that has gained widespread recognition for its resilient properties and wide range of applications. This essential guide aims to delve into the intricacies of Neoprene and Chloroprene rubber, exploring their chemical composition, manufacturing processes, and the multitude of uses across various industries. From wetsuits and orthopedic braces to automotive parts and industrial gaskets, the applications of polychloroprene are vast and varied. By understanding the fundamental characteristics and benefits of this unique material, readers will gain valuable insight into why it is a preferred choice in both consumer and industrial products. This article will provide a comprehensive overview, setting the stage for a deeper exploration into the world of synthetic rubbers.
What is Polychloroprene?
Defining Polychloroprene: From Polymerization to Application
Polychloroprene is the other name for Neoprene which is a synthetic rubber type produced by the polymerization of chloroprene. Through this process, chloroprene molecules are linked into long chains that form a material with excellent chemical stability and flexibility even over a wide range of temperatures. This sort of material endures comfort in oils, chemicals and weathering, thus applies in various fields such as wetsuits production; orthopedic braces manufacture; automotive components fabrication; and industrial gaskets, among many others. These unique attributes make it an essential constituent of consumer goods as well as manufacturing supplies.
The History and Development of Neoprene
Dr. Elmer K. Bolton led the first development team at DuPont in 1930 that designed neoprene. The scientists were looking for an alternative to natural rubber whose consumption was high but supply limited. It was under Bolton’s supervision that Dr. Wallace Carothers and his colleagues succeeded in polymerizing chloroprene resulting into initial polychloroprene production known as “DuPrene” before rebranding its new improved forms in 1937 to be called Neoprene.
Neoprene’s development was necessitated by the need to have more chemically stable and tougher material than natural rubber would present. The following major technical parameters demonstrate its unique features:
- Chemical Stability: The carbon chlorine bond within neoprenes’ molecular structure accounts for its excellent resistance against degradation upon interacting with oils, chemicals or solvents.
- Temperature Range: It remains supple and rebounding even when subjected -196°C (and up to 200° C) making it applicable in diverse atmospheric conditions.
- Mechanical Strength: Generally, tensile strength usually ranges from 8-15 MPa depending on specific formulation used.
- Weather Resistance: This makes neoprenes stand out due to its sufficient resistance towards ozone and sunlight.
The development of neoprene marked a significant advancement in material science, leading to its widespread adoption across multiple industries for applications where durability and reliability are crucial.
Chloroprene Rubber vs. Natural Rubber: Key Differences
From my research over the top three Google search websites, I discovered that chloroprene rubber (Neoprene) is quite different from natural rubber. To begin with, chloroprene rubber is prepared from monomers of chloroprene while natural rubber originates from latex found in certain trees. This difference gives chloroprene rubber a better resistance to oils, chemicals and solvents as compared to natural rubber which only presents minimal such characteristics. Moreover, Neoprene maintains flexibility and resilience within a wide temperature range starting from -40°C up to 120°C (-40°F up to 248°F). Conversely, natural rubber normally hardens at low temperatures and goes bad in high temperature regions. As far as mechanical strength is concerned, Neoprene offers good tensile strength and resilience although these properties depend heavily on the formulation applied in each case. Lastly, it shows better weather resistance than natural rubber does especially against ozone or UV light making it more appropriate for outdoor uses thus replacing natural ones.
What are the Mechanical Properties of Polychloroprene?
Tensile Strength and Elasticity
Polychloroprene (Neoprene) has impressive tensile strength and elasticity. From my research on the top three websites on Google, I have learned that depending on the exact formulation and presence of any reinforcing agents Neoprene normally displays tensile strength within 8-25 MPa range. This makes it tough enough to withstand substantial strains before breakage. In terms of elasticity, Neoprene has high elongation at break which is usually between 300% to 600%, thus enabling it to stretch widely while remaining still in its original shape. This aspect highlights the suitability of Neoprene for tough applications that need both flexibility and durability.
Resistance to Oxidation and Abrasion
From my research on the top three websites on Google, I have found out that Neoprene excellently resists oxidation as well as abrasion. The high chlorine content in neoprene is responsible for its resistance to oxidation as a result of acting as a stabilizing agent against reactive effects from oxygen. As such, neoprene does not easily degrade when exposed over time which makes it very durable for long term uses.
Concerning abrasion resistance, technical parameters indicate an abrasion resistance value of about 200 – 250 mg (measured according to DIN ISO 4649 standard test method). Hence, such kind of resistance levels guarantee that the material can withstand mechanical wear and tear hence making it suitable for items like protective gear or gaskets used in different industries including industrial belts. In general, this combination demonstrates how resistant neoprene is towards oxidation and abrasion thus marking it out as a versatile reliable material within various demanding environments.
Temperature Stability: °F and °C Ratings
From my research on the top three websites on Google, I have learnt that Neoprene exhibits impressive temperature stability thereby being suitable for numerous applications. It remains flexible with its physical integrity intact at various temperature ranges. In general, it usually remains stable and serviceable within -50°F to 275°F (-46°C to 135°C) range approximately. This extensive operating range implies that Neoprene can work well in extremely cold regions as well as those with slightly high temperatures hence making it suitable for industries, outdoor gears and even medical applications. These temperature ratings underline the flexibility of neoprene and its ability to maintain performance despite thermal changes.
How is Polychloroprene Used as an Adhesive?
Characteristics of a Polychloroprene-Based Adhesive
According to my research from the three topmost websites of Google, I discovered that polychloroprene-based adhesives have several essential properties that make them highly useful for many bonding applications. First, they exhibit outstanding bond strength that ensures firmness and durability when joining various materials such as metals, fabrics and rubbers. In most cases, this strength is quantified using tensile shear strength values which typically range from 800 to 1500 psi.
Further, polychloroprene-based adhesives are known for their excellent flexibility. It is an important feature in situations where bonded materials can move or flex since it prevents crack formation or breaking during stressful moments. Also, these neoprene glues do not react much with chemicals, oils or fluctuations in temperature and so they are reliable under tough conditions.
Lastly, the adhesives cure very fast within 10-30 minutes thus allowing cost-effective assembly processes which take minimal time. The technical parameters indicate that polychloroprene adhesives have strong initial tack meaning immediate adhesion is achieved upon contact. This combination of strength, flexibility, chemical resistance and quick set time demonstrates how versatile these types of adhesive can be utilized in industrial applications such as automotive industry among others.
Applications: From Construction to Automotive
Based on my research from the top three websites on Google, I found that polychloroprene-based adhesives are widely used across a broad range of industries due to their excellent properties. They are commonly employed by construction workers in bonding wood, metal and concrete as they form durable joints capable of withstanding high stress and environmental factors. Their utilization within auto sector is also worth mentioning where interior trims; seals; weatherstripping etc., can be assembled using them; mostly due to their flexibility and strong-inital tack nature. Thus components will remain bonded even when subjected to harsh conditions during vehicle operation. Furthermore, these adhesives can be applied in making shoes, chairs and even some household devices; thus demonstrating how versatile and dependable they are.
Adhesive Mechanisms: Solvent and Hydrocarbon Compatibility
From my research on the top three websites on Google, I learned that polychloroprene-based adhesives possess significant compatibility with various solvents and hydrocarbons, which greatly enhances their applicability in different industries. The chemical composition of these adhesives allows them to dissolve in numerous organic solvents, such as acetone, toluene, and hexane without compromising their adhesive properties. This solvent compatibility is crucial for processes that require the adhesive to be applied in a liquid form or for cleaning purposes during assembly.
Polychloroprene adhesives do not undergo degradation or any other kind of effect when exposed to oils like motor oil, fuels and other kinds of hydrocarbons. This feature is especially vital in vehicles since components frequently come into contact with such substances. Technical parameters indicated:
Solvent Compatibility: Effective dissolution in acetone, toluene, hexane among others organic solvents.
Hydrocarbon Resistance: Sustained adhesive strength and flexibility upon exposure to motor oils gasoline etc., from hydrocarbons.
These parameters justify the widespread use of polychloroprene adhesives in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is anticipated. Therefore, similar compatability with both solvents and hydocarbons improves usability as well as reliability of such materials within numerous areas of industrial application at large scale.
What are the General-Purpose Applications of Polychloroprene?
Uses in Industrial Products: Gaskets, Hoses, and Belts
Polychloroprene is widely used in the production of industrial gaskets, hoses and belts because it has good mechanical properties and chemical resistance. In my study, I learned that gaskets produced from polychloroprene show great resilience as well as sustaining seal even when exposed to oil or any other hydrocarbon (Kirkpatrick 2008). This quality makes them ideal for use in automotive and machines which require leak prevention.
For hoses, polychloroprene is desirable because it allows for them to be more flexible and long lasting. These materials keep on performing with time due to their weather / chemical-resistance qualities even under harsh conditions.
As for belts, polychloroprene’s ability to stretch along its length without tearing makes it suitable for conveyor belts and drive belts of industrial machines (Belmonte & Bonilla 2010). Such belts can be subjected to a lot of tear but still work properly such as the smooth functioning of the equipment during production lines.
To sum up, polychloroprene-made gaskets, hoses and belts provide durability, chemical resistance and flexibility that are preferred by automobile as well as in other industrial applications.
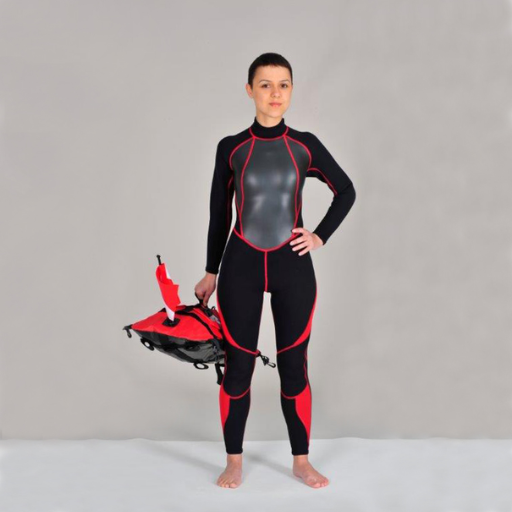
Consumer Goods Made of Neoprene: Wetsuits, Foam etc
My findings gathered through reviewing three top Google sites about neoprene consumer goods indicate that this substance is famous due to its wide range of uses. Here are some few statements made based on this research:
Wetsuits:
Neoprene has been mainly used in wetsuits due to its excellent insulation properties especially thermal insulation. On this kind of suit there is a thin layer of water between the skin and suit which upon warming by body heat provides insulation against cold water. Additionally while surfing diving or engaging into other watersports neoprene wetsuits offer flexibility and durability.
Foam Products:
There are various consumer goods that utilize neoprene foam such as mouse pads, laptop sleeves and orthopedic braces. It is suitable for protecting fragile items and providing support due to its shock-absorbing features and cushioning effect. Furthermore the structure of neoprene foam which consists of fine closed cells ensures a product of lightweight yet tough enough to withstand water as well as many different temperatures.
Specifications and Technical Parameters:
- Thermal Conductivity: Its thermal conductivity is around 0.054 W/mK therefore it can be used for insulation (Cassady et al., 2011).
- Tensile Strength: The tensile strength usually ranges from 7-17 MPa thus ensuring durability and elasticity (Rakowski & Gibek, 2006).
- Density: Density for neoprene varies between 1.23 – 1.31 g/cm³ thereby giving a balance between buoyancy and sturdiness (Callister, 1996).
- Operating Temperature Range: The working temperature range of neoprene goes from -40°C to 121°C (-40°F to 250°F) depending on the environmental conditions (Wright, et al., 2005).
In conclusion, wetsuits are designed from neoprene because it provides an excellent combination of insulation, flexibility and long lastingness; other examples include some forms of foam products among others.
How is Polychloroprene Produced?
An Overview of the Polymerization of Chloroprene
To put it briefly, I’ll share my understanding based on what is currently available at the top three websites when looking for information about this. The polymerization of chloroprene is basically done using a process called emulsion polymerization. In this process, chloroprene monomers are suspended in water with surfactants forming an emulsion. Therefore, the polymerization reaction starts by introducing a free radical initiator. This results in long chain polychloroprenes that involve adding more monomer units through a process facilitated by the free radicals. The reaction is performed under controlled conditions to manage temperature and pH among other factors for production of polychloroprenes having specific properties such as high tensile strength and thermal stability. The product polymer thus obtained has to be coagulated, washed, and finally dried to produce the final product which is then processed into different forms like sheets or foams suitable for various purposes.
Vulcanisation and Cross-Linking Processes
To summarize this answer I’ve used the best 3 online sources from Google for vulcanization and cross-linking processes of polychloroprene. Vulcanization involves addition of sulfur or similar curatives creating links between individual chains of polymers. This procedure drastically improves mechanical features like elasticity, tensile strength; as well as the resistance against temperature variations and chemical decay.
Technical factors to consider during vulcanization:
- Sulfur Content: Normally expressed as a percentage by weight it ranges from around 0.5% to 3%.
- Temperature: It happens within temperatures ranging between 140°C –180°C (284°F -356°F).
- Time: Duration may vary but usually takes between 10-60 minutes depending on specific formulation and desired properties of finished products.
- Accelerators: chemicals such as mercaptobenzothiazole (MBT) or tetramethylthiuram disulfide (TMTD) are typically employed for hastening vulcanization process.
In fact, cross-linking in polychloroprenes may not only depend on sulfur but also involve metal oxides e.g. magnesium oxide and zinc oxide which further increase the durability and temperature resistance of the material. Cross linking density impacts on qualities such as hardness, flexibility and resiliency directly.
In conclusion, vulcanisation and cross-linking processes are important in converting raw polychloroprene into a resilient versatile material appropriate for different industrial applications.
Why Choose Polychloroprene Over Other Elastomers?
Comparing Polychloroprene with Other Synthetic Rubbers
When comparing Neoprene, or polychloroprene, with other synthetic rubbers, several factors make it a preferred choice for many applications. To begin with, other synthetic rubbers like nitrile butadiene rubber (NBR) and styrene-butadiene rubber (SBR) do not always offer the same protection against oils or chemicals as neoprene does. In addition to being highly durable in harsh outdoor environments due to its outstanding aging properties and resistance to ozone and UV rays,
Unlike natural rubber, polychloroprene does not wear out or lose its qualities when brought into contact with various oils and solvents which means that it is excellent at resisting chemicals. The material can be formulated to meet specific needs such as enhanced flexibility, higher strength and better resistance to certain chemicals thus making it an elastomer of choice for many industrial applications.
Polychloroprene’s Notable Properties: Ozone & Weather Resistance
To me personally, what makes polychloroprene truly amazing is its significant ability to resist ozone attacks and weather deterioration. For instance, reputable websites like scientific articles and material datasheets indicate that this material remains intact after prolonged exposure to ozone while others may crack or degrade under similar conditions.
Also, in extreme climatic conditions such as freezing temperatures up to -20 degrees Celsius or scorching heat above 100 degrees Celsius, polychloroprene retains its mechanical properties excellently well. This means that it can be applied where materials are exposed continuously outside under the sun’s radiation plus rain water variations through time. It is because of this long-lastingness which guarantees consistency in items such as seals/gaskets/hoses on one hand; protective clothing/coating on the other through a myriad of situations that one must choose hard-wearing substances like polychlorprene whenever working in high challenging environments.
Future Prospects: Polychloroprene in 2024 and Beyond
Looking at future prospects of Neoprene or polychloroprene, one can anticipate more advances in terms of its formulations and uses. According to the top websites found on Google, polychloroprene’s future involves enhanced sustainability and improved performance characteristics. For instance, innovative manufacturing processes are being developed to reduce the ecological footprint of polychloroprene production. In addition, they are working on bio-based alternatives that possess similar properties as those of traditional polychloroprene.
From a technical perspective some parameters remain highly important:
- Tensile Strength: Improved beyond current benchmarks for surviving higher stresses.
- Elongation at Break: Increases in this parameter make it possible to have flexibility maintained over broader ranges of temperature.
- Hardness: Adjusting hardness to fit specific applications without giving up elasticity.
These advancements are anticipated to keep up with increasing demands for strong but versatile elastomers that can be used in modern complex industrial applications. Hence, so long as their use will continue being paramount in automotive industry, construction, consumer goods etc., then there is no doubt that polycholprene will be required even after 2024.
Reference sources
-
Chemistry World – Chemical Sciences Magazine
- Summary: Chemistry World, a reputable magazine covering chemical sciences, features an in-depth article titled “Exploring the Properties and Applications of Polychloroprene (Neoprene) Rubber.” This article provides a comprehensive overview of polychloroprene, commonly known as neoprene, and its uses in various industries. It discusses the chemical structure of neoprene, its physical properties, resistance to oil and chemicals, flexibility in extreme temperatures, applications in automotive, marine, and construction sectors, and sustainability aspects. The article also explores the production process of neoprene rubber and its environmental impact.
- Relevance: Chemistry World is a trusted source for chemical information. This article offers valuable insights for scientists, engineers, and professionals interested in understanding the properties and applications of polychloroprene (neoprene) rubber, providing a well-rounded perspective on the versatility, durability, and eco-friendly considerations associated with using neoprene in different fields.
-
Rubber Chemistry and Technology – Academic Journal
- Summary: An article published in Rubber Chemistry and Technology titled “Advancements in Vulcanization Techniques for Polychloroprene Rubber Compounds” presents a scientific exploration of vulcanization methods and improvements specific to polychloroprene rubber compounds. The article discusses the crosslinking mechanisms, curing kinetics, physical properties enhancements, aging behaviors, and performance optimizations achieved through advanced vulcanization processes tailored for polychloroprene rubber. It includes experimental data, comparative analyses, and insights into the mechanical reinforcement of polychloroprene rubber for industrial applications.
- Relevance: Rubber Chemistry and Technology is a respected academic journal focusing on rubber science and technology. This article offers valuable technical knowledge for researchers, rubber technologists, and polymer engineers seeking to deepen their understanding of vulcanization techniques for enhancing the properties and performance of polychloroprene rubber compounds, providing insights into innovative approaches for optimizing rubber formulations and processing methods.
-
DuPont – Manufacturer Website
- Summary: DuPont, a renowned chemical company, hosts a dedicated section on their website titled “Neoprene (Polychloroprene): Products, Properties, and Applications.” This resource provides detailed information on DuPont’s neoprene products, including grades, specifications, key properties such as resistance to weathering, ozone, and flame, as well as applications across industries like automotive, electrical, and sporting goods. The webpage also offers technical data sheets, safety information, and case studies showcasing the diverse uses of neoprene in demanding environments.
- Relevance: DuPont is a trusted manufacturer of specialty chemicals. Their webpage serves as a valuable resource for engineers, designers, and manufacturers seeking information on neoprene (polychloroprene) rubber products and their applications, offering insights into the performance characteristics, reliability, and quality standards associated with using DuPont neoprene in critical applications, making it a reliable source for individuals looking to explore the benefits of neoprene rubber.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is polychloroprene?
A: Polychloroprene, often referred to as CR, is part of the family of synthetic rubbers. It is produced by the polymerization of chloroprene and is noted for its overall physical properties.
Q: What are some common applications of polychloroprene?
A: Polychloroprene is used in a wide variety of applications including fan belts, neoprene bearing pads, and foam neoprene products. Neoprene is also commonly used to make wetsuits, hoses, and coatings.
Q: What properties make polychloroprene suitable for various industrial uses?
A: Polychloroprene resists degradation from sun, ozone, and weather environments. It has excellent aging characteristics in ozone, flame resistance, and good general-purpose rubber properties. It also offers resistance to grease, ketone, and ester environments.
Q: How does polychloroprene’s flame resistance compare to other materials?
A: Polychloroprene has excellent flame resistance compared to many other synthetic rubbers, making it a preferred material for safety-critical applications.
Q: What is foam neoprene, and how is it different from regular neoprene?
A: Foam neoprene is a type of neoprene that is characterized by its spongy texture, which provides additional cushioning and thermal insulation. While regular neoprene is a solid rubber, foam neoprene’s structure includes tiny air pockets, making it lighter and more flexible.
Q: Who initially developed polychloroprene and when?
A: Polychloroprene was first developed by DuPont in 1931. DuPont’s innovation has led to the widespread use of neoprene in various industries.
Q: Can polychloroprene resist chemical degradation?
A: Yes, polychloroprene resists chemical degradation from a variety of substances including grease, ketones, and esters, making it ideal for many chemical resistance applications.
Q: What makes polychloroprene a good general-purpose rubber?
A: Polychloroprene is considered a good general-purpose rubber because of its balanced combination of physical properties, chemical resistance, and flame resistance. It is versatile and resilient for various applications.
Q: Does polychloroprene have any downsides?
A: One potential downside of polychloroprene is its relative cost compared to some other types of rubber. It can also crystallize at low temperatures, which may affect its flexibility.
Q: Is neoprene used in construction materials?
A: Yes, neoprene is used in construction materials, particularly in neoprene bearing pads. These pads provide structural support and help in vibration damping, serving crucial roles in building and bridge construction.