What is Pad Print and How Does it Work?

Image source: https://theprint.blog/
Understanding the Pad Printing Process
The pad printing process involves several major steps that should be adhered to for a successful transfer of image or text onto the intended object. Here is a brief explanation as obtained from the top three websites in Google:
- Etching the Plate: This is where an etched plate containing the desired image or text, mostly made of photopolymer or steel, is created. It creates an indented area on the plate.
- Applying the Ink: Afterward, ink is added onto this etched plate. To take out extra ink, a doctor blade slides over its surface leaving only ink in the etched recesses.
- Picking Up the Ink: Another way to pick up the image is by pressing a silicone pad (often referred to as tampon) on top of this ink-filled etching. The flexibility of this pad enables it to adhere with ease and collect even layering of ink from all sections involved.
- Transferring the Ink: Then, pressing onto an item being printed was done using the now ink filled pad having an imaged on it. Due to its ability to conform different shapes and surfaces, it can accurately put impressions on items that have curved surfaces or those that are unevenly contoured or textured.
- Completion: Finally, either through air drying after printing or by means of any suitable curing method for given types of inks; completes this process called ‘pad printing’.
The Role of the Pad Printer
Comparing Pad Printing to Screen Printing
When comparing pad printing to screen printing, several distinguishing features become apparent. Pad printing works best with objects having three dimensions and those without a flat surface because of its adaptable silicone pads thus making it suitable for objects such as curved drinkware, buttons, and electronic components. Conversely, screen printing is more appropriate for flat surfaces or larger areas such as T-shirts, posters, and fabric signs.
Pad printing can produce smaller images with finer details especially on tiny items while screenprinting is long lasting and has bold color application, though it’s poor for intricate work on small pieces or ones that are not smooth.
Additionally, the two techniques have varying speeds of production. Pad printing is usually better in terms of efficiency for minute jobs with high magnification and ornate patterns. Screen-printing can handle large scale jobs at lower costs that require heavy ink deposits.
How to Use a Pad Print Machine Efficiently
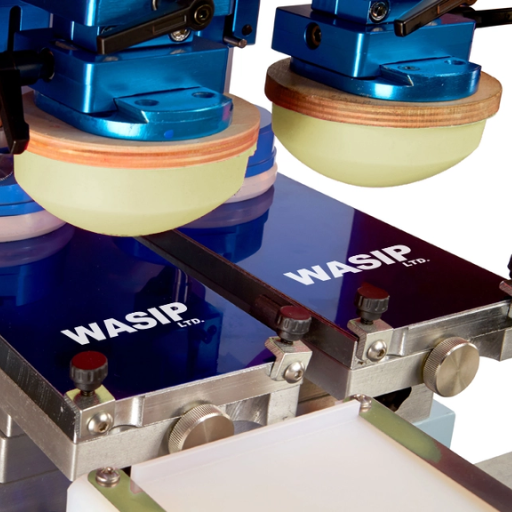

The use of a pad print machine requires following a systematic approach:
Preparation
- Select the Right Pad and Ink: For your products, choose silicone pads that match the shape of their surfaces, and select an ink suitable for the materials you are printing on.
- Set Up the Machine: Ensure all parts are clean and properly assembled. Adjust pad and ink cups to align with your printing plate.
Operation
- Fine-Tune Settings: The machine should be adjusted to have right pressure and speed based on material being printed on as well as design requirements. These settings help in achieving sharp details and consistent print quality.
- Test Prints: To confirm alignment, adhesion of ink, image clarity; test prints can be done using sample product. Correction of any problems may also be done at this stage.
Maintenance
- Regular Cleaning: Machine parts like pad, ink cup etc., must be cleaned regularly to avoid clogging by excessive amounts of ink.
- Monitor Ink Viscosity: Consistency is retained by continually monitoring ink viscosity throughout the process of printing; otherwise mix the ink when it’s necessary.
Basic Components of a Pad Printing Machine
Several key components work together in pad printing machines to transfer ink from the printing plate to the product surface. Among these are:
- Cliché (Printing Plate): The cliché contains the engraved image and is filled with ink before being pressed onto a silicone pad.
- Silicone Pad: Flexible, this pad picks up inked images from clichés and deposits them on products. It is meant to match perfectly with designs of products enabling accurate printings.
- Ink Cup: The cup that holds and dispenses ink on the cliché. Furthermore, it also helps regulate viscosity of ink and keeps it wet while printing is ongoing.
- Drive System: This coordinate movement of the silicone pad as well as the ink cup for efficient printing purposes by positioning accurately and maintaining even pressure.
- Control Panel: Operators use control panel to adjust; print speed, pad pressure, cycle times among others hence quality printouts are assured at all times.
Pad Print Equipment: Necessary Tools and Supplies
Some elements are needed for setting up and maintaining a pad printing operation:
- Printing Ink: Pad printing relies on specially formulated inks to produce vibrant, durable prints.
- Printing Pads: Different product surfaces and print requirements necessitate pads made of silicons of different sizes and shapes.
- Clichés: These are the engraving images holders that are accurate and long lasting.
- Cleaning Supplies: In addition, printing plates ought to be cleaned using cleaning agents as well as tools while tools such as solvents and thinners help reduce ink viscosity and clean any parts of equipment.
- Solvents and Thinners: These are used to adjust ink viscosity and clean equipment parts.
- Doctor Blades: Doctor blades are used to control ink distribution over clichés.
- Fixtures and Jigs: Custom fixtures and jigs help hold products securely in place during the printing process to ensure precise prints.
- Spare Parts: To avoid any downtime, it is important to have extra supplies. Pads, print plates, Ink cups
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Pad Print Machine
- Preparation:
- Select and Mix Ink: Start by selecting suitable ink type for the application you are after. Stirring should be done to mix ink properly with the aid of stirrers and spatulas until the desired color consistency and viscosity is attained.
- Clean the Equipment: Check that all parts including pads, clichés and doctor blades are clean. Remove any dirt particles using appropriate cleaning agents like solvents, brushes etcetera.
- Setting Up the Machine:
- Install the Cliché: Fix the selected printing plate (cliché) in position on your pad print machine. Depending on what equipment you have this will mean lining up and securing cliché.
- Load the Ink Cup: Pour out some mixed ink into the cup meant for holding ink then stick it to your machine. Ensure it is well aligned with cliché.
- Adjustment and Calibration:
- Align the Silicone Pad: Pick a silicone pad which suits your printing surface best. Stick it to its right position on machine while ensuring it makes an even contact with cliché.
- Adjust Print Settings: Based on material and ink specification, set up pad pressure, speed as well as print cycle timing under this machine information.
- Printing Process:
- Ink Pickup: When silicon pad come into contact with cliché that has already been applied with ink, it picks up an image that can be printed .
- Transfer: Silicone pad shifts from one place to another where they stamp down upon release of adhesive tape which leaves behind an impression created from pigment droplets applied during prior step.
- Repeat: Repeating each stage for every item being printed will enable consistent quality control as well as minor corrections if required within this manufacturing process chain too!
- Post-Printing:
- Curing: Put these items exposed into UV curing systems or dryers immediately if at all UV or other curable inks have been used.
- Quality Check: Look at such prints for any imperfections, irregularities or discrepancies requiring adjustment so that they can be produced up to the quality standard.
- Cleaning and Maintenance: Once you are through with printing, clean all parts of your machine. Regular tune-ups will increase life expectancy of your printer while ensuring consistent high print quality.
What Types of Ink Are Used in Pad Printing?
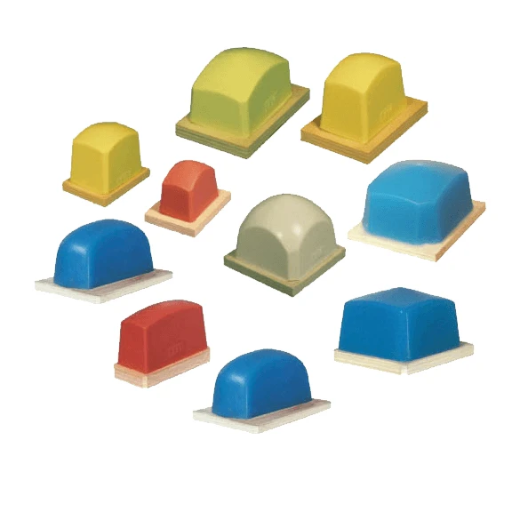

Different pad printing inks are widely used because each type is designed for particular applications and surfaces.
- Solvent-Based Inks: These are very common due to the fact that they dry quickly and bind well with various materials such as plastic, metal, or glass.
- UV-Curable Inks: They cure instantly when exposed to UV light making them the best option for fast production lines having exceptional endurance and chemical resistance.
- Epoxy Inks: This kind of ink is known for being highly adhesive as well resistant to abrasion; therefore, it is used in the process of printing on difficult substrates like metals and ceramics.
- Water-Based Inks: While less common in pad printing, water-based inks are an environmentally friendly option that can be used for printing on materials like paper and some plastics.
- Silicone-Based Inks: These inks have been developed specifically for use on silicone material thereby presenting a good adhesion and elasticity.
Different Types of Pad Printing Ink
When it comes to pad printing, selecting the right type of ink is crucial for achieving optimal results. Based on the content from leading sources, primary types of pad printing inks can be categorized as follows:
- Solvent-Based Inks: These are preferred for their versatility and fast-drying abilities and work well on substrates such as plastics, metals and glass. Their strong bonding properties make them a favourite choice.
- UV-Curable Inks: These inks are recognized due to their quick curing process when exposed to UV light, they perform well under high-speed production environments. They have exceptional strength and resistance against chemicals hence suitable for harsh conditions.
- Two-Component Epoxy Inks: These inks are most valued for their highest adhesion properties with a good wear resistance especially on difficult surfaces like metals and ceramics.
The Importance of Pad Printing Ink Cups
Pad printers use ink cups to maintain the consistency of ink application in the pad printing process. The following are some of its functions:
- Ink Regulation: The cup confines the ink so that its viscosity is not altered and also controls it from evaporating too much, which can lower printing quality.
- Clean Printing Surface: By wiping off any superfluous ink from the plate as it draws back, the ink cup plays a role in which only required amount remains on etched area. This ensures clean and even prints on every new stroke.
- Reduced Waste: These cups of ink hold more ink at a given time and therefore reduce wastage thus, making this process cheaper while being environmentally friendly.
By using these components, it ensures accurate and beautiful imprints thereby optimizing material utilization rates as well as lowering operational expenses.
How to Choose the Right Ink for Your Pad Printing Applications
To choose the right ink for your pad printing applications, there are several important factors to consider to ensure that the performance and quality of print is optimal. In a nutshell, here’s a guide based on some of the best websites:
- Substrate Compatibility: The first consideration is determining the type of material you will be printing on. Different substrates such as plastics, glass, metals or ceramics may require unique ink formulas so as to bond well and gain durability.
- Curing Method: Establish if you need air-drying inks, heat-curing inks or UV-curing inks on the basis of how fast you want your production set up and speed to be. The drying time for UV-curing inks is faster compared to other types of inks; hence they are resistant to environmental conditions.
- Ink Properties: To evaluate suitability of an ink for a pad printer, properties such as adhesiveness, hardness, chemical resistance and opacity ought to be taken into account. Good quality inks do not break down under different operating conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance: It is essential that you ensure that the ink adheres to industry safety standards and guidelines particularly where it involves food contact applications, medical devices or children’s toys.
- Color Matching: Consider whether the color requirements can be met by using color matches that closely resemble those specified by Pantones. So one may resort to custom color matching services which are normally made available upon request in order to satisfy specific branding needs.
What Are the Advantages of Pad Printing?

Benefits Over Other Print Processes
Common Applications of Pad Printing
Pad Printing Technology Innovations
The need for increased efficiency and precision has fuelled significant improvement in pad printing technology during the last years. This has resulted to an automated pad printing system that enhances fast production, consistency and leaves less work behind. These are equipped with control features that are sophisticated, have programmable settings that enable accurate adjustments and repeatability in the printing process.
Another breakthrough is the use of environmentally friendly inks and cleaning solutions. Such sustainable materials meet the emerging needs for manufacturing practices that do not harm the environment. Besides minimizing environmental impacts of pad printing in terms of a reduced ecological footprint, these also ensure compliance with stringent environmental regulations.
Digital technologies have been integrated into pad-printing systems which revolutionized it as well. Through digital imaging systems, real-time monitoring can be done using quality control checks enhancing precision and reducing defects to a minimum level possible. Furthermore, computer-aided design (CAD) software used in pad printers speeds up design processes thereby enabling rapid prototyping and customization.
Collectively this helps boost the abilities of pad printing machine making it a much more flexible and effective tool for various industrial tasks.
How to Maintain Your Pad Printing Equipment

To have your pad printing equipment endure and function optimally, it is important to maintain it. The following are some crucial steps:
- Regular Cleaning: Clean the pads, plates and ink cups after every use so as to avoid a buildup of ink which can lead to varying print qualities. Use appropriate cleaning solutions recommended by the manufacturer.
- Inspection and Replacement: Check for wear and tear on the pads regularly and replace them when necessary. Look out for other damaged items like the doctor blades or seals.
- Lubrication: Observe manufacturers’ instructions on lubricating moving parts to prevent friction and wearing out. Apply right type of lubricant in proper amounts.
- Calibration: Occasionally calibrate your machines if you want accurate prints all along. This involves checking the alignment and pressure settings.
- Environmental Control: Keep your work place clean, free from dust particles. Contaminants interfere with print quality as well as damaging machine parts.
- Training: Train both users of this machine in its operation and care for them. Proper handling significantly extends machinery life span.
- Scheduled Maintenance: As per manufacturer’s recommendations, stick to a regular maintenance plan that may include deeper inspections, part swapping etc.
Cleaning and Maintaining the Pad Print Machine
For a pad printing machine to work efficiently and last longer, it must be properly cleaned and maintained. Below are some important recommendations:
- Daily Cleaning: Clear the pads, plates, and ink cups of any ink residue or debris every day. Using a solvent that is recommended by the manufacturer preserves print quality.
- Ink Cup Maintenance: Thoroughly clean ink cup to remove hardened ink residues that may affect print results and hinder smooth movement of the pad.
- Plate Cleaning: Use a soft cloth with an appropriate solvent to carefully wipe off any leftover ink on plates taking care especially around fine details in the plates.
- Inspecting Pads: Regularly inspect pads for wear and tear signs. Change those showing cracks or divots to avoid compromising on the quality of prints.
- Lubrication: Lubricate moving parts according to recommendations from manufacturer thus reducing frictional force & wear out for optimal performance.
- Checking Seals and Blades: Examine doctor blades’ state together with seals. As operating components they should not possess dents or other forms of damage.
- Environmental Control: Keep working areas free from dust or contaminants that could interfere with machine performance or output quality during printing operations.
- Operator Training: All operators should be trained how to use, maintain including handling and cleaning protocols in order to operate effectively when using a pad printer machine.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Pad Printing Equipment
Like all machinery, pad printing equipment can have problems which interfere with the printing process. Here are a few common issues and their respective trouble shooting tips:
- Ink Coverage and Transfer Issues:
- Problem: Inadequate ink coverage on the substrate.
- Troubleshooting: Insufficient ink viscosity; Adjust composition of inks; Clean the pad and plate, examine doctor blade for damages or wearing out; Ensure even distribution of the pressure applied by a pad;
- Image Distortion or Misalignment:
- Problem: Printed images appear stretched, compressed, or misaligned.
- Troubleshooting: Get the correct alignment of pad to plate. Consistently place the substrates. Check pads and plates for those that are worn out instead of being damaged as well as machines setup verification.
- Ink Drying Too Fast or Slow:
- Problem: Ink dries too quickly on the pad or remains tacky on the substrate.
- Troubleshooting: Modify an ink formula by incorporating retarders (to slow down drying) or accelerators (to speed up drying). Make sure that appropriate environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity are maintained for ideal ink performance.
The Longevity of Pad Printing Plates and Pads
Pad printing plates and pads have lifespans which are very essential to the efficiency and quality of the printing process. The life expectancy of these parts can depend upon a number of factors that includes the material used, complexity of the subject being printed, and the maintenance measures undertaken thereof.
Pad Printing Plates: Plates fabricated from stainless steel usually outlive those produced from materials such as photopolymer or ceramic. When correctly applied, steel plates can last over one million impressions. Photopolymer plates are for shorter runs typically offering tens to several hundreds of thousands of impressions prior to replacement. By regularly cleaning and handling them properly, the life span of these printing plates may be significantly increased.
Pad Printing Pads: The longevity of the pads depends on their constituents which is commonly silicone. Depending on print conditions and care taken during use, good quality pads can be useful for 50-100k impressions. Properly cleaned and not exposed to harsh chemicals; when not in use they should be stored in cool dry places all this contributes to longer usage time.
Reference sources
-
Inkcups – Pad Printing 101: The Ultimate Guide
- Inkcups offers an extensive overview of pad printing, discussing the capabilities of pad printing machines and their versatility in printing on various substrates. This guide is a comprehensive resource for understanding the technical aspects and applications of pad printing technology.
- Source: Inkcups
-
Printing International – What is Pad Printing? A Step-by-Step Guide
- Printing International provides a thorough step-by-step guide on pad printing, detailing what is required to start pad printing and how the process works. This source is valuable for those seeking to understand the fundamental principles and operational steps of pad printing.
- Source: Printing International
-
ITW Transtech – Pad Printing Ink Types: Everything You Need to Know
- ITW Transtech delivers an in-depth look at the various types of pad printing inks available, including single and two-component inks. This source explains how to choose the best ink for different applications, ensuring high-quality and repeatable results in pad printing.
- Source: ITW Transtech
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is pad printing?
A: Pad printing is a versatile printing process that can transfer a 2D image onto a 3D object. It involves using a silicone transfer pad to pick up ink from an etched plate and then pressing it onto a substrate.
Q: How does a pad print machine work?
A: A pad print machine works by collecting a small amount of ink from the pad printing plate using a sealed ink cup. The pad lifts away with the ink and moves forward to press it onto the desired object, completing the pad printing process.
Q: What materials can be printed using pad printing?
A: Pad printing is suitable for printing on a variety of materials, including plastic, metal, glass, ceramics, and rubber, making it highly versatile for many industries.
Q: What are the advantages of using a cup pad printing machine?
A: A cup pad printing machine offers precise ink control and reduces ink waste, as a small amount of ink remains inside the sealed ink cup. It also helps in maintaining consistent color fidelity in color pad printing.
Q: How many colors can pad printing use?
A: Pad printing can use multiple colors, but single color pad printing is common for simpler designs. Complex designs can involve multiple printing cycles with different colors.
Q: What are the steps in the pad printing process?
A: The pad printing process involves several steps: (1) the pad is compressed onto the ink-covered plate, (2) the pad lifts away with a tacky ink film inside, (3) the pad moves forward, and (4) the pad is compressed onto the substrate, releasing the ink.
Q: Can pad printing be used for detailed designs?
A: Yes, pad printing is used for detailed designs as it can accurately transfer intricate patterns from the printing plate onto various substrates, even those with irregular surfaces.
Q: What type of ink is used in pad printing?
A: Pad printing ink varies depending on the substrate material. The ink formula is crucial for adherence and durability, and pad printing supplies include a variety of inks to choose from based on the specific application.
Q: How is offset printing different from pad printing?
A: Offset printing is typically used for flat, large-scale printing on paper, while pad printing is ideal for transferring images onto small, irregular objects. Each process serves distinct purposes based on the substrates and print requirements.
Q: Why is tampo printing sometimes used interchangeably with pad printing?
A: “Tampo printing” is the European term for what is commonly known in the U.S. as pad printing. Both terms refer to the same printing process that uses a silicone pad to transfer ink onto a substrate.