Given its transformative nature, resin 3D printing has changed our approach to architecture and design prototyping for various industries. Contrary to conventional printing techniques that use filaments, resin printing employs liquid photopolymer resins, which are set in layers to produce intricate objects with high levels of detail. This method makes it possible to have a higher resolution or better finish and make complicated geometries that would be challenging to achieve with other methods. In this article, we will go into the basics of resin 3d printing, explain how they work mechanically, and talk about their importance in different sectors like engineering, healthcare, and art. Brace yourself for an astonishing glimpse of the world of resin 3D printing and its capacity to reshape manufacturing and design.
What is a resin 3d print, and how does it differ from other 3d printing technologies?
Image source: https://3dprintingcenter.net/
The process of a resin 3D print involves exposing liquid resin to UV light to solidify it into layers. This differs from other 3D printing techniques, such as Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), which involves using thermoplastic filaments that are then layered on top of one another. The main differentiating factors are thus in the material properties and resolutions; whereas FDM prints possess rougher surface finish and limited resolution, Resin prints have smoother finishes with better details. Moreover, resin printing allows for a more intricate design that cannot be reproduced using traditional filament-based methods. Precision and ability to make high-quality prototypes and models differentiate resin 3D printing from others.
Overview of resin 3d printing technologies
There are four main methods of 3D printing technologies for resin: stereolithography (SLA), digital light processing (DLP), multi-jet modeling (MJM), and LCD printing.
- Stereolithography (SLA): It is one of the earliest and most widely used resin printing methods. In this case, a laser beam is used to cure layers of liquid resin until it turns into a solid object. SLA is known for producing prints that have high resolution and a good surface finish.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA, DLP uses light to cure resin but has a digital light projector that flashes an entire layer once. This increases the speed of the printing process while maintaining high degrees of detail and accuracy.
- LCD Printing: This technology uses an LCD screen as a light source and cures resin layer by layer, like DLP. It is generally cheaper and can print detailed models, too, although its layer resolution may vary from printer to printer.
These technologies all have distinct advantages and uses, making them adaptable to various fields requiring precision and exquisite designs made from resins using 3D printers.
Differences between resin 3d prints and filament 3d printing
Since its inception, resin 3D printing and filament (FDM) 3D printing have differed in several areas. The first distinction is in the materials used; during resin printing, liquid photopolymer resins cure when exposed to UV light, while filament 3D printing uses thermoplastic filaments that are extruded and cooled down to produce layers. Because of this difference, print resolutions vary, with resin prints often achieving greater detail and smoother finishes than filament prints, which usually show layer lines.
Furthermore, there are differences in the processes for creating models by these two methods. Resin printers cure a whole layer simultaneously (SLA/DLP), making them faster when producing intricate components. Still, filament printers build objects one layer after another, which might be slower for more complicated designs. However, filament printers are more user-friendly and safer for beginners since the materials employed are not as dangerous as uncured resins. Finally, the demands of post-processing also differ; it is common for resin prints to require thorough cleaning and curing, while a majority of filament-made objects come out of the printer nearly complete without much finishing work.
Advantages and disadvantages of resin 3d printers over other types of 3d printers
Compared with other 3D printing systems, resin 3D printers have several advantages. The foremost is excellent print quality; they produce highly detailed and intricate models with smooth surfaces suitable for dental, jewelry, and prototyping areas. Also, their simple printing of complex geometries supports new designs that may be difficult using filament printers.
Despite the above benefits, there are some disadvantages worth considering. For instance, liquid resins require careful handling due to their potential toxicity and need for proper ventilation during printing. Moreover, resin-based printing often involves multiple processes after completion, like cleaning and curing, which take longer to conclude. Thermoplastic filaments tend to be less costly than resins, while these machines have smaller build sizes, making it impossible for larger objects to be printed. This makes them unsuitable for beginners but appropriate tools for specific uses.
How does the resin 3d printing process work?
Stereolithography (SLA) or Digital Light Processing (DLP) is the main resin 3D printing process. First, a digital model is divided into thin layers projected onto a vat of liquid resin. To shape this resin to suit the image of the first layer, it gets cured with light from a laser or UV projector at specific points and then solidifies. After every curing step, the build platform goes down for new liquid resin to cover the earlier printed layer. This cycle is repeated after each cycle until all layers are completed by fabrication of the entire object. Upon completion of printing, the model is detached from the vat, extensively cleaned for uncured resin removal, and later subjected to UV light to allow optimal strength and long life.
Basics of the resin print process
First, the resin printing procedure commences by having a digital 3D model that will be converted into a printable file format. Usually, the users resort to slicing software that divides the model into layers suitable for printing. The sliced model is then sent to the resin printer, which uses a light source like UV or laser to selectively expose and harden each resin layer in a vat. Every treated layer links itself with the previous one to make up the building from the bottom. After printing has been done, cleaning of the object using isopropyl alcohol must take place to eliminate any residual resins left in it, and often, there is post-curing under UV light for extra strength and crispness. This method creates prints with very clear details and smooth surfaces, making it ideal for small structures and prototypes.
Steps involved in SLA 3d printing
- Model Preparation: You begin by drawing your 3D model using CAD programs. After the design, the model is exported in a format that can be used in slicing software like STL or OBJ.
- Slicing the Model: Use slicing software to convert the 3D model into thin layers. This software allows users to adjust layer height, exposure time, and support structures.
- Printer Setup: Fill the resin vat with appropriate photopolymer resin and calibrate the printer according to the manufacturer’s specifications for proper layer adhesion and alignment.
- Printing Process: Begin printing whereby a light source selectively cures each resin layer. In contrast, new resin flows into position for the next layer as the platform lowers after each one has been completed.
- Post-Processing: Once printing is completed, carefully remove the object from the vat. Clean the print in IPA to remove any uncured resin residue.
- Final Curing: It should also be noted that UV light cures cleaned prints, further improving the mechanical properties of the final part while assuring its complete hardening.
-
Finishing Touches: Sand or polish as necessary until the desired surface finish is acquired, and add any other fine details or assembly components if needed.
How to cure the resin after printing
Drying in a convection oven after printing is necessary to ensure the printed object has optimal strength and durability. Here are the steps for effective resin curing:
- Preparation: Once printing is complete, carefully remove the print from the build platform and clean it by immersing it in isopropyl alcohol (IPA). This will remove any uncured resin. This measure is essential to prevent tacky residues on the surface.
- Air dry: You can also use a soft cloth or paper towel to pat off any remaining alcohol before allowing your print to air dry completely.
- Ultraviolet Exposure: Put your cleaned prints in a UV light box or utilize natural sunlight for curing. See to it that all surfaces get equal exposure to UV light, as this will help harden the resin completely. Depending on the type of resin used and the intensity of UV lights, recommended exposure times can vary between 15 minutes and 60 minutes.
- Inspection: Check your print for soft areas and stickiness after drying. If there are any, additional curing may be needed.
- Final Examination and Finishing Touches: Inspect for imperfections when the object is well cured; do not hesitate to sand or paint if required, as aesthetics should be enhanced during the finishing process.
These steps ensure that your SLA print has good mechanical properties and a long life span.
What are the key components of a resin 3d printer?
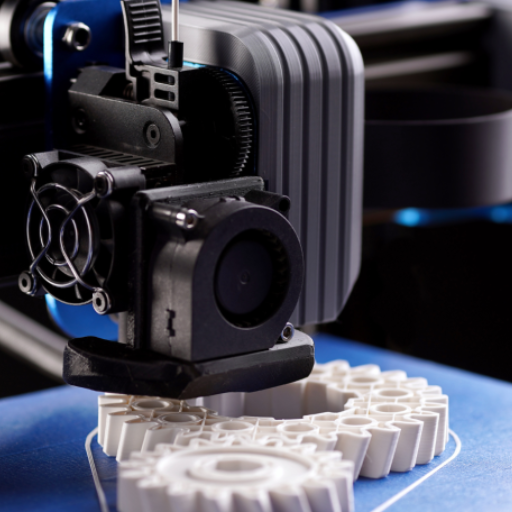

Basically, a resin 3D printer is composed of several basic parts that operate together to enhance the printing process:
- Light Source: This could be a UV LED or laser that cures the liquid resin layer-by-layer, transforming it into a solid.
- Build Platform: This is the very place where the model is built. The non-sticky surface covering makes this printer component convenient for removing printed materials quickly.
- Resin Vat: This container holds the liquid resin when printing occurs. The lower part has to be transparent enough to pass through light emitted by these sources.
- Resin: Photo polymer material that solidifies on UV light is available in different forms for diverse applications.
- Control System: These encompass electronics and software used to manage print jobs and control the movement of the build platform and light source.
-
Z-Axis Assembly: This part permits accurate vertical movement, enabling the printer to produce sequential layers. By understanding these components, users can better understand how resin 3D printers work and perform appropriate maintenance and machine operations.
By recognizing these components, users will understand how resin 3D printing works, ensuring smooth usage and maintenance of their printers.
Explaining the resin tank
The resin tank is the main component of a resin 3D printer that acts as a container for the photopolymer resin used in printing. It has a clear bottom to allow the light source to cure the resin layer by layer. Resin tanks, on the other hand, are often made from materials intended to be resistant to scratches and durable enough for use while printing with build plates that cycle in and out of contact. Moreover, some advanced models may have films or membranes at their bottoms that enhance the model release and reduce wear on the tanks themselves. Besides taking great care of it, thereby preventing contamination and damage, it will greatly influence its print quality and durability if not handled appropriately.
Understanding the role of the light source in resin printers
The resin printer functions through the initiation of curing of the liquid photopolymer resin by the light source. It is worth noting that a majority of these printers often employ UV (Ultraviolet) light to solidify only certain regions within the resin, thus forming the layers of an object as required. LCD screens, DLP (Digital Light Processing), and lasers are some of resin printers’ most common light sources. Each of these technologies has advantages; for example, while LCD can deliver excellent resolution at high speeds, DLP provides exquisite detail and quicker curing rates as it employs projectors. The lighting source should be properly calibrated and maintained due to its intensity of print quality and layer adhesion uniformity, which determine how well this equipment works.
Importance of software in resin 3d printing
The efficiency of the whole printing process, output quality, and user experience can be affected by good software used in resin 3D printers. The software acts as an intermediary between the printer and its users and facilitates the slicing of 3D models into manageable printable layers. Also, advanced slicing software offers the possibility to adjust parameters such as exposure times, layer thicknesses, or support structures for better optimization regarding specific targeted materials and goals. Some other modern programs have an automatic generation of supports, tools for repairing broken meshes, and a pre-print simulation that predicts potential problems before starting a print job, thus reducing the chances of waste. Moreover, ongoing updates from these developers provide compatibility with new resins and machines, making them relevant to 3D printing enthusiasts.
What types of resin are used in resin 3d printing?

Common types of resin for different applications
When considering the best kind of resin for a specific application in 3D printing, there are many resins to choose from with their distinct characteristics and uses:
- Standard Resin: These resins are perfect for prototyping and general 3D printing tasks. They are user-friendly and produce high-quality prints, which makes them suitable for everyday applications.
- Flexible Resin: These can be used to make certain goods, such as gaskets or seals that require elasticity or objects that would benefit from a rubber-like touch.
- Rigid Resin: They are increasingly being adopted by numerous industries manufacturing functional prototypes or parts likely to experience stress/strain since they have better strength and durability than other resin types.
- Dental Resin: The resins applied during dental procedures meet stringent health standards. Because they do not react with body tissues, these materials act as ideal biocompatible compounds when producing models, surgery guides, and orthodontic devices.
- Casting Resins: In the jewelry and art fields, casting resins are often used to make high-fidelity patterns necessary for investment casting operations. It provides incredible detailing and a fine finish.
- High-Temperature Resin: These substances remain stable even at extreme temperatures, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive sectors, where components face high heat conditions throughout their life span.
These different types of resin enable users to choose the right materials for their projects, resulting in optimal outcomes when using 3D printing.
Properties and characteristics of SLA resin
Versatility and diversity of properties that change according to the formulation are the hallmarks of SLA (Stereolithography) resins. These include:
- Resolving High Details: SLA resins are used in jewelry, dental, and model-making applications because they produce complex prints with fine detailing and smooth surfaces.
- Various mechanical attributes: Different types of resins can yield varied strengths, flexibilities, and thermal resistances, allowing for customization based on project-specific needs.
- Speed: Under ultraviolet (UV) light, SLA resins solidify rapidly, leading to fast printing times. The ability to make denser layers enhances the overall strength of the printed object.
- Poor UV Stability: Although SLA materials are great for producing detailed prints, some standard resins do not have good UV resistance and could deteriorate when exposed to sunlight.
- Post-Processing: After printing with SLA resin, objects often need further curing and finishing, including washing and UV curing, to enhance their life span and outlook.
These features mean that SLA (Stereolithography) resins suit many applications since these may require delicate or minute operations.
Choosing the right resin material for your project
Several considerations necessitate that one chooses the right resin for their 3D printing project depending on their needs.
- Application Requirements: What do you want to use it for? If you are making highly detailed models, such as for dental or jewelry applications, opt for high-detail SLA resins. Go with tough or engineering-grade resins for functional prototypes with strength and durability requirements.
- Mechanical Properties: Evaluate your project’s mechanical needs. Where flexibility is needed, choose flexible resins, whereas standard or rigid resins would be ideal for rigid applications. Tensile strength and impact resistance differ across each resin type, hence influencing end-use performance.
- Environmental Conditions: Consider whether the final product will be exposed to ultraviolet light or moisture. So, if your print is outside, apply UV-resistant resins that avoid degradation. Heating applications may require high-temperature resins to help cope with environmental stress.
These factors can then be balanced to select a resin that meets your project’s functional and aesthetic needs.
How to maintain a resin 3d printer?

To ensure the best performance and life span of a resin 3D printer, you must maintain it. Below are some activities one has to do to maintain it:
- Regular Cleaning: After each print, clean the build plate and resin vat to remove excess resin; use isopropyl alcohol and a lint-free cloth for effective cleansing.
- Check for Clogs: Check for clogs in the printer’s nozzle and resin lines; clear blockages promptly to avoid print failures.
- Level the Build Plate: This is important because it checks whether the build plate is leveled. It helps achieve consistent adhesion during prints.
- Store Properly: Keep resin bottles sealed and stored in a cool, dark place where premature curing cannot occur. Always check on expiration dates before using.
- Software Updates: Keep your printer’s firmware slicing software up-to-date to enjoy the latest features and improvements
- Use Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear gloves and goggles when handling resin to protect yourself from its potentially harmful effects.
These maintenance practices will greatly enhance the reliability and output quality of your resin 3D printer.
Routine maintenance tips for resin printers
These are additional routine maintenance tips compiled to ensure the smooth running of your resin 3D printer.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Set up a timetable for regular maintenance, including daily inspection for visible resin spills and weekly cleaning of internal parts like the LCD screen and mirrors.
- Monitor Print Environment: Ensure that the printing environment has stable temperature and humidity levels, as extreme changes can affect print quality. Minimize issues by locating in a controlled space.
- Inspect for Wear: Periodically examine this FEP film in the vat and replace it if it shows any wear, which can cause defects in prints. You should change this film once it loses its functionality after numerous prints.
- Keep Software Organised: Keep your different slicing software settings and profiles for various resins arranged well. This helps simplify printing and guarantees optimal settings are employed.
- Educate on Disposal: Be acquainted with proper disposal methods for uncured resin and other waste materials to avoid environmental pollution while following local guidelines.
When implemented, these procedures will go a long way in improving the durability of your resin 3D printer’s longevity and efficiency.
Common issues and troubleshooting in sla 3d printing
Despite this fact, some common SLA printing challenges can affect the quality of prints. Below are some common problems and their troubleshooting steps.
- Layer Adhesion Problems: If your prints aren’t sticking well between layers, you will need to check the exposure time settings. Increasing the time, however, can improve adhesion, but be careful not to overexpose the layers, which may cause other problems.
- Incomplete Prints are caused by a lack of resin or insufficient exposure time. Ensure your resin vat is adequately filled and adjust your exposure time to suit the specific resin and print complexity.
- Print Warping or Shrinking: Ensuring your printer is calibrated properly can help with warping. It’s advantageous to design supports correctly and ensure that the print environment remains thermally stable, thus avoiding drafts and temperature fluctuations.
- Surface Defects: For any visible defects on the printed object, inspecting for scratches or damage on FEP film should be done since it affects print quality. Besides, smoother finishes can be achieved by cleaning the LCD screen and using higher-quality resins.
- Overly Smooth or Glossy Finish: If the surface finish is too glossy, try changing to another resin type. Altering printing parameters such as lift speed and retraction time could help minimize this condition.
Knowing these issues and providing corresponding solutions will address them effectively, hence improving the overall performance of your SLA 3D Printer.
Cleaning and storing resin 3d printer components
Proper maintenance is important to ensure the endurance and continuous functionality of resin 3D printer parts.
- Cleaning Components: Once printing is done, safely detach the printout from the build platform and soak it in isopropyl alcohol (IPA) to wash off any uncured resin. For wiping the build plate and resin vat, use a soft cloth or a piece of paper towel soaked in IPA; this will prevent any scratches. These components must be cleaned immediately after they have been used since otherwise cured resins could harden.
- Storing Resin: Always keep unused resins in cold, dark places to protect them against UV degradation. Ensure that bottles are tightly closed to avoid moisture that can ruin your prints. Additionally, opened bottles should be labeled with a date for efficient tracking of their durability.
- Maintenance of FEP Film and LCD Screen: The FEP film, on the other hand, can be cleaned by gently wiping it with a clean cloth, or one may opt to use special-purpose cleaning agents that do not cause scratching, but one must be careful while doing this. Use microfiber cloths when cleaning an LCD screen so that dust does not accumulate on it because these obstructions may affect print quality. It’s always wise to check these parts regularly to detect early signs of damage.
If you follow such practices, your resin 3D printer will be well maintained, which results in better prints and long equipment life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How does resin 3D printing work?
A: Resin 3D printing works using a light source to cure liquid resin into solid layers, building up a 3D object layer by layer. This process is known as stereolithography or SLA. DLP 3D printers and LCD 3D printers are other common types using similar principles but different light sources.
Q: What is stereolithography (SLA) in resin 3D printing?
A: Stereolithography (SLA) is a 3D printing process that uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solidified layers. It’s widely used for producing detailed and intricate parts, as the laser allows for high precision.
Q: What are the different types of resin used in 3D printing?
A: Different types of resin used in 3D printing include standard resin, tough resin, flexible resin, and castable resin. Each type offers varying properties suitable for different applications, such as durability, flexibility, or ability to burn out cleanly for casting.
Q: How do DLP 3D printers differ from SLA printers?
A: DLP 3D printers use a digital light projector to flash an image of each layer onto the resin, curing a whole layer at once. On the other hand, SLA printers use a laser to trace the shape of each layer. DLP 3D printers are typically faster but may have lower resolution than SLA printers.
Q: How does LCD 3D printing work?
A: LCD 3D printing works by using an LCD screen to project UV light onto a layer of liquid resin. The UV light cures the resin layer by layer, building up the 3D object. This method allows for high-resolution prints and is generally more affordable than other resin 3D printing methods.
Q: What are some typical uses for resin 3D printing?
A: Resin 3D printing is commonly used for creating detailed prototypes, dental models, jewelry, and small-scale production of intricate parts. Its high precision and quality make it suitable for applications where detail is critical.
Q: How do resin 3D printers compare to FDM printers?
A: Resin 3D printers use liquid resin and light to create objects, offering high precision and smooth surfaces ideal for detailed work. FDM printers use plastic filament and heat to build objects layer by layer and are better suited for larger, less detailed parts. They are typically more affordable and easier to use.
Q: What are the advantages of using resin 3D printing?
A: Resin 3D printing offers high precision, fine detail, and smooth surface finishes. It is well-suited for creating detailed prototypes, small intricate parts, and professional-grade models. Different types of resin can also be used to achieve specific material properties.
Q: Can resin 3D printers produce functional parts?
A: Yes, resin 3D printers can produce functional parts, especially when using tough or flexible resins. These materials have properties that make them suitable for various applications, such as functional prototypes, mechanical parts, and wearables.
Q: Are there any specific safety precautions when using a resin 3D printer?
A: Safety precautions are essential when using a resin 3D printer. Always wear gloves and protective eyewear when handling resin, as it can be toxic and irritating. Ensure proper ventilation in the workspace to avoid inhaling fumes. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for safe handling and disposal of resin materials.









