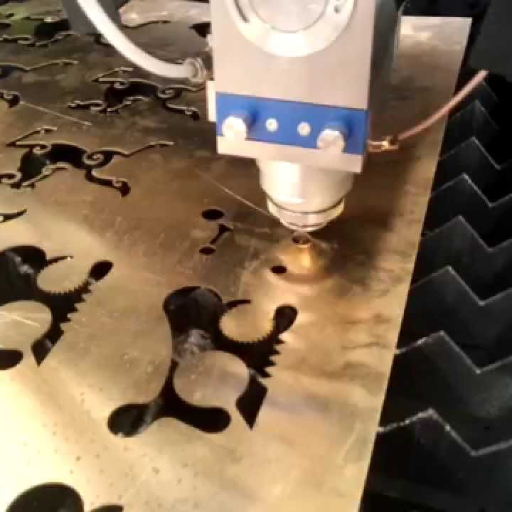
At the forefront of advanced manufacturing technology, laser cutting is unrivalled for its precision and flexibility in producing intricate designs and parts. In this area, brass has emerged as a highly favored material for different applications such as delicate jewelry items or complicated mechanical components due to its unique combination of strength, malleability, and aesthetic appeal. This is a comprehensive guide that aims to demystify brass laser cutting by examining its merits, technical considerations, and what it can do for designers and engineers. In the upcoming sections, we are going to delve deep into the inner workings of laser cutting technology including its methodologies, best practices as well as how it can be applied efficiently to turn brass into refined products. Whether you are an expert wishing to hone your skills or perhaps an inexperienced enthusiast keen about exploring the possibilities of laser cut brass; this manual will provide you with all the necessary tips and insights required to unlock limitless opportunities inherent within these two dynamic processes.
Why Choose Laser Cut Brass for Your Projects?
Advantages of Laser Cutting Brass
Laser cut brass is outstanding in industrial and creative projects for a number of significant reasons. Firstly, there is no better accuracy that can be achieved using laser cutting technology. This technique allows for complex patterns and sharp clean cuts that cannot be compared to the traditional way of doing it thus ensuring fit between components during assembly process. Secondly, one important advantage of laser cutting is reduced material wastage which enhances efficiency in cost and environmental sustainability. It also offers great flexibility as regards intricate designs or shapes that might otherwise have been difficult or impossible to create at all. Furthermore, the fastness and effectiveness with which laser cuttings work ultimately minimizes the time taken to produce the items thereby enhancing quick turnarounds on respective projects. From what I have seen, choosing laser cut brass not only increases the quality of your end product but also simplifies manufacturing process hence making it better than many other materials used for various purposes
Comparing Brass to Other Metals in Laser Cutting
In the context of laser cutting, there are several key parameters that need to be considered when comparing brass to other metals for suitability in different projects. I will break them down.
Reflectivity
Firstly and most urgently, brass is typically more reflective than metals like aluminium which makes it safe and effective to cut with lasers. The high reflectivity may reflect the beam of light back thus damaging the machine itself. Brass contains all the important factors needed for a better cutting experience.
Thermal Conductivity
Brass also has moderate thermal conductivity levels. This is crucial because very highly thermally conductive metals like copper can lose heat quickly which makes them difficult to cut as they would require lasers with higher power ratings. Brass lies in between, taking in and transmitting heat effectively but not using excessive amounts of energy to do so.
Material Thickness
Thus excelent flexibility allows brass to be cut at various thicknesses making it fine for different applications. By way of illustration, even though it cannot handle extremely thick dimensions as steel does; it performs well over a wide range that caters for most project requirements, which is a significant advantage providing capability for both fine/ detailed work and robust parts.
Cut Quality and Speed
Laser-cut brass tends to have higher quality cuts with sharp edges and minimal burring on average. As a result, this kind of precision reduces the necessity for extra finishing steps hence saving time and money spent on additional processing. Moreover, largely due to reduced post-processing needs, laser cutting brass is relatively faster compared with many other metals. In tight production schedules or productivity improvements we need speed that can only be achieved through efficiency.
Cost
On the financial side, brass offers a competitive cost option against precious or other exotic metals balancing performance and price effectively. Comparatively speaking it may be costly as opposed materials like mild steel but its quality benefits utilities’ usefulness often outweighs this expense when considering numerous applications.
To sum up, brass stands out as the best option for many applications because of its optimal blend of reflectivity, thermal conductivity, versatility in thicknesses, excellent cut quality and speed as well as cost-effectiveness. It must be emphasized that while considering metal for laser cutting, these factors should be kept in mind with regard to one’s specific project requirements.
Reflective Nature of Brass in Laser Cutting
In laser cutting operations, the reflective nature of brass poses distinct challenges and considerations. This high reflecting metal can cause the laser beam to bounce back towards the laser source, resulting in damage on the cutting equipment as well as precision problems. To alleviate these troubles, pulse lasers and specialized optics are often used with laser machines for cutting. It means that instead of reflecting back, the laser cuts through efficiently without any danger of reflection back to its direction. In other words; knowledge about how brass reflects light is paramount for achieving excellent cutting results and protecting machinery.
How Does Laser Cutting Work with Brass?
Roles of Fiber and CO2 Lasers in the Cutting of Brass
Fiber lasers and CO2 lasers are both vital to cutting brass, but they accomplish different parts of this difficult process. Shorter-wavelength fiber lasers are especially efficient at cutting brass, being very precise and rapid. This kind of laser passes through brass more effectively, which leads to cleaner cuts and less thermal damage around it. In contrast, CO2 lasers have a longer wavelength and are conventionally designed for diverse materials. However, in terms of cutting brass, CO2 lasers can require increased power as well as slower cutting speeds in order to achieve the same levels of accuracy and cut quality that fiber lasers would provide. Although advanced CO2 laseres which use beam-modifying technology exist that can overcome these challenges, generally speaking fiber lasers tend to be preferred because they perform well when it comes to efficiency while cutting brass sheets especially at thinner gauges.
Laser Parameters for Cutting Brass Effectively
To laser-cut brass effectively, a few underlying parameters need to be adjusted very minutely. These fine-tunings help to ensure that the laser beam passes through the brass material without causing any damage either on the material or on the cutting device itself. The main parameters considered are highlighted below.
- Laser Power: Arguably, this is the most important factor with regard to laser cutting of brass. To penetrate through its shells, brass requires a high power laser. However, higher power levels usually means that thick sheets can be cut into it. But finding a good balance is crucial for a stronger melting and possible damage caused by too much energy.
- Cutting Speed: Quality of cut as well as productivity in the process depend on how fast or slow laser moves across brass. In cases where there is faster cutting speed, production rates might increase but at expense of either clean cuts or accuracy of these cuts in some cases while lower rates may enhance precision but lose out on efficiency.
- Pulse Frequency: When using pulsing lasers, their pulse rate highly influences how effective they become when used for cutting out brass. Higher frequencies will result in smoother cuts because less heat gets dissipated from the laser onto the work piece reducing chances of thermal damages.
- Focus Point of the Laser: Careful attention has to be paid towards positioning the focus point properly based upon thickness of brass sheet being processed. A misdirected beam produces an imperfect cut either too shallow or leaving excessive burn marks around edges.
- Gas Pressure and Type: The choice of assisting gas such as nitrogen or oxygen significantly influences brass-cutting process – nitrogen purges provide burn-free cuts whereas oxygen enables more efficient combustion through materials but also promotes oxidation at cut edges.
Knowing and adjusting these factors is essential for those wishing to achieve optimum results in bi-metal machining by lasers. This hinges on balancing power with speed; frequency in choosing focal-point along with gas application so that specific requirements corresponding to each particular brass component being cut can be met by the user. By making slight modifications to any one of these parameters, technicians are able to achieve sharp clean cuts that meet their very specific wishes.
Strategies for Tackling the Challenges of Laser Cutting Reflective Metals
Brass, aluminum, and copper are among the reflective metals that present difficulties in laser cutting because they have a high reflectivity index and also very good thermal conductivity. In this regard, it is important to approach these challenges from various angles based on my personal experience. First of all, one has to select an appropriate laser beam with wavelength; for example, fiber lasers are more effective in reflective metals than CO2 lasers because they have shorter wavelength that lowers reflection and increase absorption by the metal. Alternatively, using continuous wave pulse mode rather than continuous wave helps mitigate heat accumulation hence reducing chances of warping as well as achieving finer cut curve. On top of that another method involves having higher power setting so that penetration into metal can be done quickly at first thereby minimizing chances of reflection which can damage the laser system. Finally, assist gases such as nitrogen gas can be used which leads to less oxidation and may help push molten material out of cutting channel cleaning up well the cut path. With such thoughtful application of each strategy not only enhance quality but also improve efficiency in cutting reflective metals among other knowledge about limits and possibilities connected with usage or laser tech.
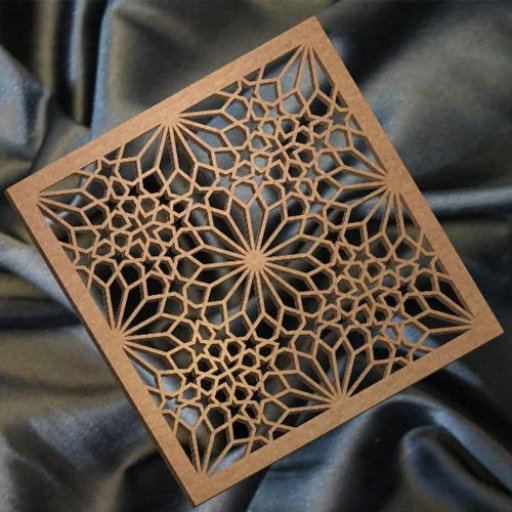
Exploring the Applications of Laser-Cut Brass Parts
Decorative Uses of Laser-Cut Brass
Not only is laser-cutting brass used in industry, but the decoration and art sectors find it significantly important. The ability of a laser machine to cut complex designs, patterns and words on brass makes it an essential tool in the production of beautiful decorative elements. Here are some popular uses for laser-cut brass:
- Art Installations and Sculptures: Laser cut brass has become increasingly popular with artists who want to create intricate sculptures or large-scale installations. Detailed cutting lets artists create multi-layered, complex works which glitter in light offering dynamic, shifting shadows.
- Interior Design Elements: Brass can be lased to form panels for interior design as well as other luxury accents that are meant to uniquely fit into spaces. There are ideal aspects such as room dividers, wall decorations or customized lightings that add elegance and warmth in any set up.
- Jewelry and Fashion Accessories: Delicate jewelry pieces like earrings can be created using the precision of laser cutting while fashion accessories have also benefited from this innovation. From this perspective designers can also make unique patterns not achievable through old school ways of metal working.
- Furniture Accents: Pieces of wooden furniture might have brass insets or metal furniture might have decorative coverings made with lasers. This gives the furniture a more expensive custom-made touch thus raising its aesthetic value.
- Signage and Branding: Employers seeking high-end branding materials may choose to use engraved signs on brass which is done by laser technology. Brass signage adds sophistication and resilience whether it is needed inside or outside an office block.
Each application is an example of how laser cutting produces clean, precise results that look good too. Combining the warm color of the brass with detailed design work carried out using a laser opens up new worlds for decorators everywhere.
Industrial Applications for Laser-Cut Brass Components
Highly valued in many industrial sectors, laser-cut brass components are esteemed for their precision, versatility and durability. The following are some of the key industrial applications highlighting how wide these components can be used.
- Electronics and Electrical Components: Its excellent conductivity makes brass suitable for use in electrical connectors, terminals and switches. The laser cutting allows the production of highly detailed components that fit into very close tolerances needed for electronics.
- Automotive Industry: Laser-cut brass parts are utilized in automotive manufacturing to make complex features like radiator fins, electrical connectors and luxury car decorations. Precise cutting helps ensure that it fits into modern cars complicated systems well as ensuring its compatibility.
- Aerospace and Aviation: Light weight high-strength materials are the most demanded in the aerospace industry. Laser cut brass is used on parts requiring both precision tolerances and durability such as; control panels, aircraft interior decorative inlays among others including connectors.
- Plumbing and HVAC Systems: One of the advantages of using brass for plumbing fixtures and HVAC systems is its corrosion resistance. By employing cutting through lasers, various shapes as well as sizes of components such as valves, fittings and even ornamental grilles can be made hence ensuring that they function well while retaining some aesthetic appeal at times.
- Custom Machinery and Equipment: Industrial sectors calling for custom or bespoke machines rely on laser-cutting techniques to manufacture intricate designs hence making specialized pieces with different functionalities from those meant for other machines. For specific operational requirements, this technique permits different mechanical apparatuses to be made up with unique gears, embellishments among others.
- Prototyping and Model Making: Laser cutting’s accuracy makes it ideal for prototyping almost all industrial applications’ components. It is a preferred material when making functional prototypes or models during design since it combines aesthetics with machinability thereby allowing engineers/designers to test their designs easily.
Brass by itself has unique properties which when combined with the precision offered by laser cutting result into practical solutions that are aesthetically appealing in a range of industries from electronics to aerospace. The ability to make highly detailed and long-lasting parts makes laser-cut brass invaluable to industrial manufacturing and design.
Optimizing the Laser Cutting Process for Brass
Choosing the Right Laser Cutter for Brass
Several factors must be considered when choosing a laser cutter for brass to ensure that the final products have the highest precision or quality. Firstly, power is an important factor in selecting a laser. Brass requires a powerful laser to cut through it without discoloring or causing excessive heat damage. A fiber laser cutter is commonly recommended for metal cutting especially on metals such as brass due to its efficiency in producing sharp and smooth edges when cutting metal materials.
Secondly, the thickness of the brass being cut determines what kind of laser cutter should be used. For thicker pieces of brass, higher power lasers provide fluid cuts that do not compromise speed or quality. On the other hand, intricate works are required for delicate designs made from fine brass and any slight warping could destroy them.
Lastly, software compatibility and ease of use are fundamental aspects to consider while buying a laser cutter. Complex software allows for greater detail in designing and ability to calculate various cutting options which are important in some industries such as aerospace industry where special orders of very detailed machine parts can be requested by clients. From my experience with these machines, it is advisable to invest heavily on high-end brands that come with strong software support because they will last longer creating accurate and high-quality components out of brass.
Molten Metal Prevention in Brass Laser Cut Parts
Preventing molten metal related errors during laser cutting process includes maintaining the integrity and quality of finished products as well as improving safety during production. Some strategies I have found useful include: optimization gas flow rates must be done accurately first before proceeding with other considerations. Precise mixture and flow of assist gases like nitrogen or mixtures of nitrogen-oxygen can help cool down the cut path thus preventing molten material throwing off track known as molten metal errors. Another one is having an accurately calibrated focal point above metal surfaces (for best cut quality). Finally, keeping consistent power-setting levels based on thicknesses/types of brass leads to uniform cutting conditions. These guidelines when followed along with regular maintenance of the laser cutter as per the manufacturer’s guidelines dramatically reduce the likelihood of molten metal errors and ensure that quality brass parts are made.
Laser Wavelengths Selection and Cutting Gases
The utilization of right wavelength in laser and choosing cutting gas is essential for effective laser cutting procedures especially on materials like brass. I would argue that an appropriate laser wavelength is the bedrock; different materials absorb wavelengths differently, whereas for a material such as brass, fiber lasers are more likely to offer superior absorption rates compared to CO2 lasers, permitting cleaner cuts and less thermal damage. Similarly, determination of cutting gases can matter considerably towards achieving better cuts. For instance, oxidation free edges may be possible using nitrogen for components like welding or painting while oxygen could lead to faster cut speeds but also oxides. To sum up, understanding this correlation between laser wavelength and choice of cutting gas is crucial to optimization of cutting processes, obtaining high quality finishes in addition to improving overall efficiency during production of these items from brass.
Laser Engraving vs. Laser Cutting on Brass: What You Need to Know
Understanding the Differences between Engraving and Cutting Brass with Lasers
In order to achieve precise outcomes based on your project’s requirements, it is important to have a clear understanding of the difference between laser engraving and laser cutting when working with brass. These two processes are similar in that they both exploit the power of lasers to control brass; nevertheless, they differ significantly regarding their goals and their results.
Laser Cutting is mostly focused on dividing, or separating brass materials into distinct shapes or parts using lasers directed heat, which melts the metal along the desired cut line. This technique is highly precise and it enables complex designs and clean edges, which are necessary for intricate components and detailed craftsmanship.
On the other hand, laser engraving does not cut through the brass. Instead it vaporizes a thin layer off of its surface in a controlled way to create designs, text or markings directly on the brass. It is used for serial numbers, decorative patterns or logos that can be added to brass items with fine detail and permanence.
Here are several key parameters that affect how well we can engrave or cut through a material such as brass using lasers:
- Laser Power: More power is better suited for thicker sheets of brass while less power works best for engraving so as not to damage unnecessarily metals.
- Speed: Both cutting and engraving depend on how fast the laser moves over the metal. Fast speeds result in cleaner cuts but may not leave deep enough etchings or be as clear.
- Focus: The precision of focusing the laser determines how finely either cutting or engraving will be done. Wrong focus causes blurred edges while cutting or unclear engravings.
- Frequency (Pulse Rate): By varying pulse rates for an engraver one can determine just how deep incisions should go; in case for cutter – this factor affects quality/regularity of cut edge edges.
- Gas Assist: In cutting there could use gases like nitrogen and oxygen which would drastically improve quality in terms of reduced oxidation conditions, speed of the cut.
Through comprehending and optimizing these parameters, you will be able to settle on the most suitable laser process for your brass projects which in turn leads to results that meet or surpass your expectations. This means understanding these facets is essential for high quality efficient production, whether it’s achieving accuracy through laser cutting or creating detailed designs in brass via laser engraving.
Can You Engrave and Cut Brass in One Go?
Absolutely, yes, it is really possible to engrave and cut the brass in one-step method that can be very efficient for various projects. From my own experience, I have had the opportunity to observe how technology has made this much easier with lasers. The above mentioned parameters such as laser power, speed, focus, pulse rate together with gas assist can be adjusted so as to handle both tasks together. Precise settings are required; for instance lower energy levels for engraving then raise when cutting through brass until we get the desired job accomplished. It is not only a time saver but also it ensures that there is uniformity of work and quality of output at all times. However, one must remember that successful results depend on understanding the materials of brass and proper utilization of laser tools throughout the process towards achieving what is intended at once.
From Idea to Reality: Ordering Custom Laser Cut Brass Online
How to Prepare Your Design for Brass Laser Cutting Services
To get your design ready for brass laser cutting services, there is a meticulous process, which ensures that your ideas are transformed into the final product in an accurate and efficient manner. The first thing to do is use vector design software like Adobe Illustrator, AutoCAD or Inkscape that have precise paths for lasers to follow while cutting. Scale your design to the size of brass you want cut as it is and remove any intricate details that could complicate the cut or weaken the material’s strength. Minimize line thicknesses until they are thin enough for the service, which might be something like 0.001 inches (0.0254 mm) representing cuts on paper. Moreover, everything else must be converted to outlines and then choose a file format with which the machine will easily understand what it should do; this means DXF or SVG format in most cases.
Before submitting ensure that you check your own work for errors or any forgotten details because it can save a lot of resources and time. Finally, consult with your chosen cutting service about specific guidelines if any and other requirements so as to eliminate more complexities making it easier for them to handle your custom project brass.
Reliable Laser Cut Brass Service Providers
It’s necessary to find reliable service providers for laser cut brass in order to achieve high-quality results. From my experience these include: technical competence levels of the provider; how much experience they’ve got in handling similar projects; lastly but not least, customer service standards of their staffs are also very important.
Firstly, ascertain whether such kind of provider has state-of-the-art laser cutters capable of accurately producing intricacies from a piece of brass henceforth asking if they have professionals who can best handle such kinds of materials without spoiling them . The conditions under which past projects were accomplished help explain their prowess. Secondly, one must consider how responsive and clear they communicate especially during enquiries about their operations including some material handling and design suggestions. Lastly, look for any feedbacks given by past clients about the services they received from this provider. This is why industry experts may have some references.
Your choice of a provider based on these factors will significantly determine your success in laser-cutting brass.
Tips for Affordable and Quality Laser Cutting Brass Services
For sure, striking a balance between finding someone who can give you affordable services of laser cutting brass that are of high quality is not easy. In order to achieve that here are the tips I follow to ensure my projects are cost-effective and with high quality:
- Material Sourcing: One of my initial steps is to source for own brass material if available. Different suppliers have different prices and by comparing them or buying in bulk, one can make considerable savings. However, it’s crucial to ensure that the material meets the specifications required for laser cutting.
- Design Optimization: It might also save you a lot of money when you optimize your design. Closely nesting parts onto a sheet so as to reduce wastage is among the things I do. Alternatively, simple designs that cut time significantly decrease costs but don’t compromise on quality.
- Choosing the Right Provider: This cannot be overstated. Not all service providers will offer the same level of services. Thus I usually go for those who specialize in brass or have done extensive work on this. They tend to be more efficient and knowledgeable regarding their field which means their rates will be reasonable while they still provide me with what I require.
- Long-Term Relationships: Establishing a long-term relationship with your service provider may result in better prices and service delivery. For example, some providers give discounts to loyal customers.
- Batch Processing: If possible, I try to group my projects or wait until I have enough pieces to cut in a single run. Most providers offer better rates for larger batches due to the reduced setup time and material handling efficiencies.
- Communication: Clear and open communication with your provider about your project’s budget and quality requirements can lead to suggestions from their side on how to optimize costs further.
- Testing and Prototyping: Before committing to a full run, I suggest doing a smaller test or prototype. This enables early detection of possible problems that may prove costly if left unattended.
Considering these points has enabled me to always balance between the cost and quality of my brass laser cut projects.
Reference sources
1. Online Article: “Precision Laser Cutting of Brass: Techniques and Best Practices” – Metalworking World Magazine
- Source: Metalworking World Magazine
- Summary/Annotation: This article from Metalworking World Magazine offers an in-depth overview of the techniques and best practices for precision laser cutting of brass. It covers essential aspects such as the importance of selecting the right laser equipment, optimal settings for different thicknesses of brass, and troubleshooting common issues like burr formation and heat-affected zones. The article also discusses the benefits of laser cutting for brass, including high precision, minimal material wastage, and intricate design capabilities. Metalworking World Magazine is a reputable source in the metalworking industry, ensuring the content is accurate and practical. This source is valuable for readers seeking detailed information on achieving precision and quality in laser-cut brass projects.
2. Academic Journal: “Influence of Laser Parameters on the Quality of Brass Cutting” – Optics and Laser Technology
- Source: Optics and Laser Technology
- Summary/Annotation: This peer-reviewed paper published in Optics and Laser Technology examines the influence of various laser parameters on the quality of brass cutting. The study includes experimental data on the effects of laser power, cutting speed, and assist gases on cut quality, edge smoothness, and thermal effects. It provides a thorough analysis of how these parameters can be optimized to enhance the precision and efficiency of the laser cutting process for brass. As an academic journal, this source offers high credibility and technical depth, making it essential for readers interested in a rigorous scientific understanding of the factors affecting laser-cut brass quality.
3. Manufacturer Website: “Laser Cutting Brass: Capabilities and Applications” – Epilog Laser
- Source: Epilog Laser
- Summary/Annotation: Epilog Laser’s website provides comprehensive information about their laser cutting capabilities for brass, including technical specifications, equipment used, and real-world applications. The site features case studies demonstrating the precision and versatility of laser-cut brass in various industries, such as electronics, automotive, and decorative arts. It also offers guidelines for preparing brass for laser cutting, tips for achieving clean cuts, and insights into optimizing the cutting process for different brass grades. Epilog Laser is a leading manufacturer of laser cutting systems, ensuring authoritative and practical insights. This source is crucial for professionals seeking reliable information on the capabilities and practical applications of laser-cut brass.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A: Which is the optimum laser for a brass sheet?
Fibre lasers are thought to be the best type when it comes to cutting of brass sheets because they have a high power output and can efficiently cut metals. It is important to note that, unlike CO2 lasers, fiber lasers have shorter wavelengths that make them more precise and effective in terms of brass cutting.
Q: Can copper and brass alloys be effectively cut using laser beam technology?
A: Do we need laser beam technology to do much with copper and brass alloys? Yes, of course, this works quite well by employing a high-power fiber laser. These materials can be laser cut because the fiber laser’s short wavelength is less reflected and more absorbed by the materials, leading to better cutting efficiency.
Q: What limitations are there associated with the use of laser cutting on copper and brass?
A: There may occur some challenges associated with these materials because they have very high reflectivity and thermal conductivity making it difficult for optics to work as required by minimizing efficiency. To address these difficulties, powerful fibre lasers use beams having enough energy for quickly melting and removing solid metal which helps reduce exposure times of the material to light while also decreasing reflections.
Q: How does brass sheet thickness affect laser cutting?
A: You will find that practically all aspects affecting the quality of any given article are directly related to its thickness. The process of laser cutting depends on this factor particularly involving thick brass as thicker sections require even higher amounts of energy from a carbon dioxide laser needed for melting or vaporizing them. Fiber lasers having high power rating can pierce through thicker sheets made out of bronze but this may call for slower speeds during operation so as not leave ragged edges behind which would then necessitate several passes before attaining a clean finish.
Q: Is it possible to use CNC laser cutters for brass cutting as well as engraving?
A: Yes, CNC laser cutters with fiber lasers can be used for both cutting and engraving of brass. This provides a wide range of applications on brass and copper due to the versatility of CNC control which allows precise adjustments necessary for the varying requirements of cutting and engraving.
Q: How does the amount of laser power relate to brass and copper cutting?
A:Laser power is an extremely important factor in their cutting. These substances can be more effectively melted through with higher intensity due to increased laser power. For efficient cutting, such materials, because of their high reflectivity as well as thermal conductivity aspects, may require highly powered lasers that can rapidly push the beam into its molten state.
Q: Are there any particular techniques for improving the quality while applying fiber laser on bronze sheets?
A: Yes, gas flow optimization, increasing power output and proper beam focusing can help improve the quality of cuts when using a fiber laser on bronze sheets. It is also possible to achieve cleaner cuts by managing heat input through pulse settings so as not to cause warpage on the material.
Q: What effect does beam wavelength have on a fibe5r las8er’s ability to cut brass or copper?
A:The shorter wavelength means that fiber lasers have more focused beams than CO2 lasers which are better absorbed by such metals instead of reflecting off them. As a result, more efficient cutting action takes place since greater absorption occurs making fiber lasers capable machines for reflective materials like copper and brass.