What is Laser Engraving on Metal?
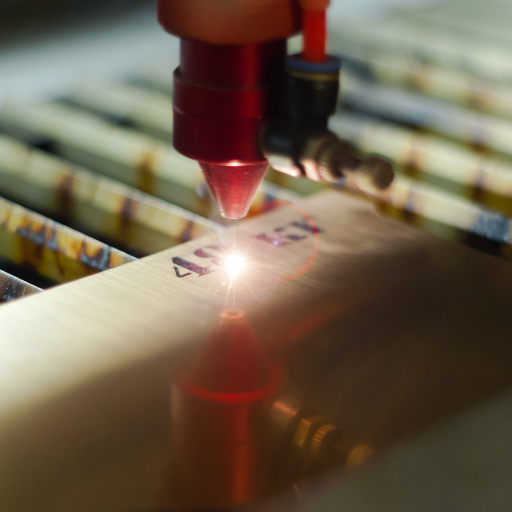

Understanding the Laser Engraving Process
The process of engraving with a laser begins with the design or text being created using specialized software, which is then transferred to the engraving machine. The machine is able to produce a concentrated light beam by means of a laser source such as Fiber or CO2. This beam of light when it is focused is directed on the metallic surface by utilizing either lenses or mirrors. When moving over metal surface, the laser generates a lot of heat resulting in localized melting, oxidation, vaporization that leads to permanent mark. On metal surfaces this allows for precise replication of detailed and intricate designs.
Factors that play a part in the engraving process include; type of metal used, power settings for lasers, and also its speed and focus. Laser reacts differently depending on the metals; for example compared with aluminum softer metals like stainless steel often demands high power settings. The quality and depth of engravings may require these settings to be adjusted accordingly.
Moreover there are precautions for safe use of machines used for laser engraving. Protection goggles should be worn during the procedure so as not to get intense light emitted from it while proper ventilation is equally important because some harmful fumes may be released during the process. Laser engraving can yield highly accurate and good quality prints that can apply in various applications ranging from industrial uses through artistic endeavors when done correctly.
Differences Between Laser Engraving and Laser Etching
The Benefits of Laser Engraving on Metal
The various advantages of laser engraving on metal make it an ideal choice for different purposes. To start with, laser engraving provides unmatchable precision and accuracy which allows creating complex patterns and tiny elements that are hard to be done by traditional methods of engraving. Moreover, this aspect of it can be useful in artistic purposes as well as industrial applications that require detailed specifications.
Secondly, the technology does not use a physical medium to touch the object being marked; therefore, there is no abrasion. As a result, there is minimal wastage in terms of material and the metal remains intact making it suitable for fragile or high-valued objects.
It also has the advantage of permanency. Laser engravings are incredibly resistant to damage caused by constant use, and they are capable of surviving all kinds weather extremes. These qualities make them perfect for marking parts or tools that need long-term labels or brand names.
Also, this technology works on many types of metals like aluminum, stainless steel or brass among others. Thus, any business in any industry can opt for laser engraving depending on its individual requirements.
Lastly, it is highly efficient and can be automated leading to reduced operational expenses as well as quick production processes. Consequently companies enjoy increased productivity and scalability whether the order calls for custom one-off pieces or large-scale manufacturing runs.”
What Types of Metals Can Be Laser Engraved?
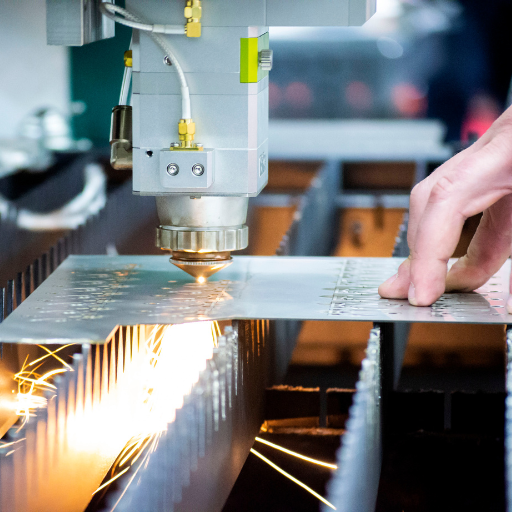

Laser engraving is a versatile option for different applications because it can be used with a variety of metals. Some of the common metals that can be laser engraved are:
- Stainless Steel: It is durable and non-corrosive, making it ideal for industrial and medical equipments
- Aluminum: Light in weight and may serve various purposes such as Aerospace, Automotive and Consumer Electronics.
- Brass: It is known for its beauty and thus often used in musical instruments or decorations.
- Copper: It has good conductance properties both electrically and thermally making it fit for electrical components.
- Titanium: Lightweight yet robust enough to withstand high force; this metal is integral part of airplanes, dental implants and most sporting gears’ manufacture.
- Gold and Silver: They are used commonly as precious materials in the manufacture of jewelry or other high quality items.
Engraving on Stainless Steel
While talking of etching stainless steel, the operation exploits laser technique’s precision and effectiveness to make fine marks that remain permanent. These are the things to take into account:
- Durability and Precision: Stainless steel laser engraving means that inscribed lines last longer and cannot be easily worn off. This makes it a good option for cases where one wants long lasting plain inscriptions.
- Applications: Stainless steel is widely used in various industries such as medical equipment, kitchenware, automotive parts, and industrial machinery due to its resistance to corrosion and high durability. Laser engraving works best in cases where there is need for complex designs or detailed information like serial numbers and barcodes.
- No Contact Process: One of the major benefits of using laser engraving is that it does not involve making contacts with materials; hence there no need for touching any element. This minimizes or eliminates contamination risks while upholding the integrity of stainless steel surfaces.
- Speed and Efficiency: Laser engraving is fast enough for automation and can be made cost-effective whether completing small or large production runs. It guarantees consistent quality as well as replicability of markings- crucial in industry.
Marking Different Metal Surfaces
Marking various metal surfaces with laser technology requires the adjustment of several parameters to the optimum. Here are the main points which are derived from top sources:
- Laser Compatibility: Different metals react differently when it comes to laser engraving. For example, aluminum, brass, copper and titanium each have unique thermal properties that influence the engraving process. By adjusting laser parameters appropriately, you will achieve accurate and neat marking on different metals.
- Adjustable Parameters: The laser power, speed, focus distance and wavelength should be adjusted depending on the metal being engraved. These changes help in achieving necessary depth and clarity of markings whether for simple inscriptions or complex designs.
- Surface Preparation: The best results for laser engraving are obtained on clean and well prepared metallic surfaces. In order to clear up any oxide formation, coat or contaminants in the metal surface so that laser interaction is direct with base material leaving clear-cut and long lasting marks.
Using Lasers on Coated Metal
Laser engraving coated surfaces of metals presents distinctive challenges and possibilities. Anodized aluminum, painted steel and other such things as protective or pensive treatments are some of the materials that are usually used in coating metals.
- Layer Interaction: The laser must take off the covering without interfering with the metal support’s structure. This necessitates close control of various laser specifications among which include power, speed and frequency. Changing these parameters allows the laser to pass through the layer without going too deep into the metal, which maintains its composition.
- Optimal Settings: Coating types differ from each other in their response towards a given laser application technique. Correct wavelength use and proper focus adjustment is vital. For instance, anodized aluminium generally needs less power than painted steel due to having a thinner cover.
- Application Versatility: Laser engraving on coated metals finds wide use across multiple industries including aerospace and consumer electronics for high contrast and long-lasting marks. Laser precision enables intricate patterns, textual information or barcodes to be replicated accurately on these surfaces.
Which Laser Types are Best for Engraving Metal?

Using a CO2 Laser for Metal Engraving
These wavelengths are absorbed by wood, glass and plastics for this reason they are used in engraving non-metallic materials such as these. When it comes to engraving metals though, CO2 lasers can also be good but usually there is something extra that needs to be done so that they can give high-quality results. Another way of doing that is by applying a special coating or marking spray that interacts with the laser making it possible for it to leave a mark on the metallic surface. This process is often adapted for anodized aluminium, stainless steel and other coated metals which produce excellent contrast and durability.
Nonetheless, when it comes to metal engraving, CO2 lasers tend to require more energy and longer process times compared with fiber lasers. For desired depth and clarity of the etching, the settings on the laser must be optimized including power levels, speed and frequency. Further improving this efficiency of the laser or general quality of engravings may come through things like incorporating pass-throughs or pre-treating metal surface. These parameters should be carefully selected and adjusted in order to utilize CO2 lasers effectively for accurate and long lasting metal engravings.
Advantages of Fiber Lasers for Metal Engraving
Metal engraving using fiber lasers has numerous benefits. They have got a wavelength that is far shorter at typically 1.06 micrometers compared to CO2 Lasers and this makes it possible for metals to absorb them better, a fact that leads to improved efficiency and precision during engraving. Moreover, they are acknowledged for their high beam quality which allows for finer and more details in engravings. On top of this, they generally require less power so as to deliver the same results thus being energy efficient.
Moreover, processing times can be reduced greatly by the faster processing speeds that they have. They have also less maintenance due to their solid-state design hence longer operational life spans and lower operating cost over time. In addition, they can work on a range of metal types such as stainless steel, aluminum, brass as well as precious ones like gold and silver. Fiber lasers represent the ideal choice when it comes to manufacturing long-lasting metal engravings of good quality for many industrial sectors including.
Deciding Between CO2 and Diode Lasers
Considering the specific needs of your application is vital when deciding between CO2 and diode lasers for metal engraving. The longer wavelengths (10.6µm) in CO2 lasers make them useful on many nonmetallic materials while they can be used on metals with special coatings or additives. They are versatile, cost-effective, and suitable for various materials such as wood, acrylic, leather.
On the other hand, diode lasers are smaller and usually used in engraving more delicate materials or metals for detailed work. They have a reputation for working faster and being simpler to use than CO2 lasers often requiring less maintenance. The precision of diode lasers is very high; hence they may not be as powerful as CO2 lasers while cutting through thicker, tougher materials.
The decision whether to choose between CO2 and Diode laser will depend on material type, precision required, efficiency and maintenance requirements. For versatility at large costs, CO2 laser is a solid choice. Nonetheless, if you need more targeting, exceptional performance tasks should consider diode applications.
How to Use a Laser Engraver for Metal Engraving
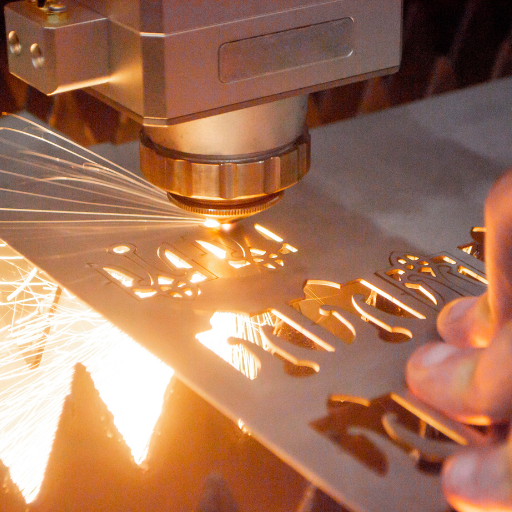
Metal engraving using a laser engraver is performed through various processes to ensure accuracy and safety.
- Prepare Your Design: You should begin by either designing or selecting the one you want to be engraved. Utilize design software that works with your laser engraver to finalize the layout as well as adjust for issues like image size and resolution.
- Choose the Right Settings: You will modify the laser power, speed, and frequency in relation to the desired depth of engraving as well as the type of metal being used. For best settings, make reference from guide books of manufacturers.
- Prepare the Metal Surface: Clean metals surface thoroughly until dust, oil or other debris are removed. This would guarantee an even and crystal-clear outcome after engraving.
- Load the Metal into the Engraver: Place your metallic object on top of this equipment. It should be placed correctly and firmly since it might shift during processing.
- Run a Test Engraving: In case you are not sure about that, do small inconspicuous area test or work on a sample piece made from same material. Confirming these settings helps you make amends where necessary.
- Engrave the Metal: Now do it fully upon getting satisfaction from preliminary results. Keep monitoring it for a consistent quality throughout till any emerging threats are addressed instantly.
- Post-Engraving Finishing: Once completed with engraving process, clean away debris present at the engraved section while buffing may also be done depending on project specification.
Setting Up Your Laser Engraving Machine
These are the essential steps that should be followed when setting up your laser engraving machine:
- Unbox and Inspect: Loosely unpack your gadget and examine all the parts to ensure they are not damaged during shipping. Make sure every part listed in the user manual is there.
- Assemble the Machine: Go by the maker’s instructions to piece together this device. This commonly involves sticking on a laser module, attaching control boards, and reinforcing the frame.
- Install Software and Drivers: Get manufacturer-issued software as well as drivers. These will help you create and manage some of your designs for engraving purposes.
- Connect the Machine to a Computer: Link your machine with a computer using USB or another specified manner. The software should recognize it.
- Calibrate the Machine: Adjusting bed levels, aligning the laser module, setting focal lengths among others, are some of how you can get correct calibration of a laser hence accurate engraving results.
- Test the Laser: Try doing an engraving test on any material before embarking on work to make sure that everything is right including set up parameters.
- Safety Check: Ensure there is enough ventilation for air circulation while someone is working with this machine; also make sure that everyone has goggles from any possible mishaps as well as knowing where emergency switches are.
Laser Power and Speed Settings for Metal
Precision is vital in manipulating the laser power and adjusting speed, to ensure one gets maximum results when working on metal. Different metals and types of lasers have different settings recommended for them. The following are general rules:
- Stainless Steel:
- Power: 20W (or higher)
- Speed: 200-300 mm/s
- Aluminum:
- Power: 15-20W (or higher)
- Speed: 100-200 mm/s
- Brass:
- Power: 20W (or higher)
- Speed: 100-200 mm/s
An engraver should start with these default or basic configurations and adjust accordingly depending on the specific nature of the material being engraved and the desired engraving depth. It is always important to refer to the user manual as well as conduct test engravings for fine-tuning settings on your machine and materials.
Laser Safety Tips
It is essential that safety measures be put in place while working with a laser engraving machine so as not to only protect individuals but also safeguard environment. These top laser safety tips include:
- Protective Eyewear: An operator must wear appropriate safety goggles capable of filtering out lasers at specified wavelengths to prevent potential eye injury from direct or reflected beams of lights.
- Ventilation: For fumes produced during engraving exercise, ensure there is sufficient movement of air within your working area; use a smoke ejector fan if possible.
- Material Safety: You should only engage safe materials that can be engraved by your particular type of laser. Some materials release toxic fumes or catch fire when engraved upon. Check their MSDSs (material safety data sheets) and manufacturer recommendations every time.
- Machine Enclosure: Make sure you run this device inside an entirely enclosed unit so that you don’t expose yourself to its light incidentally; some contain automatic switches that turn off once opened.
- Emergency Shutdown: Be conversant with it’s position as well as how it works in case something goes wrong; such knowledge will help you switch it off quickly when need arises.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your machine tidy always ensuring proper functioning especially by checking for any damaged or worn-out part and replacing them appropriately for operation safety.
What Are the Applications of Laser Engraving on Metal?
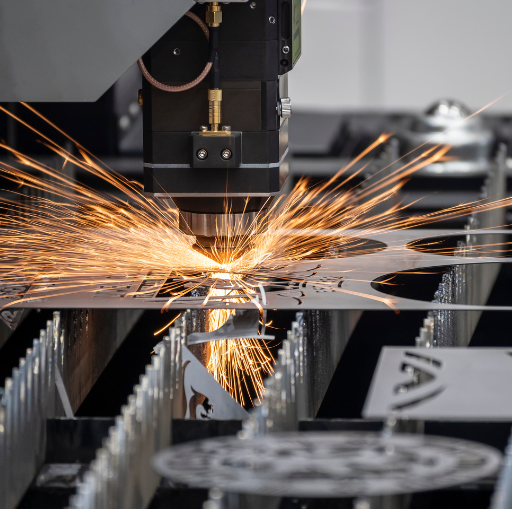

Industrial and Commercial Uses
Metal laser engraving is a common practice in industrial and commercial applications due to its precision, efficiency, and versatility. Laser engraving in industry can also be used for marking parts of the machines with serial numbers, barcodes and QR codes so that they can be traced during inventory management. This is because these two industries require permanent labels to be engraved on critical parts bearing part numbers as well as safety warnings to cater for regulatory compliance.
On the other hand, commercially it has become valuable to personalize luxury goods and jewelry through laser engraving. A good example of this would be rings, watches or bracelets having a detailed design that will attract those who want customized things. Similarly, it produces excellent brand promotional items and customized signs because it generates clear-cut engravings. From industrial traceability to commercial customization there are several reasons why metal laser engraving remains unparalleled in terms of adaptability towards diverse requirements.
Personal and Custom Engraving Projects
High-Precision Metal Marking
What Should You Consider When Choosing a Laser Engraver for Metal?

When buying a metal laser engraver, there is a lot to think about. These considerations include: Power and Wavelength – Ensure that the Laser Engraver has enough power and accurate wavelength to effectively mark your particular metal.
- Power and Wavelength: Find an engraver which provides high precision and accuracy so as to obtain detailed, accurate markings within short notice.
- Precision and Speed: Look for an engraver with high precision and speed in order to get fine, precise markings in good time.
- Compatibility with Materials: Check whether the engraver can work on different metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, or titanium.
- Software and Usability: Put into consideration the ease of use and compatibility of the software provided with the system so that it works smoothly with your existing system thus not causing any problems during operation or design integration.
- Maintenance and Durability: Choose a device that requires little maintenance yet robust enough to withstand constant usage without affecting its performance significantly.
- Safety Features: Verify if safety features are incorporated in the laser engraver that protects users from laser radiation hazards among other dangers.
With these factors in mind, you will be able to choose a reliable laser engraving machine that suits your specific needs for marking metals properly.
Evaluating the Laser System and Technology
While evaluating a laser system & technology there are basic aspects which must be considered carefully to ensure you have chosen well. First of all consider what type of laser source is being used; fiber lasers are commonly used for metal etching because they are more stable than CO2 lasers hence need less maintenance over long periods. Also check out beam quality as well as consistency since they contribute much towards clean engravings therefore systems not providing this should not be sought after instead opt those having superior beam control. Automation capabilities should also be taken into account—these include features like automatic focusing and real-time monitoring which can increase productivity and output quality considerably during manufacturing processes.
Furthermore, it is essential to look at the cooling system of a laser engraver. Efficient cooling mechanisms are important for maintaining optimal performance and extending the life of the laser especially during extended operation. Another crucial feature that should be considered is whether the device can be easily integrated with design software; this seamless compatibility ensures a smooth workflow from designing to marking. Finally, it is essential to consider manufacturers’ support services plus warrantee packages such as comprehensive warrantees offered by reputable companies and competent customer service which will give peace of mind in long term.
So, through these considerations made attentively, you will have an assurance that your laser system purchase will provide high quality and dependable performance which suits your specific engraving needs.
Determining the Right Laser Power
Finding the Best Laser Engraving Machine for Your Needs
Reference sources
-
xTool – Metal Laser Engraving: The Ultimate Guide
- This comprehensive guide explores metal laser engraving in detail, covering the types of metals suitable for laser engraving, the technology used, and best practices for achieving high-quality results.
- Source: xTool
-
Monport Laser – Choosing the Right Laser Power: A Comprehensive Guide to Engraving Metal
- Monport Laser provides an in-depth guide on determining the appropriate laser power for engraving metals, discussing various factors that affect laser engraving quality and efficiency.
- Source: Monport Laser
-
Permanent Marking – How to Laser Engrave Metal: A 5-Step Guide
- This resource offers a practical, step-by-step guide to laser engraving metal, including selecting the right materials, understanding laser settings, and ensuring proper preparation and execution for optimal results.
- Source: Permanent Marking
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is metal laser engraving?
A: Metal laser engraving is the process of using a laser engraver or laser marking machine to etch designs, texts, or patterns onto the surface of the metal. This technique uses laser light to melt or vaporize the metal, creating permanent marks.
Q: What type of laser is best for engraving metal?
A: The best type of laser for engraving metal depends on the specific metal material you are working with. Fiber lasers are generally preferred for their precision and efficiency, while CO2 lasers can also be used for certain types of metals when combined with marking sprays or pastes.
Q: Can I laser engrave metal with a CO2 laser?
A: Yes, you can laser engrave metal with a CO2 laser, but you may need to use a marking spray or paste to achieve the desired results. CO2 lasers typically require these materials to effectively engrave the surface of the metal.
Q: What safety precautions should be taken when laser engraving metal?
A: Safety precautions include wearing protective eyewear, ensuring proper ventilation to deal with fumes generated during metal engraving, and following the manufacturer’s guidelines for operating the laser engraving machine.
Q: What are some common applications of metal laser engraving?
A: Metal laser engraving can be used in a variety of applications including creating custom jewelry, marking industrial parts, producing personalized gifts, and etching metal plaques. It is widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics.
Q: How does the laser engraver interact with different metal types?
A: Different metal types react uniquely to laser engraving. For example, aluminum requires less laser energy compared to harder metals like stainless steel. The size of the engraving and the engraving speed may also need to be adjusted based on the metal material.
Q: What are the differences between laser etching, engraving, and marking?
A: Laser etching metal refers to creating shallow marks by melting the surface, laser engraving involves deeper cuts into the metal, and laser marking generally changes the color of the metal surface without removing any material. Each technique has its own specific uses and benefits.
Q: What factors should be considered when choosing a laser for metal engraving?
A: Considerations for laser engraving metal include the type of metal material being used, the desired depth and detail of the marking, the size of the engraving project, and whether you need versatility for various metal parts. The right type of laser and settings will ensure optimal results.
Q: What is laser annealing, and how is it different from engraving?
A: Laser annealing involves heating the metal without removing any material, resulting in a color change on the surface of the metal. It differs from laser engraving, which removes material from the surface. Laser annealing is often used for marking metals with a smooth, high-contrast mark.
Q: What materials or consumables are needed to laser engrave metal?
A: Depending on the type of laser and metal, you may need marking sprays or pastes, especially when using a CO2 laser to engrave metals. Additionally, proper ventilation systems and protective gear are essential for safely handling the fumes and particles generated during metal engraving.