What is MDF and How is it Made?
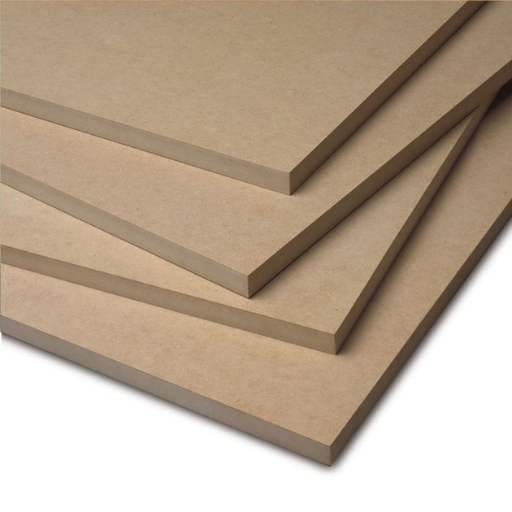

Image source: https://skumatimba.co.uk/
Understanding Medium Density Fiberboard Composition
Optimization of its applications in various areas, for instance, laser cutting requires one to understand the make-up of MDF. The main ingredients are wood fibers, usually derived from hardwood or softwood particles, wax and an adhesive resin binder. Generally speaking here is how it can be broken down:
- Wood Fibers: 82-85%
- Resin: 10-12%
- Wax: 2-3%
Technical parameters such as density, moisture content and thickness are also vital when dealing with MDF. These include:
- Density: Ranges from around 600 kg/m³ to about 800kg/m³. Higher density boards mean better strength and durability thus ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Moisture Content: Should be between 4% and 11%. Incorrectly maintained moisture levels will negatively affect the quality of cuts made on a work-piece.
- Thickness: Normally varies between 3mm to 60mm. The choice of thickness depends on the specific project requirements—thinner boards are suitable for detailed, intricate designs while thicker boards offer enhanced stability and strength for larger projects.
How is MDF Different from Plywood?
As popular choices in woodworking and construction, Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF) and plywood have many differences in composition, strength and uses. The MDF is produced from fine wood fibers bonded together with a mixture of resin and wax making it smooth with a uniform surface without any grain patterns. Conversely, plywood is made up of thin slices of wood stuck together such that the grain on each layer runs perpendicular to the layer above or below it thus increasing its strength and preventing twisting.
Generally, plywood is stronger and lasts longer than MDF because it has a cross-grain structure hence it is used for applications requiring structural strength such as subfloors or wall sheathing. On the other hand, that MD has a homogenous structure making it easy to work on by machinists including detailed works like cabinet making or molding. Nevertheless, while this can be highly advantageous for designs, MDF tends to be more vulnerable to water destruction as opposed to plywood which due to its stacked surface demonstrates greater moisture resistance. Based upon these big differences selection between MFD or Plywood depends upon specific project requirements.
Common Uses of MDF in Furniture and Construction
MDF, with its smooth surface and ease of processing, is also widely used for furniture and construction. It is often found in the cabinets, shelves and mouldings which are precise and flawless in their designs. MDF can be easily molded into any shape or painted to take on intricate details like those found in custom fittings.
In construction work, MDF forms part of the internal decoration such as wall panels, wainscoting, backing countertops etc. Similarly it serves well for door panels and interior cabinetry. Due to its susceptibility to damage by water it cannot be used neither in outdoor nor structural components but remains affordable, consistent and flexible in a variety of interior designs and decorative projects. These features make it ideal for crafts that require great precision with a smooth finish at the end of the project.
How Does a Laser Cutter Work with MDF?

The Science Behind Laser Cutting and Engraving
Types of Laser Cutters Suitable for MDF
Three main types of laser cutters are widely used for MDF: CO2 lasers, fiber lasers, and diode lasers.
- CO2 Laser Cutters: These are the most popularly used machines for MDF because they are efficient as well as accurate. The power ratings allocated to CO2 lasers range from 40W to 150W commonly, thereby rendering them applicable in both engraving and cutting operations. Their strong beam and cleaner intricate cuts make these great for precision works.
- Fiber Laser Cutters: Fiber lasers can also be used on MDF although this is less common in woodwork with the availability of a few applications that allow it to perform an engraving function. Fiber lasers use different wavelength than CO2 ones which may lead to more detailed engravings. Still, they tend to be more costly and not very effective when dealing with thicker sheets of MDF.
- Diode Laser Cutters: Diode laser systems offer cost-effective alternatives that suit hobbyists or small projects. Usually these have lower power compared to the CO2 laser but they can still engrave MDF while cutting through thinner sheets. They are portable and user-friendly; hence suitable for do-it-yourself fans as well as small workshops.
Key Considerations When Cutting MDF with a Laser
To obtain good results and keep your machine running for long, there are a number of factors you must consider when cutting MDF using laser:
- Laser Power and Speed Settings: Attaining accurate cuts without burning or charring can only be achieved if the power and speed settings of your laser cutter are adjusted. When working on thicker MDF, higher power settings are needed while lower ones work best for thin sheets as well as detailed engravings. Run tests after trying different powers to ascertain the ideal combination for certain material thickness.
- Ventilation and Fume Extraction: MDF contains adhesives and resins that produce toxic fumes when cut with a laser. In order to maintain a safe work environment and protect yourself from such fumes, it is important to ensure proper ventilation in addition to having a fume extraction system. It is also better to operate it within a space where there is enough air flow as well as use an appropriate fume extractor.
- Material Preparation: Accurate results can only be achieved if you cut flat and clean MDF. If this does not happen, then your machine will produce irregular cuts which may damage its components. Besides keeping the surface steady during engraving process so that there will be no movement during cutting thus leading to improved accuracy.
- Focus and Lens Maintenance: The quality of your cut will greatly depend on the focal length used by your laser cutter. Regular checking plus hunkering down for focus calibration makes sure that it matches your actual material’s thickness levels for all the time you put together the device; ensuring effective performance of course. Additionally, dirty lenses decrease efficiency at which lasers cut as well as lead to depreciation in quality of cuts hence the need for ensuring they remain free from dust or any other kind of dirt.
- Testing and Calibration: Before proceeding with the whole project, experiment on some scrap MDF; doing this allows adjustments in case one desires them, otherwise if everything goes according to plan, you will be able to get precise outcomes. The performance of your laser cutter should also be calibrated regularly for consistent results.
What are the Benefits of Using Laser Cut MDF?

Precision and Accuracy in MDF Cutting
Customization and Design Flexibility
Efficiency in Production and Prototyping
What are the Challenges in Laser Cutting MDF?

Dealing with MDF Density and Thickness
Managing Wastes and Emissions
MDF and Formaldehyde – Safety Considerations
How to Achieve the Best Results with Laser Cut MDF?

Optimizing Laser Settings for MDF
Choosing the Right Laser Power and Machine
Consider the following key factors when selecting the right laser power and machine for cutting MDF:
- Laser Power: Higher wattage lasers, around 80-150 watts approximately, are more suitable to cutting thicker MDF materials efficiently. Lower wattage lasers like those within 40 – 60 watts range would be better for finer cuts and details on thinner MDF sheets.
- Machine Type: CO2 laser cutters are highly recommended for MDF because they have high precision and can cut through a variety of thicknesses. These machines are widely available and offer a good balance of cost and performance.
- Bed Size: The laser cutter should have a large enough bed size to accommodate your sheets’ dimensions of the MDF. With larger bed sizes you can handle bigger projects but also you are given more flexibility in material placement.
- Cooling System: An integrated cooling system (such as water-cooled systems) helps maintain optimum operating temperatures, preventing overheating while ensuring consistent performance.
Consult product reviews and compare specifications to choose an appropriate piece of equipment that matches your project’s requirements effectively and produces excellent results with regard to laser cutting MDF.
Tips for Minimizing Char and Burn Marks
- Optimize Laser Settings: Find the proper balance with speed and power settings on your laser cutter so that it cuts through the MDF without excessive burning. Generally speaking, faster cutting speeds combined with lower power settings could reduce char marks as well as burn marks.
- Use Air Assist: To blow debris and flames away from the path of the laser, incorporate an air assist feature into it. It enhances not only how well things get cut but also minimizes chances of getting burnt by cooling down the region being cut thereby removing flammable particles themselves
- Masking Tape: Apply masking tape over the surface of your MDF before cutting it. This layer functions as a buffer between any excess heat caused by scorching thereby preventing scorch marks on it besides being easily peeled off, leaving an uncovered cut edge.
- Multiple Passes: Consider multiple lighter passes as opposed to cutting through thicker materials in one pass. This can help decrease the amount of heat accumulated in one area at a time reducing burns and charring.
- Proper Focus and Lens Maintenance: Make sure the laser is properly focused and that the lens and mirrors are clean and well-maintained. A well-focused beam will produce a cleaner cut with less heat dispersion thus minimizing burn marks.
How to Maintain and Troubleshoot Your Laser Cutter?
For your laser cutter to last long with optimal performance, it needs to be maintained properly. Here are some important tips for maintenance:
- Regular Cleaning: Periodically clean the lenses, mirrors and other optical parts so as to avoid residue accumulation that may affect the cutting precision and power. Take caution while cleaning not to scratch the surfaces and use appropriate cleaning agents.
- Check and Replace Filters: You should frequently replace air and exhaust filters to ensure proper ventilation and suctioning in the machine hence preventing overheating as well as maintaining cleanliness of the cutting area from debris or fumes.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Keep lubricating the guide rails as well as other moving components in order to avert wear out by regularly doing this. Stick to manufacturer’s recommended lubricant.
- Calibration: Periodic calibration is necessary for maintaining accurate cuts on laser cutters since you have to align its beam with that of laser then check if the bed is flat.
- Software Updates: Updating machine software and firmware enhances bug fixes as well as improvements it might have had.
When troubleshooting issues:
- Check Connections: Always ensure all cables and connections are firmly plugged in because loose connections can cause power loss or communication problems.
- Error Codes: Refer to the user manual for error code meanings. In addition, most laser cutters have diagnostic capabilities that will help you identify what is wrong with your machine.
- Test Runs: Perform test runs on scrap material in order to identify cutting problems without any wastage of valuable materials.
- Consult Manufacturer: If problems persist, consult support team or professional technicians who deal with repairing such kinds of machines directly from manufacturers
Regular Maintenance Practices
For effective operation of your laser cutter, you must do the following regular maintenance practices:
- Inspect Optics Regularly: CAlways examine laser optics which include lenses and mirrors for dirt, dust or damage. They should be cleaned with appropriate lens cleaning solutions and lintless wipes to ensure perfect performance of the laser.
- Clean the Machine: Dust, cutting debris and residue should be removed from both the inside and outside parts of the machine. In this case, it would also entail cleaning the cutting bed as well as filters exhaust system.
- Check and Tighten Belts: The belts and pulleys must be inspected for wearing out while ensuring that they are rightly tightened. Loose or worn out belts affect cutting precision.
You will greatly prolong your laser machine’s life span and achieve accurate cutting by consistently following these maintenance steps.
Common Issues and Their Solutions
- Laser Not Cutting Through Material: This happens frequently due to incorrect settings or dirty lens. Make sure that your power and speed settings correspond to what you are cutting. Wipe out any dusts or residues on mirrors or lenses causing barriers in way of the beam with a clean piece of cloth.
- Burn Marks on Edges: Too much power settings or slow speed can result in burn marks. Modify the power setting so that there is a balance between it and speed. Besides, you can minimize burn marks by using defocused lasers as well as putting mask tapes over materials being cut.
- Inconsistent Cutting Depth: Varying depths during cut could be occasioned by uneven materials thickness or misaligned focus beam. Check whether material have even surfaces throughout its entire area if not make necessary changes to enable it attain acceptable flatness standards all around. Also, refocus the laser as per manufacturer’s instructions for use after having checked it again; moreover, see to it that the cutter bed is horizontal.
By handling these common problems through recommended solutions given earlier, your laser cutter will improve significantly in terms of efficiency, providing more accurate cuts.
Ensuring Longevity of Your Laser Cutting Machine
Therefore, long life and optimum performance of your laser cutter requires following a regular maintenance timetable and best practices. Below you will find some brief steps from top-rated sources:
- Regular Cleaning and Inspection: It is important to regularly clean the machine’s lens, mirrors and ventilation systems as this helps in preventing dust accumulation which could decrease performance. In addition, surfaces should be wiped down while assessing any wear or damage.
- Proper Ventilation: The machine has to be placed in a well-ventilated room where the exhaust system is clear. A good exhaust system must be used to get rid of fumes created during cutting that can settle on any part of it.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Follow instructions given by the manufacturer for maintenance strictly. At this point lubricate all moving parts, recheck optics alignment as well as replacement of worn out parts where necessary. Firmware updates need to be done at regular intervals alongside continuous system tests so that its effectiveness does not degrade.
- Use Quality Materials: Since these are intrinsically damaging materials; use only those recommended by the manufacturer without impurities which normally result into poor cutting results.
- Operator Training: Proper instruction for operators should take place always consequently ensuring that they know how to operate it safely, keep it maintained as well as solve simple problems encountered when using it. This way less costly mistakes are made since there will be no mishandling due to non-understanding thanks to all users being versed with how a particular laser machine works, what keeps it going and what makes such machines fail unnecessarily.
Reference sources
-
Xometry – Medium-Density Fiberboard (MDF): How to Laser Engrave
- Xometry offers a comprehensive guide on laser cutting and engraving MDF, highlighting the processes involved, necessary equipment, and best practices to achieve precise results. This source also discusses the advantages and challenges of working with MDF.
- Source: Xometry
-
LaserPecker – MDF Laser Cutting: A Beginner’s Guide
- LaserPecker provides an informative guide tailored for beginners, explaining the fundamentals of laser cutting MDF. It covers essential techniques, preparation steps, and safety considerations, making it a valuable resource for anyone new to MDF laser cutting.
- Source: LaserPecker
-
Baison Laser – How to Choose the Best Laser Cutter for Your MDF Projects
- Baison Laser explores the criteria for selecting the most suitable laser cutter for MDF projects. The article delves into the capabilities of different laser cutters, material compatibility, and performance metrics, ensuring users can make informed decisions.
- Source: Baison Laser
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is MDF laser cutting?
A: MDF laser cutting involves using a laser machine to precisely cut or engrave medium density fiberboard (MDF). This process allows for intricate designs and custom laser cut parts that are ideal for various applications.
Q: How do I prepare MDF parts for laser engraving?
A: To prepare MDF parts for laser engraving, ensure that the MDF board is clean and free from any debris. It’s important to select the right sizes for the laser cutter, and to configure your laser machine settings depending on the thickness of the MDF.
Q: What thickness of MDF board should I use for laser cutting?
A: The most common thicknesses for laser cutting MDF are 3mm MDF and up to 6mm MDF. Thicker MDF can be harder to cut and may require a more powerful laser machine, like a Trotec or a Glowforge.
Q: Can I use a laser machine for both engraving and cutting MDF?
A: Yes, you can use a laser machine for both engraving and cutting MDF. The same laser head is typically used, but you will need to adjust the settings accordingly for engraving versus cutting to get the best results.
Q: What variations in MDF are suitable for laser cutting?
A: While standard MDF is commonly used, there are also other variations such as HDF (high-density fiberboard) and masonite, which can also be laser cut. Always check the specifications of the material to ensure it’s suitable for your laser cutter.
Q: Why should I consider custom laser cut MDF for my projects?
A: Custom laser cut MDF allows you to create precise and intricate designs that might be challenging to achieve with traditional cutting methods. This is particularly useful for creating detailed parts and components for various applications.
Q: Are there any limitations when using a laser engraver on MDF?
A: One limitation is that MDF cannot be easily bent or shaped after cutting. Additionally, MDF produces sawdust and smoke during the cutting process, so ensure proper ventilation and safety measures are in place.
Q: What safety precautions should I take when using a laser to cut MDF?
A: When using a laser to cut MDF, always wear protective gear, ensure proper ventilation, and regularly clean the laser machine to avoid any build-up of sawdust. Also, keep a fire extinguisher nearby as MDF fiberboard can be flammable.
Q: Can I use a laser to cut other materials in addition to MDF?
A: Yes, a laser machine can cut a variety of materials including wood board, acrylic, and certain types of plastics. Always check the material compatibility with your specific laser engraver to ensure safety and efficacy.