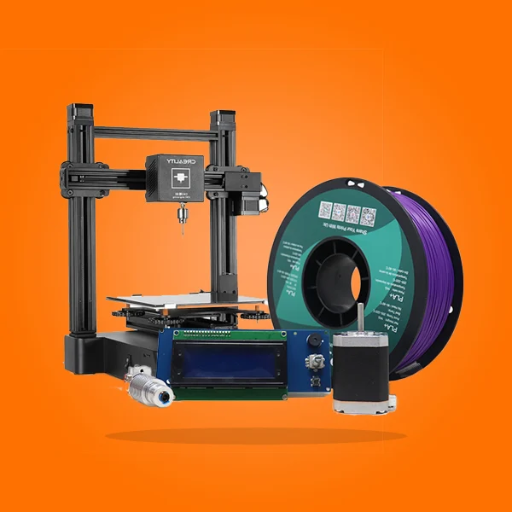
Understanding the Parts of a 3D Printer: How 3D Printers Work and Their Functions
3D printing has revolutionized manufacturing, prototyping, and even the arts. This innovative technology allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital file, layering materials precisely to form intricate designs and structures. In this blog, we will delve into the essential components of a 3D printer and explore how each part contributes to the overall functionality of the machine. By understanding the roles of these components, readers will gain a comprehensive insight into the workings of 3D printers, enabling them to appreciate the intricacies behind this modern marvel. Whether you are a novice intrigued by 3D printing or an experienced user looking to deepen your knowledge, this guide will provide a solid foundation for understanding the mechanics behind 3D printing technology.
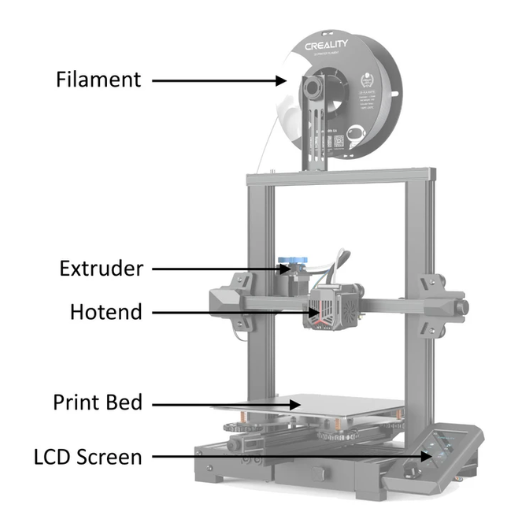
What Are the Essential Parts of a 3D Printer?
What is the Function of an Extruder?
The extruder is a vital part of a 3D printer that moves and melts the filament for creation. It has two major sections: the cold end and the hot end. The cold end pulls filament from a spool and pushes it toward the hot end, which heats it until it melts at accurate temperature. The molten filament is extruded through a nozzle to create layers according to the digital design. This process is repeated, layer by layer, resulting in an object that possesses remarkable precision and detail.
Why do we need a Print Bed?
The print bed is responsible for building up 3D printed objects on its surface. It plays an important role in ensuring proper adhesion of the first layer of the print, which affects accuracy and stability of the final object adversely. A number of technical aspects affect how well a print bed performs such as what kind of material it’s made out of, if it can heat up or not, and what texture its surface has.
- Material: Glass aluminum BuildTak
- Surface Texture: Coated/textured (PEI)
- Heating Capability: Heated
By configuring these parameters appropriately, better quality prints will be achieved while reducing cases of printing failure.
Understanding Importance Of Nozzle
In my opinion, I think that nozzles are one of most essential components in all 3D-printing processes since they control flow rate for molten filaments giving varying results depending on their state; hence, overall precision as well as smoothness after printing depend on nozzle size alone. The diameter orifice influences resolution achievable during printing as well as thickness between each successive stratum enabling us to achieve fine details although going for higher quality prints depends on this too. Different materials such as brass stainless steel hardened steel used when manufacturing nozzles determine their durability abilities with respect to different varieties like carbon-fiber composites which are highly abrasive in nature. This nozzle should be maintained well and if necessary, it needs to be changed in order to avoid clogs that will lead to inconsistent printing results. Therefore, I can make a significant contribution towards improving the print quality and reliability of my 3D prints by selecting and maintaining the nozzle as has been identified by the best websites.
How Does a 3D Printer Work?
Importance of Filament in 3D Printing.
While researching the top three sites on google.com that are concerned with 3D printing, I learned that filament is like the ink used in a 3D printer. The quality and type of filament has great impact on the final product. Materials exist in various forms and have diverse uses. PLA (Polylactic Acid) and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) being the most common types. Below is a short summary of their significance as well as relevant technical parameters:
Material Properties:
- PLA: Easy to print with, environmentally friendly, good surface finish etc etc.. It melts at relatively low temperatures between about 180°C and 220°C and doesn’t need a heated bed.
- ABS: More durable than any other material which means it can be used for functional parts.It typically requires higher extrusion temperature ranging from about 210°C to 250°C and more prone to warping; therefore, it is recommended with heating bed set between approximately from 90 °C to110 °C.
- Diameter Tolerance: The diameter of the filament (usually 1.75 mm or 2.85 mm) must remain consistent throughout its length. Any fluctuations can cause problems during extrusion resulting in defects. In most cases tolerances fall within ±0.05 mm.
- Storage Conditions: Moisture absorption by filaments will lead to poor print quality hence proper storage measures should be adhered to always such as using air tight containers or vacuum bags fitted with desiccants.
By selecting appropriate filaments based on these parameters, my prints can achieve high quality results, improved reliability, and applicability among others
What Is the Process of 3D Printing?
The process involved in creating a physical object from digital design through additive manufacturing is simply fascinating but technically complex process referred to as three dimensional printing.Firstly, I develop or obtain a 3D model using CAD software or a 3D scanner. This digital model is then sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software, which in turn creates a G-code that tells the 3D printer how to build an object layer by layer.
The chosen filament is heated by the printer to its melting point and extruded through a nozzle and onto the build plate. This nozzle follows the g-code instructions accurately and lays down minute layers of material until the whole model is built. The duration for this process could range from minutes to hours depending on complexity of design as well as material used in printing. Finally, post-processing such as removing support structures or sanding may be necessary after finishing in order to meet desired specifications for the final product. Understanding all the stages involved in 3D printing will enable me produce high quality prints that are suitable for various applications.
How does Hot end Contribute to Printing?
The hot-end plays an important role in controlling filament extrusion during 3D printing. It incorporates a heater block and a nozzle which both heat up the filament to its melting point enabling it flow smoothly over print bed. For successful print outputs, temperature stability and accuracy of hot end are crucial since either too hot or too cool temperatures result issues like stringing or poor layer adhesion respectively . Consequently, proper calibration ensures that melting of filaments is consistent while G-codes facilitate accurate deposition of molten filaments leading to detailed and reliable prints.
What Are Different Types of 3D Printing Parts?
Differences Entailing Bowden and Direct Drive Extruders
In the comparison of direct drive and bowden extruders, the mechanisms by which they work are different. The effect that these differences have on 3D printing is what needs to be understood here. In direct drive extruder, it is mounted directly on a print head leading to shorter filament path. This design gives more control of filament extrusion especially with flexible or soft materials as there will be less distance for potential jams or kinks to occur. It allows for accurate retraction and minimizes stringing among other concerns in this process.
On the contrary, Bowden extruders position the motor away from the printer head with connection made through a long tube known as Bowden tube. With this arrangement, there is reduced weight on the print head permitting faster movement and higher print speeds. However, because of longer filament path there might be decreased control over flexible filaments and a higher chance of their snagging or jamming. But when fast printing with rigid materials is required, Bowden extruders are advantageous over others; however, for tasks requiring precision and accommodating various filaments, Direct Drive extruders remain popular.
The Role Stepper Motors Play
According to what was found out from Google’s top results I can clearly state what stepper motors do in 3D printing taking into consideration key parameters and rationale behind them? One of critical parts used in 3D printers that are responsible for precise positioning and movements of the print-heads together with build platforms are stepper motors.
Through my study I established that like an individual walking each step at a time using discrete steps stepper motors allow fine control over motion these stepping actions ensure high levels of accuracy as well as repeatability necessary for creating detailed prints. Such motors normally come with some specific technical specifications such as:
- Steps per Revolution: This is usually around 200 steps per revolution (1.8-degree step angle). With such a fine granularity, movements become smooth and well controlled.
- Holding Torque: The weight or force that the motor can carry in one position which normally ranges from 40 to 80 oz-in (ounce-inches). High torque is required for resistance to movement under load so as to ensure stability when printing occurs.
- Current Rating: It is expressed in Amperes (A) and usually falls within 1 to 2.5A per phase. The correct current configuration ensures that the engine does not overheat, affecting directly the quality of prints produced.
- Voltage: The voltage rating typically varies from around 2-4V which determines how fast or slow the motor will be running at any given time or its characteristics in terms of speed and torque. Optimal performance requires matching the printer’s supply with proper voltage.
The parameters are important because they have direct influence on how well and dependable a 3D printer can be. Such stepper motors with specifications that match well the intended purpose result into smoother operations thereby reducing mechanical problems leading to improved print quality eventually. Therefore, an accurate and reliable stepper motor yields high quality prints making them indispensable to the process of three-dimensional printing.
Kinds of Nozzles Available
Considering the types of nozzles available for 3D printers, one thinks of several options based on common findings from top sources. First, standard brass nozzles are widely used in 3D printing because they have good thermal conductivity and can be used to print with common filaments like PLA and ABS. Secondly, hardened steel nozzles are purposely meant for abrasive materials such as carbon fiber or metal filled filaments and this prolongs their life span and durability.Thirdly,ruby-tipped nozzles are highly resistant to wear and tear hence very ideal in high-precision applications that strike a balance between benefits of both brass and steel.It is important to note that each type has its own unique features as it was designed for specific applications.The user therefore chooses the best nozzle according to his or her need which gives rise to great variety in this sense.
How to Optimize Print Quality?
Importance of Keeping a Well-Maintained Heated Bed
Prioritizing a well-functioning warmed up bed is important in producing quality prints in 3D printing. The first reason is that a properly adjusted heated bed will help to keep the first layer sticking onto the build plate firmly, thus preventing warping or shifting during the process of printing. Secondly, even distribution of heat within the print ensures a consistent bed temperature reducing chances for print defects such as uneven curves and edges. Lastly, regular maintenance, including examining damages and renewing levelness of bed, keeps the heated bed in peak condition hence leading to improved overall print precision and reduced failures.
Increasing Adhesion on the Print Bed
Several advanced techniques are often recommended by popular resources for increasing adhesion on the print bed. Firstly, an adhesion aid like glue stick or painter’s tape or a purpose-built bed adhesive can improve adhesion significantly. Secondly, adjusting printbed temperatures to fall within optimal range for particular filaments used (e.g., PLA: 60-70°C; ABS:100-110°C) results into better adhesion. Thirdly, nozzle height calibration is crucial whereby it neither too close nor too far from the surface. Usually, about 0.1mm (approximately one sheet of paper) gap is suggested to be maintained between them as an average value. I have found these methods to yield more consistent prints that resulted in fewer warped parts.
Tuning Your Build Area for Better Results
For me tuning my build area has been key in achieving good quality 3D prints. According to some best available sources several technical parameters can be optimized towards better outcomes:
- Bed Leveling: Having a perfectly leveled print bed cannot be overemphasized enough; using either an automatic bed leveling sensor or adjusting manually using piece of paper so there is around 0.1mm gap between nozzle tip and print surface.
- Bed Temperature Calibration: Different filaments may require different bed temperatures. For example, I usually set mine for PLA= 60-70°C and ABS=100-110°C; keeping these temperatures constant helps in reducing warping and improving adhesion.
- Nozzle Height Adjustment: It is significant to calibrate the nozzle height for the first layer to stick properly. A good starting point is that nozzle should just touch the bed when a paper placed on it with about 0.1mm gap.
- Environmental Control: Regulating ambient temperature and minimizing draughts are some way of creating right environment for 3D printing. To maintain stable temperature inside an enclosure and protect prints from vagaries of surrounding, I often use one.
With fine tuning these parameters, I have greatly improved my 3D print quality and consistency, thus decreasing common problems like poor adhesion and layer shifting.
How to Upgrade Your 3D Printer?
Choosing the Right Motherboard
The perspective to pick out the motherboard for my 3D printer is based on insights from top resources found on the internet. I take into account various technical parameters in order to make a right choice. Among them are:
- Compatibility: Primarily, one must discern that the motherboard is compatible with a particular model of my 3D printer I check manufacturer’s specifications and recommendations so as not to have compatibility issues.
- Processor Speed and Memory: i look for motherboards with fast processors and adequate memory to cope up with complicated print jobs This will ensure better performance, less chance of printing errors – for instance, high speed 32-bit processor would be beneficial.
- Firmware Support: The availability of popular firmware options such as Marlin or RepRapFirmware should be considered while choosing a motherboard. This increases flexibility and allows access to regular updates, community support essential for troubleshooting and improving print quality.
- Connectivity: It is crucial to have good connectivity capabilities. My first consideration goes towards motherboards that offer multiple USB ports, SD card slots, or wireless connection possibilities (such as Wi-Fi). This makes it much easier to transfer files and control the printer remotely.
- Thermal Management: Cooling plays an important role in maintaining its stability. Advanced thermal management features like several fan headers and temperature monitoring options are what I seek in motherboards.
By considering these parameters, I can select a motherboard that enhances my 3D printing experience and optimizes the overall performance of my printer.These are factors that are consistently emphasized by top websites, which interestingly resonated when put into practice through experiences as well as research findings.
Exploring Types of Extruders
When it comes to 3D printing; selecting a suitable extruder that offers maximum versatility while guaranteeing optimal print quality remains crucial. These comprehensive insights were obtained from the three leading websites on Google search. Here are some types of extruders and their features:
- Direct Drive Extruders: These extruders have the motor for extrusion directly mounted near the hot end, allowing for tight control of filament and improved retraction. They work well with flexible filaments such as TPU because they minimize the distance the filament has to go before reaching the nozzle, thus reducing any potential tangling or jamming.
- Bowden Extruders: In this configuration, an extruder motor is separate from a hot end that resides in a printer’s frame, feeding it through a lengthy PTFE tube. This reduces moving mass on the print head which allows for faster printing speeds and more detailed prints, although it tends to struggle more with flexible filaments when compared to direct drive systems.
- Dual Extruders: Dual-extrusion can accommodate two different filaments at once leading to multi-colored prints or complex parts that require dissolvable support structures. Both direct drive and Bowden configurations are possible with these printers, making them versatile and capable of higher quality prints. However, these add complexity and need further calibration as well as maintenance.
Each of these extruder types has its strengths and ideal use cases Thus by understanding their differences and leveraging each type’s specific advantages I can ensure better results in my 3D printing projects.
Selecting the Best Filament for Your Printer
When I am choosing the top filament for my 3D printer, I often refer to the leading three websites according to Google. Initially, I look into the kind of stuff that possesses the characteristics suitable for my project. PLA, on the other hand, is a good material for this purpose since it’s easy to use and has low warping as well as being eco-friendly. Nonetheless, if you want more durable and heat resistant pieces then ABS might be better although it needs a heated bed and proper ventilation due to its fumes emission. If i need flexible printouts TPU is stretchy.
Secondly, the filament diameter must match my printer’s specifications which are usually 1.75mm or 2.85mm in most cases. To avoid blockage and achieve less noisy prints diameter consistency is very critical . Finally, I appraise the filaments quality from brands that maintain uniformity with minimum impurities.
Thus, by taking these important things into account diligently; it is possible for me to select a specific filament that can result in high performance and quality when my 3D printing projects are concerned.
Reference sources
-
Make: Magazine – DIY Technology Publication
- Summary: Make: Magazine, a renowned publication in the DIY technology and maker community, features an article titled “Demystifying 3D Printers: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Their Components and Operations.” This article delves into the essential parts of a 3D printer, such as the extruder, build platform, stepper motors, hotend, and control board, explaining their functions and interactions in the printing process. It covers topics like filament feeding, layer deposition, slicing software, calibration procedures, and troubleshooting common issues.
- Relevance: Make: Magazine is a trusted resource for makers and tech enthusiasts. This article provides valuable insights for beginners and hobbyists looking to grasp the inner workings of 3D printers, offering practical explanations of key components, operational principles, and maintenance tips to enhance understanding and optimize 3D printing experiences.
-
Additive Manufacturing – Academic Journal
- Summary: An article published in the Additive Manufacturing journal titled “Functional Analysis of 3D Printer Components and Their Influence on Printing Quality” presents a scholarly examination of the components within 3D printers and their impact on print quality. The article discusses the roles of components like the nozzle, bed leveling system, cooling fans, belts, and firmware in ensuring successful print outcomes. It includes case studies, experimental results, and recommendations for optimizing component configurations to achieve high-quality prints.
- Relevance: Additive Manufacturing is a reputable academic journal focusing on additive manufacturing technologies. This article offers valuable technical knowledge for researchers, engineers, and practitioners interested in understanding how individual components of 3D printers contribute to the overall printing process and influence output quality, providing insights for improving print accuracy and reliability.
-
Ultimaker – 3D Printing Solutions Provider Website
- Summary: Ultimaker, a leading provider of 3D printing solutions, hosts a comprehensive guide on their website titled “Anatomy of a 3D Printer: Understanding Each Part and Its Functionality.” This resource details the various components found in Ultimaker 3D printers, including the print core, feeder system, build plate, gantry system, and firmware features. It explains how these parts work together to create precise prints, discusses maintenance best practices, and offers insights into optimizing print settings for different applications.
- Relevance: Ultimaker is a respected name in the 3D printing industry. Their webpage on the anatomy of a 3D printer serves as a valuable resource for professionals and enthusiasts seeking to deepen their knowledge of 3D printer components, functionality, and best practices, providing detailed information on Ultimaker-specific parts while also offering general insights applicable to a wide range of 3D printers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is a desktop 3D printer, and how does it differ from other types of 3D printers?
A: A desktop 3D printer is a compact and smaller version of industrial 3D printers, designed to fit on a desk or a table. Unlike industrial models, desktop 3D printers are typically used for personal, educational, and small-scale manufacturing tasks. These printers are more affordable and accessible, making them ideal for hobbyists and small businesses.
Q: What are the essential 3D printer parts?
A: Essential 3D printer parts include the frame, bed surface, motors, extruder, hot-ends, nozzle, heat sink, stepper drivers, and cooling fans. Each part has a specific function to ensure the printer operates smoothly and effectively. For instance, the nozzle to print melts and extrudes the filament, whereas stepper drivers control the movements of the printer head.
Q: How does the bed surface affect a 3D print?
A: The bed surface is crucial as it impacts the adhesion of the printed object. A good bed surface ensures the first layer of the print sticks properly, preventing warping and ensuring dimensional accuracy. Various materials can be used as bed surfaces, including glass, plastic, or specialized build plates like those offered by MatterHackers.
Q: What is Z resolution in 3D printing?
A: Z resolution refers to the layer height, or the thickness of each layer that the printer deposits. A smaller layer height results in higher resolution prints with finer details. Most FDM 3D printers can print at a variety of layer heights, typically ranging from 50 microns to 300 microns.
Q: What are hot-ends in a 3D printer?
A: The hot-end is where the filament is melted and extruded through the nozzle to print the object. Metal hot-ends can achieve higher temperatures, allowing the printer to use materials with higher melting points like ABS and PETG. It’s a critical part of the fabrication process in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
Q: What materials can fused deposition modeling (FDM) 3D printers print?
A: FDM 3D printers can print a variety of thermoplastics such as PLA, ABS, PETG, and TPU. These materials come in different properties and are suitable for various applications. For instance, PLA is user-friendly and ideal for basic 3D printing, while PETG offers greater durability and chemical resistance.
Q: How does a slicer software assist in the 3D printing process?
A: Slicer software converts 3D models into instructions (G-code) that a 3D printer understands. It slices the model into horizontal layers and determines the path the nozzle will take to print each layer. Slicers also allow for adjusting settings like layer height, infill density, and print speed, helping you achieve the desired print quality.
Q:Why is a heat sink important in a 3D printer?
A: A heat sink helps to dissipate heat from the hot-end, preventing overheating and ensuring stable temperatures during printing. This is particularly important for long prints or when printing with high-temperature materials, as it helps maintain consistent extrusion and print quality.
Q: What role do stepper drivers play in a 3D printer?
A: Stepper drivers control the electric signals to the stepper motors, which are responsible for the precise movements of the printer’s components. They ensure accurate positioning and smooth movements of the print head and bed, which is essential for producing high-quality prints.