Flame cutting is a widely used technique in the metalworking industry that shapes steel and other ferrous materials for various uses. It employs controlled high-temperature flames to cut through thick metal surfaces efficiently, hence becoming an indispensable tool for fabricators, construction workers, and artists, among others. In this article, we shall be looking at the flame-cutting process, how it works, its advantages, and any disadvantages or limitations. Therefore, understanding this method comprehensively will help readers realize its importance and relevance in today’s manufacturing sector.
What is Flame Cutting and How Does it Work?
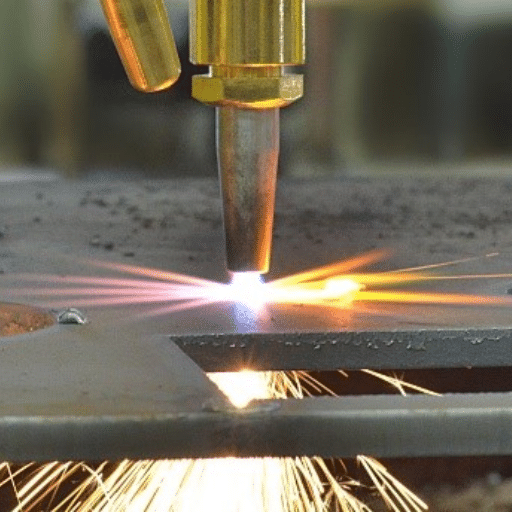
Image source: https://esab.com/
Also referred to as the oxy-fuel cutting system, flame-cutting is a process that burns fuel gas like acetylene with pure oxygen to create a scorching flame. This mixture produces intense heat exceeding 3,000 degrees Celsius. The first step involves preheating the metal surface using the flame during cutting while an ignition point is reached, and then the oxygen stream is directed towards it. As a result of the rapid oxidation of metals caused by this action, kerf is formed, thus enabling cuts to take place quickly. What makes flame-cutting more popular than other methods is its accuracy and speed, which allow it to be used in heavy-duty industrial applications or even artistic metalwork.
What is the Flame Cutting Process?
The flame-cutting process involves several steps necessary for efficiently cutting through metals. Initially, the oxy-fuel flame preheats the metal surface until it reaches a temperature high enough to ignite. Once this heat level has been achieved, pure oxygen in a concentrated stream is directed at the surface, whereby upon contact with oxygen, the metal ignites and oxidizes, resulting in quick and effective cutting. This method makes straight cuts possible and allows for adjustment depending on the material’s thickness. Also, it can work on different kinds of metals like steel or iron, among others, which makes it versatile in metal fabrication.
What Equipment is Used in Flame Cutting?
For flame cutting to take place, there must be some equipment such as cutting torches, fuel gas supply systems, oxygen supply systems, etcetera so on and so forth but most importantly, what I need are those three things mentioned earlier, which are always considered essential in all cases where oxy acetylene welding is to be done successfully. Cutting torches should be designed to mix fuel gases (usually acetylene) with oxygen, creating flames whose temperatures can reach up to 8000°F or more. I also need pressure regulators for controlling the gas flow rate while still ensuring safety during operation, thus making sure that everything goes according to plan without any accidents taking place; goggles, gloves, and clothing resistant against heat & sparks;
How Does Oxy Fuel Cutting Differ from Other Methods?
Flame cutting differs from other methods like plasma cutting or laser cutting mainly because it is more straightforward and flexible than them. The former employs combustion reactions between fuel gases and oxygen. At the same time, the latter uses high-speed ionized gas to melt metals at incredible speeds, respectively. Still, these two techniques have their advantages over one another depending on what needs to be achieved when working with different thicknesses of materials, especially ferrous ones. On the one hand, there’s no doubt about the precision offered by lasers when dealing with thin sheets; however, this very same light source cannot penetrate through thick slabs easily, hence requiring multiple passes, which take a longer time as well as being expensive in the end since more energy is consumed during the process than necessary.
Advantages of Flame Cut Steel

Flame-cut steel has many advantages, leading to its choice in different industries. Firstly, it is a cheap method, especially when dealing with big projects, since the equipment and operational costs are lower than other cutting techniques. Flame cutting can also handle thick materials effectively, which makes it suitable for heavy-duty tasks like structural steel fabrication. Another benefit of this process is that it can rough out cuts quickly in manufacturing environments where time matters most. Besides, the heat from the flame enables good edge quality for subsequent welding processes. Finally, flame-cutting equipment is portable and can be used anywhere from workshops to on-site construction, thus increasing its versatility.
Why Choose Flame Cutting Over Other Methods?
Adaptability and cost-effectiveness have made flame-cutting one of the most preferred methods. It is said that according to experts from different industries, flames are very effective when it comes to thickness cutting because they do not limit themselves like other methods, such as plasma or laser cutting, which are limited by material thicknesses but instead allow heavy-duty operations. Moreover, these machines tend to be cheaper than others while being more portable, thus making them suitable for places without enough space or even on-site jobs. In addition, flames produce clean edges after their cuts, making them easier to weld and ensuring structural strength during subsequent fabrications. Therefore, people choose this method over others because of its affordability, versatility, and efficiency, making it applicable to many metal fabrication projects.
What Are the Benefits of Using Acetylene in Flame Cutting?
Flame cutting has some significant advantages when used as a fuel gas. The most important of these, in my opinion, is that it can burn at temperatures up to 3,500 degrees Celsius, which are necessary for efficient cutting through the different types of metals. Moreover, acetylene burns with much higher energy outputs than other gases used as fuels do, thereby resulting in quicker speeds of cuts and lower operational duration. In addition, still, its flames are neutral, so they allow better control over cuts made during this process, hence leading to cleaner edges without much heating distortion. Therefore, acetylene has high outputting heat levels, effectiveness, and control, which makes it an ideal choice for flame-cutting applications.
How Does Flame Cutting Enhance the Cutting Speed?
Flame cutting increases the cutting rate by using flames with very high temperatures combined with the best mixtures of fuel gases. Flames produce intense heat, mainly if they use gases such as acetylene, which melts metal rapidly. This is enhanced further by adjusting oxygen to fuel ratio, thus creating a perfect combustion environment for easier ignition and faster cuttings. Additionally, the ability to handle thicker materials enhances efficiency since operators can perform many cuts without changing methods or tools frequently. In general terms, the simplicity of operating them with their high energy outputs contributes significantly to reducing the time taken compared to other methods.
Disadvantages of Flame Cutting
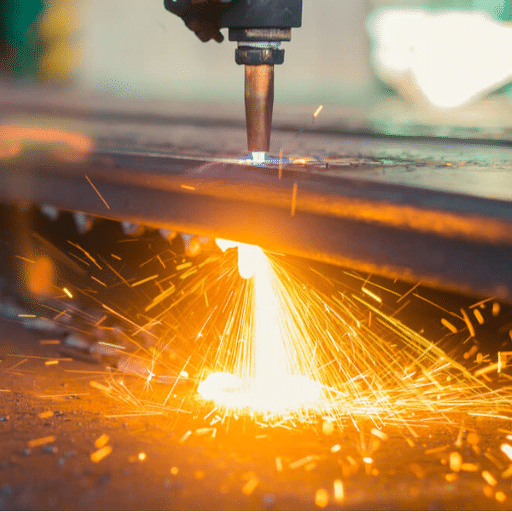

While flame cutting has many benefits, it also has limitations. One of these is that it can cause heat distortion in thinner materials; this happens when the intense heat warps the metal and weakens its structure. It also gives off noxious fumes and sparks, meaning that safety measures must be taken against fire or respiratory problems. Another disadvantage is logistical difficulty due to reliance on gas cylinders — they are heavy and hard to move around with while also needing careful storage as acetylene and oxygen are highly flammable. Finally, the broadness of cut produced by flame cutting may render it unsuitable for detailed work where precision matters most; other methods like laser or plasma cutting offer better alternatives.
What Are the Limitations of Flame Cut Techniques?
Flame-cutting techniques have several disadvantages, even though they are effective in different applications. First, heat is required during the process, which can cause thin metals to warp or change their properties. Secondly, compared with modern cutting methods like laser or plasma cuts, which are more accurate and faster, especially on intricate designs, flame cuts take longer to complete. Furthermore, the quality of the cuts depends on the operator’s skill level and the equipment setup used, thus making some setups produce low-quality reductions than others. Last but not least, essential safety concerns contributed significantly because harmful gases were generated; therefore, strict safety standards were implemented so that operators could not get exposed to risks associated with fires and fumes.
How Does Flame Cutting Affect Material Hardness?
The hardness of materials can be significantly affected by flame cutting due to the application of extreme heat during the process. Flame cutting uses high temperatures, which often softens metals in the heat-affected area (HAZ), reducing their hardness since this heat causes alterations in the microstructure of metals, especially those with higher carbon contents. I have noticed that while being good at cutting thicker things quickly, it might make them weak on edges and thus not long-lasting strongness, so whenever accuracy or workpiece strength matters, most other methods have to come into play.
What Are Common Issues with Flame Cut Edges?
A few common problems with flame-cut edges can affect overall product quality. Regarding surface finish, unevenness, and scaling are typical side effects that require extra finishing operations to fix. Another issue is dross; here, molten material cools down, solidifying along cuts but sticking onto them, meaning more cleaning must be done for functionality’s sake. Residual stresses/distortions may arise within the HAZ, thereby complicating subsequent fabrication/joining processes due to warping or cracking tendencies, among other factors. Material brittleness could also become worse under certain conditions, leading to unreliable strengthens under load or stress around cutlines. To overcome these challenges, one must carefully consider parameters used during cutting and any possible post-treatments to improve performance characteristics like edge quality and material behavior during use.
Comparing Flame Cutting to Other Cutting Methods

When comparing flame cutting with other methods, looking at the efficiency and quality of finished edges is necessary. For example, plasma cutting gives higher precision and cleaner cuts with less dross than the former. This technique is advantageous when dealing with thinner materials because it lowers the heat-affected zone while maintaining good material integrity. Conversely, laser cutting has excellent accuracy and can achieve beautiful designs with unbeatable edge quality but may require high initial investment and operational costs; however, these machines are fast, too. Waterjet stands out due to its adaptability, where all types of stuff can be sliced through without any heating so that there is no distortion or brittleness. Every method has strengths and weaknesses; hence, one must carefully evaluate them against project requirements for best results.
How Does Flame Cutting Compare to Plasma Cut?
Flame cutting has different benefits over plasma depending on the application at hand. Firstly, it’s considered the most economical way, especially when working on thick metals, since they can easily be cut by this method, which requires a low initial investment in terms of equipment cost. Secondly, a sizeable heat-affected zone is created, leading to warping, thus lowering the quality of edges produced. On the other hand, plasma cutting is known for its speed and accuracy features, which make it ideal for use in thin sheets or intricate designs. It produces less distortion because of having narrower HAZ (heat affected zone) plus delivers clean cuts accompanied by minimum slag. Plasma systems may be expensive but usually reduce the post-processing work needed. Moreover, the decision between these two mainly depends on such factors as specific material thickness, desired edge quality required, and production efficiency, among others applicable to a given project.
What Are the Differences Between Flame Cutting and Waterjet Cutting?
In my experience, flame and waterjet cutting are operated differently and can be applied differently. Flame cutting applies a high-temperature flame to melt through metals, thus making it most suitable for thicker materials. However, this method tends to have a larger heat-affected zone, which may compromise the integrity of the material, causing more significant warping. On the other hand, waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water, sometimes mixed with abrasive materials, to ensure that no heat is affected during the process so that the original properties remain preserved in the material being worked upon. Waterjet cutting can cut a variety of materials, such as glass fiber composites, among others, whereas this would not be possible with flame cutting alone because it produces more waste and does not need much post-processing activities. For these reasons, in case I was required to choose between them, I would look at what is intended for processing, i.e., its thickness level required accuracy, etcetera.
When Should You Use Laser Cutting Instead of Flame Cutting?
There are situations where a laser cutter should be used instead of a flame cutter. One key advantage of lasers is their precision since they can accurately cut intricate shapes or fine details; therefore, they are used when tight tolerance is needed in specific applications. Additionally, laser cutting creates a narrower heat-affected zone, thereby minimizing warpage potential caused by thermal distortion on materials with significantly thinner sheets made from metals, even heat-sensitive metals. Furthermore, the laser can handle plastics and wood apart from metals, hence its versatility in various industries. Finally, the initial investment into laser technology might seem expensive, but faster production speeds and lower operational costs over a long period justify their usage in a production environment.
Applications of Flame Cutting in Industries

Flame cutting is commonly used in different industries because it cuts through thick materials well and is cheap for large-scale operations. In the steel fabrication industry, flame cutting is usually done to shape and prepare significant steel components for welding and assembly. Construction benefits from flame cutting, too; this enables the quick creation of structural elements like beams and columns. Also, shipbuilding and manufacturing industries use flame cutting to process heavy plate materials, ensuring that significant steel sections can be made fast. Another reason flame cutting finds application is its ability to handle rough cuts needed for recycling scrap metal, thus making it handy during salvage operations.
What Industries Utilize Flame Cut Steel?
Various sectors make use of flame-cut steel, such as:
- Manufacturing: Flame cutting produces heavy machinery components and automotive parts, among other equipment requiring strong, thick-cut steels.
- Construction: Flame-cut steel forms structural supports, beams, and heavy-duty construction parts, thereby enabling robust frameworks for buildings and infrastructure.
- Shipbuilding: Flame cuttings are necessary during ship crafting since they help process large plates used in creating hulls plus other structural sections with precision and efficiency.
In general, these areas rely heavily on flame-cutting technology to save money and time when working with heavy-duty materials.
How Is Flame Cutting Used in Construction?
Within construction, flame-cutting shapes and prepares steel parts for various structural applications. Flame cutting is used to cut accurate lines into large steel plates, allowing for the quick creation of beams, columns, and other necessary framework elements. This procedure guarantees precision and speeds up the entire building process, thus ensuring the timely completion of projects. Moreover, flame cutting becomes invaluable for heavy-duty constructions that require strength and durability because it can easily cut through thick materials. I can adjust my methods according to different design specifications while keeping them cost-effective and high-quality.
What Role Does Flame Cutting Play in Manufacturing?
In manufacturing, flame cutting is crucial when working with metal components. It makes an accurate cut in a thick steel plate without wasting much material, making significant parts cheaply. High-temperature flames are used to ensure fast, clean cuts that meet tight production deadlines while retaining required levels of quality. Additionally, complex shapes and designs can be produced using this method since it offers flexibility across many industries, such as automotive or heavy industry, where such shapes may be required during production processes. Workflow efficiency is greatly improved through instant alteration of cutting paths, contributing significantly to overall productivity within manufacturing operations.
Tips for Effective Flame Cutting
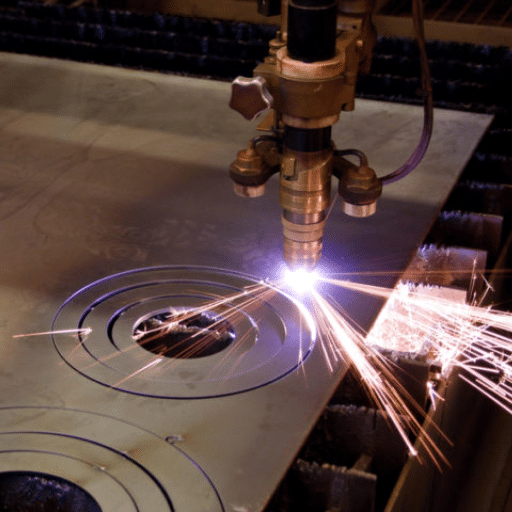
- Make Sure Your Setup is Right: To start, ensure that the gauges on your flame-cutting equipment are calibrated correctly and that you have set the oxygen and acetylene pressures as instructed by the manufacturer. This will allow you to achieve maximum efficiency while working.
- Choose the Correct Nozzle: Select a nozzle size that corresponds with the thickness of the material being cut. This will enable even cuts without causing them to overheat or become distorted in shape.
- Keep Everything Clean: It is important to keep your work area and materials free from contaminants such as rust, oil, or dirt. This can greatly improve the quality of cuts produced and extend the lifespan of various components within your setup.
- Control Speed And Angle: For straight cuts, maintain a constant cutting speed and angle. If done too quickly, they may turn out jagged, and if carried out too slowly, too much heat might be applied, leading to distortion.
- Safety First: Always wear appropriate protective clothing, such as goggles, gloves, fire-resistant clothes, etc., when using any tools involving flames or sparks. Also, ensure good ventilation and have extinguishers nearby.
-
Maintenance Culture: Inspect regularly so that things don’t fail at crucial times; check for leaks in hoses and clean tips & nozzles, among other things
How to Prepare Material for Flame Cutting?
To prepare material properly before flame cutting, safety, and the best outcome must be taken care of. Here are some of the steps to follow:
- Cleaning the Material: Eliminate any contaminators like paint, grease, rust, or dirt. A wire brush or chemical cleaner can be used to ensure that the surface is left clean, which improves the quality of the cut.
- Check on Material Thickness: Measure the width of the material accurately so you can choose a suitable nozzle size for cutting. This makes the flame-cutting process efficient and effective.
- Mark Cut Lines: Use a marker or chalk to indicate clearly where cuts should be made. This helps maintain accuracy during cutting and prevent mistakes.
- Secure Material: Clamp or hold down material firmly to prevent movement while cutting. Such steadiness contributes to straighter cuts and reduces the risk of accidents.
- Preheating if Necessary: Preheating around the cut area cleanly cuts through thicker materials, reducing warping. For this purpose, use a welding torch.
These steps lead to smoother cuts and enhance safety and precision in the process.
What Techniques Enhance the Flame Cutting Process?
I have found that several vital techniques can significantly improve flame-cutting efficiency. Initially, it is essential for one to maintain a steady speed when doing this; moving too fast may result in unevenness, while on the other hand, moving too slowly can cause excess heat, leading to warping or dinged-up edges. Secondly, I prioritize torch angle whereby holding it at about 45 degrees gives better ignition than more stable flames; thus, cleaner cuts are achieved. Furthermore adjusting oxygen acetylene ratio enhances flame quality making them sharper and more controlled cuts possible. I have also realized that keeping distance between tip of cutter and work piece should be minimum so as not allow too much slag form because this will affect accuracy levels in finishing. By mixing these approaches together, my productivity rate has increased, and accuracy levels have been improved.
How to Achieve a Straight Cut with a Cutting Torch?
If you want to cut straight when using a cutting torch, there are some techniques that you must follow. First of all, it is essential to have something that will guide you such as a straightedge; this will help ensure that the cutting torch does not deviate from its path. Secondly, ensure your hand is stable throughout and maintain an even speed of cutting because if you make any sudden move, then it might result in curved or uneven edges being formed. Another thing is to start cutting at the edge rather than the center since this reduces the chances of wandering. Moreover, the flame should be adjusted correctly, whereby its size and shape should match the thickness of the material being cut to make a neater line possible. Finally, spend enough time aligning yourself accurately by viewing the line from different angles since this can enable one to keep on track with the desired path. In summary, adopt these methods for achieving straight cuts with a cutting torch.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the flame cut process for steel?
A: Flame cutting, also known as oxyacetylene cutting, is a process that uses a torch to heat the metal to its melting point and then blows the molten metal away with a jet of oxygen. This method is commonly used to cut carbon steel and other hard materials.
Q: How does a torch cut steel?
A: A torch cuts steel using a gas mixture of oxygen and acetylene. The flame produced by this mixture heats the steel to a point where it can be quickly melted and removed, allowing the cutter to create precise cut surfaces.
Q: What are the advantages of using oxy-acetylene cutting?
A: Oxy acetylene cutting offers several advantages, including the ability to cut through thicker materials, the portability of the equipment, and the ability to produce a better cut surface than other cutting methods.
Q: Can CNC machines be used for flame cutting?
A: CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines can be used for flame cutting. This technology allows for precise control over the cutting process, enabling the creation of complex shapes and patterns in steel.
Q: What types of metals can be cut using acetylene cutting?
A: Acetylene cutting is primarily used for carbon steel, but it can also be effective for other types of metals, including stainless steel (ss) and hard metals, as long as the correct parameters are used.
Q: How can improper flame settings affect the cutting process?
A: Improper flame settings can lead to uncontrolled cutting, resulting in a rough cut surface and excessive heat that may harden or anneal the metal improperly. This can also affect the insert life of consumables used in the process.
Q: What is the melting point of steel in the context of flame cutting?
A: Carbon steel’s melting point typically ranges from 1425 to 1540 degrees Celsius (2600 to 2800 degrees Fahrenheit). The flame from an acetylene torch must reach this temperature to cut through the steel effectively.
Q: How does the cutting process differ when using propane instead of acetylene?
A: The process may require higher temperatures and different nozzle specifications when using propane instead of acetylene for cutting. Propane can be less effective for larger cutting tasks than oxy-acetylene cutting, particularly on thicker materials.
Q: What is the role of a grinder in the flame-cutting process?
A: A grinder can be used with flame cutting to smooth out the cut surfaces after the initial cutting process. This ensures a clean finish and removes any slag or oxide that may have formed during cutting.





