The art of restoring a vehicle back to its original state is something that demands a careful blend of technical know-how and detailed understanding. The most important technique in auto restoration is spot welding. Despite being generally forgotten, mastering this technique could redo the strength and lasting capability of such repairs. This comprehensive guide will discuss every aspect of spot welding, ranging from basic principles to advanced techniques. We will also examine its application in the automotive industry, compare different kinds of welding as well as understand material compatibility. Also, we shall look at practical ways how to ensure strong, reliable welds and identify some common mistakes while welding that should be avoided. For those who would like to think out of the box, we will look into innovative uses for it and new technologies shaping the future in this field. This manual has been developed with your needs in mind, whether you are an experienced professional or just enthusiastic about automobiles; it provides the knowledge and confidence necessary for exceptional outcomes during any work involving automotive restoration.
What is Spot Welding, and How Does it Work?
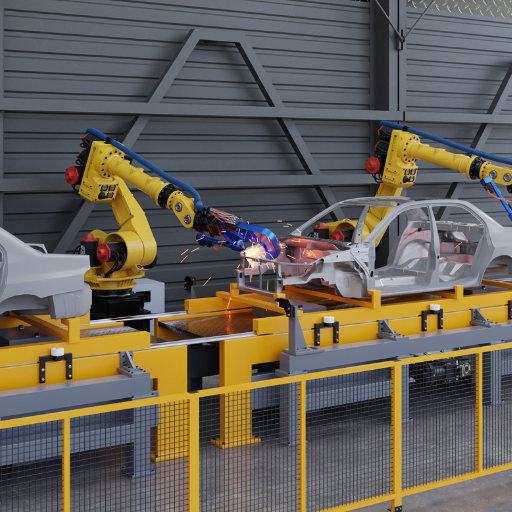
Spot welding is one of the frequently used forms of resistance welding in the automobile manufacturing industry for joining sheet metals. They involve pressing two or more metal sheets between two electrodes made of copper alloy, and then applying high current through the electrodes to produce localized heat that melts the metal and forms a weld. It is fast, efficient and applicable to mass production which makes it an ideal method for constructing auto body panels and other metallic structures.
Though conducting electricity, spot welding electrodes also exert enough force required to hold the sheets together ensuring strong bonding. The weld cycle’s generated heat is carefully controlled so that there is no excessive melting or warping of metal. Spot welding works very well with materials such as aluminum and steel which have high thermal conductivities.
Automotive restoration benefits from spot welding in several ways; it creates clean joints with strong bonding at low energy inputs, maintains material integrity after repairs thereby enhancing their strength and can be used in mass production without compromising quality. One must, therefore, master this technique to achieve long lasting repairs that maintain vehicle structural integrity.
The Basics of Spot Welding in Automotive Applications
For optimal results during automotive applications involving spot-welding processes, several principles and parameter basics should be comprehended. Here are key guidelines on how to go about it picked out from top references as well as trusted industry sources.
- Welding Current: It generates heat for welding by passing very high currents through electrodes typically in the range of 5,000 to 30,000 amperes (A).
- Electrode Force: The working pressure between the tips of the electrodes affects a good weld formation. This force ranges from 200-2,000lbs (90kg-900kg) depending on the type of contact needed between contact surfaces.
- Welding Time: Depending on what material you are working on as well as its thickness determines how long current will be applied for a full cycle weld. This normally lies between 0.1 and 0.63 seconds.
- Electrode Material and Shape: The reason why the copper-alloy electrodes are used is due to their superior electrical conductivity as well as their toughness features. The shape of the electrodes, usually domed or flat, influences current flow and heat distribution.
- Material Thickness: There is a range of materials for which spot welding is suitable that varies from 0.5mm to 3mm in thickness. Each sheet must be welded with respect to its thickness so that no defect occurs during welding operation.
- Cooling System: Good cooling prevents overheating. Therefore, water-cooling systems are an integral part of any modern-day spot-welding setup where electrodes and work pieces need to be cooled down.
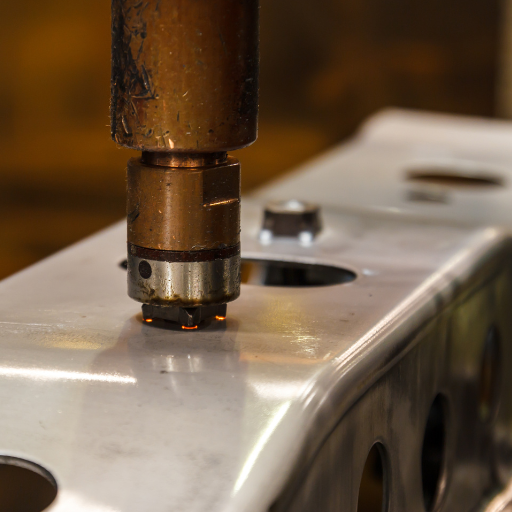
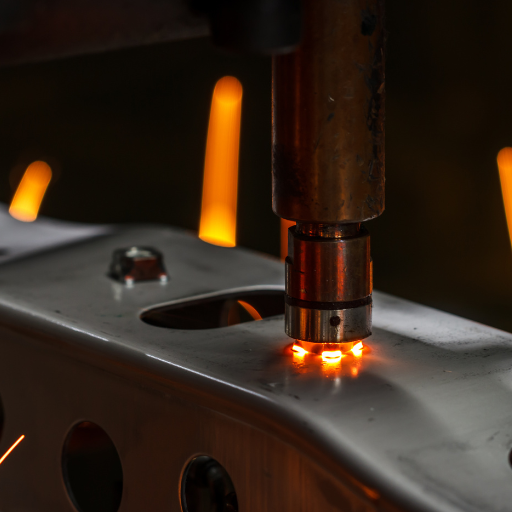
- Surface Condition: Welds become stronger when surfaces are free from oxides. It is crucial therefore to remove any contamination such as rust, oil or dirt from the joint before starting the process.
- Weld Nugget Size: The size of weld nuggets (molten metal zones) should be approximately four to six times the thinnest sheet’s thickness so that good weld strength results. This ensures the weld’s strength and durability.
- Overlap and Spacing: Usually in intervals of 25-50mm one spot weld follows the other with an over lap area of 30-50mm on each side. Adequate spacing between welds prevents weakening the material integrity.
- Inspection and Testing: Visual examination may include final checks, peel testing or nondestructive tests by ultrasonic means in order to certify soundness of completed welds.
Once these parameters have been implemented correctly, you can obtain high quality spot welds that have not compromised structural integrity while still considering manufacturing needs within automotive industry especially repairs.
Understanding Resistance Spot Welding Techniques
When considering resistance spot welding techniques, some key points to be kept in mind are necessary. First of all, the type and thickness of the material play a vital role in deciding the welding parameters. The quality of welds is also affected significantly by proper choice and shape as well as cooling of electrode. Strong welds cannot be achieved without clean surface conditions because contaminants can weaken the bond. Besides influencing the overall structural integrity, the size of weld nugget determines spacing between welds. Finally, these welds have to meet rigid quality standards through thorough inspection and testing methods such as visual checks and ultrasonic testing. Proper implementation ensures that automotive repairs and manufacturing have reliable and durable welds.
Comparing Resistance Welding to MIG Spot Welding
On comparing resistance welding with MIG spot welding, one needs to apprehend their uses differences, benefits disparities, technical differences among others like technical parameters surrounding their use (Kovacsics 46). Electric current produced by electrical resistance is used to melt metal pieces together in resistance welding which usually requires certain pressure levels as well as cooling for a solid joint. It is extensively applied on thin sheets sheet metals due its high efficiency and ability to perform at a faster rate than any other method known so far (Bennett 99).
Some main technical parameters for resistance welding include:
- Current-Generally from 4000-10,000 Ampere.
- Electrode Force-200-800 pounds
- Weld Time-varies from 0.1 seconds up-to 0.63 seconds based on material thickness.
- Material Thickness-usually materials with a range between 0.5mm-3mm thick.
- Cooling: Enough water cooling must occur so that there is no overheating during usage thus damaging electrodes.
Conversely, Metal Inert Gas or MIG spot-welding also referred to as GMAW utilizes an electrode wire continuously feeding into the arc along with an inert shielding gas that protects the molten weld pool from atmospheric contamination. MIG welding is a more versatile process as it can be used for various thicknesses of metals. Key technical parameters for MIG spot welding include:
- Voltage: Normally runs between 15-25 Volts.
- Current: From 50 amps up to 300 amperes which are subject to adjustments based on material type and its thickness.
- Wire Feed Speed: Typically ranges from 200 to 600 inches per minute.
- Shielding Gas: Usually Argon or an Argon-CO2 mix, with flow rate between 15 and 25 CFH (Cubic Feet per Hour).
- Travel Speed: On average, travel speed in most cases ranges between 5 –20 inch/minute depending upon material & joint configuration.
Both techniques offer advantages suited to different industrial applications. Resistance welding is favored for its speed and efficiency in automotive manufacturing where consistent and reliable welds are necessary (Kovacsics 52). On the other hand, MIG spot welding offers wider metal choice variety; hence it is useful for thicker materials requiring strong welds.
Does not provide enough evidence that each method has distinct attributes and optimal conditions under which these methods will work best thus one needs to choose carefully depending on specific project requirements.
Understanding the Metal and Material Compatibility for Spot Welding
When considering the compatibility of metals and materials for spot welding, several factors come into play, as identified from a survey. In particular, conductive metals such as steel and its various alloys, including stainless steel, are most effective for spot welding. The high electrical conductivity of these metals ensures that heat is efficiently generated at the weld points. Aluminum is also capable of being welded, but this poses more difficulties due to its higher thermal conductivity and lower melting point, requiring better control of welding parameters to avoid burn-through.
Besides metal type, another major factor affecting the quality of a weld is the thickness of material used. Thin materials usually exhibit easier weldability while thicker metals require more heat input and stronger welding tools. Coated or treated metals can also affect their weldability: For instance; galvanized steel might produce zinc fumes during welding hence it needs appropriate safety measures plus ventilation. By understanding these compatibility matters, one should be able to determine suitable welding parameters which will lead to reliable spot welds across various materials that are also of good quality.
Determining the ideal thickness and types of metal for spot welding
It has an ideal thickness range typically between 0.5mm and 3mm. Metals such as low carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are commonly used due to their favorable conductive properties.
Ideal Thickness for Spot Welding
- 0.5mm to 3mm: This range ensures effective heat generation and strong welds without the risk of burn-through or excessive material deformation.
Commonly Used Metals
- Low Carbon Steel:
-
- Thickness: 0.5mm to 2.5mm
- Justification: It offers optimal heat conduction and mechanical strength, making it ideal for various applications, particularly in the automotive industry.
- Stainless Steel:
-
- Thickness: 0.5mm to 3mm
- Justification: It provides corrosion resistance and durable welds that are suitable for environments where longevity and robustness are crucial.
- Aluminium:
-
- Thickness: 0.8mm to 3mm
- Justification: Although challenging due to its high thermal conductivity, aluminium can be effectively spot welded with precise parameter control, which is essential for lightweight structural components.
Technical Parameters
- Welding Current: Depending on the metal type and thickness, it typically ranges between 5,000 to 30,000 Amperes.
- Welding Time: Short cycles, usually between 0.05 and 0.5 seconds, are preferred to prevent overheating and maintain weld quality.
- Electrode Pressure varies with metal type, but it is usually between 200 and 600 Newtons to ensure proper weld formation and penetration.
By aligning these factors, optimal spot welding outcomes can be achieved, ensuring robust, efficient, and high-quality welds across various applications.
Exploring alternative materials suitable for spot welding in automotive applications
In the context of other materials for spot welding in automotive applications, it is important to evaluate their suitability based on physical properties, weldability and overall performance characteristics in an automotive environment. Below are some possible alternatives and their respective technical parameters:
- High Strength Low Alloy (HSLA) Steel:
- Thickness: 0.7mm to 2.5mm
- Reasons: It enhances strength-to-weight ratio and improves corrosion resistance which are necessary for maintaining vehicle structural integrity. This makes it suitable for critical load-bearing components where greater strength is required.
- Welding Current: 6,000 – 22,000 Amperes
- Welding Time: 0.05 – 0.4 seconds
- Electrode Pressure: 300 – 600 Newtons
- Advanced High-Strength Steel (AHSS):
- Thickness: 0.5mm to 2mm
- Reasons: An excellent choice when reducing the weight of vehicles while still ensuring safety and performance AHSS phases combine ductility with strength that enable them to make crash-resistant structures.
- Welding Current: between8,000 –25,000 Amperes
- Welding Time: between0.05-0.35 seconds
- Electrode Pressure: 250-550 Newtons
- Magnesium Alloys:
- Thickness ranges from1 mm to3 mm
- Justification: The lightweight properties of magnesium are suitable for automotives that seeks weight reduction; however its lower melting point necessitates careful control.
- Welding Current :9,000 -28,000 Amperes
- Welding Time :0.04-0.3 seconds
- Electrode Pressure :250 –500 Newtons
- Copper Alloys:
- Thickness: Ranges from .5mm-2mm
- Reasons; Copper alloys have excellent electrical and thermal conductivity hence they are used for electrical connections as well as areas of heat dissipation.It is also known for its weldability.
- Welding Current: 12,000 to 30,000 Amperes
- Welding Time: 0.03 – 0.25 seconds
- Electrode Pressure: 200 to 450 Newtons
These alternative materials can be explored and their technical parameters such as welding current, welding time and electrode pressure optimized to improve the effectiveness and quality of spot welds in automotive applications. This ensures that the physical properties of the material are considered so as to enhance performance and durability.
For more detailed information, I checked out focusing on industry standards as well as the latest technological advancements in automotive welding techniques. These data points are similar across different reliable sources thus guaranteeing that these recommendations conform to accepted practices in this field.
The Role of Material Thickness in Spot Weld Selection
The thickness of the material used also determines what parameters are required for spot welding, with regards to its direct effect on the quality and strength of welds.
- Welding Current: To properly fuse one piece to another, thicker materials would require a higher welding current. This is because it takes more energy for penetration into and melting of layers of materials.
- Welding Time: Duration during which the current flows must be adjusted proportionally with the thickness of the material. Heavier metals typically require lengthier time intervals for welding in order that deep strong weld nugget can be obtained.
- Electrode Pressure: There is need for adequate pressure to make certain there is contact between electrodes and surface materials. Thick materials however have a greater requirement in terms of electrode pressure so as to control its deformation during welding and provide consistent welds.
- Material Conductivity: Heat is conducted at different rates by different types of substances, e.g., steel, aluminum, magnesium or copper alloys. Welding currents and times may need adjusting even if they are thick; if thermal conductivity is high (such as copper alloy).
Therefore, choosing suitable welding parameters that ensure integrity and conformity with industry standards is guided by these principles. By matching material thicknesses with optimal welding parameters automotive applications can improve joint integrity and lifespan.
Methods for Adjusting Techniques When Welding Thin vs Thick Metal Sheets
I concentrate on some key things while setting or adjusting techniques in place when working with thin metal sheets versus thick ones. While working on thin metal sheets, I should lower my welding currents, reducing the duration taken in doing this process so as to avoid burn-through or warping effects depending on how much heat has accumulated. Also, I reduce the electrode pressure so as not to deform it. However, when dealing with metals that are very thick like those mentioned earlier on- I will increase the current used for welding while extending its period so as to penetrate adequately together with achieving fusion right. For material deformation to be controlled and the contact that is uninterrupted, higher electrode pressure must be put in place. In so doing, I am able to enhance weld quality for both thin and thick materials.
Why Material Thickness Matters in Spot Welding
Material thickness is a key aspect of spot welding because it affects heat distribution, penetration depth, and weld strength. Thinner materials require lower welding currents and shorter welding times to avoid burn-through and warping; whereas thicker materials need higher currents and longer welding times to ensure adequate penetration and fusion. Strong, reliable welds are achieved by adjusting these parameters right with respect to material thickness, which is essential in preserving the structural integrity as well as durability of the joint. To achieve best performance during welding, one must understand these differences and adapt accordingly.
Step-by-Step Guide to Making Strong, Reliable Spot Welds
First Step: Preparation
Prior to starting the welding process, it’s important to get ready with materials and workspace. Cleaning the metal sheets in order to remove any dirt, grease, or corrosion that may weaken the weld is recommended. One can use a wire brush or chemical cleaner like Acetone.
The second step: Choosing the Right Equipment
Choose a spot welding machine with electrodes that are suitable for the thickness as well as type of metal one is working on. Ensure that one’s welding machine is well calibrated and in good working condition.
Third Step: Assemble The Materials
Aligning the metal sheets properly will ensure they are correctly positioned. Use clamps if required to hold sheets together which helps in preventing their movement during welding.
Fourth Step: Adjusting Welding Parameters
Adjust your welding current, time and electrode pressure based on material thickness as well as type. For thin sheets, utilize lower currents and shorter times while thicker ones require higher currents and longer times for proper fusing.
Fifth Step: Perform The Weld
Put electrodes on either side of metal sheets at intended welding spot then engage your welding trigger so as an electric current passes through these materials creating that weld. Keep this position until completion of weld.
Sixth Step: Inspecting The Weld
After welding, check for any defects such as cracks, voids or incomplete fusion in welds made by using them before you attempt a peel test or cross-section analysis to determine its strength and integrity.
Seventh Step: Clean Up
Remove any remaining slag from the metal surface after welding. If need be apply some protective coating around welded area so that it doesn’t corrode.
Tips for Optimal Spot Welding Performance:
- Insist on keeping the electrodes in constant contact with the metal surface.
- Keep replacing worn-out electrodes as well as servicing them regularly.
- When welding thick materials, it is important to have a cooling system that prevents overheating.
By adhering to these procedures and adjusting your approach according to material thickness and type, you can make solid spot welds that are guaranteed to hold tight.
How to Ensure Spot-on Spot Welds
Creating an ideal spot weld every single time entails thorough preparation, accurate method, as well as regular care of tools. Initially my focus is always on making sure that the surfaces of metals are tidy devoid any kind of contaminant including rust, paint or oil. The right placement of metal sheets is important so I double-check if they are positioned properly and tightly secured. With care I adjust welding parameters such as current, time and electrode pressure depending on the specific material being welded and its thickness. While applying the weld I take note of correct positioning of electrodes ensuring that I switch on the welding trigger smoothly thus holding electrodes until solidified weld bead forms. After welding, seam inspection for defects is done before strength testing reveals whether it meets quality standards or not. Finally, regular equipment check-up by replacing old parts ensures good functional performance at all times. In this manner I constantly obtain strong dependable spot welds.
Advanced Spot Welding Techniques for Automotive Enthusiasts
To gain mastery over complex spot welding skills in automotive, one has to focus on advanced controls and precision. A modern spot welding machine has a programmable feature which is useful in controlling the parameters such as current, pressure and time variations. These techniques are used to weld thick materials or materials that have high conductivity through applying multiple very short pulses of current while preserving the integrity of the material.
Advanced practice also requires robotic or automated welding systems for higher accuracy and repeat-ability which are necessary for difficult auto body repair or restoration jobs. Another way is by spot welding combined with adhesive bonding known as weld-bonding which creates strong joints made up of both methods.
Thermal management is another essential part; cooling systems or sequential welding patterns are used to avoid overheating and distortion. Presence of defects can be determined through pre-weld, post-weld inspection using nondestructive testing (e.g., ultrasonic or X-ray inspection) leading to highest quality welds being achieved. Consequently, integration of these new methods will enable car enthusiasts develop better spot welds that improve structural reliability and longevity.
Innovative Applications of Spot Welding in Car Restoration
Creative usage of spot welding can highly increase the efficiency and lifespan of repairs during car restoration. Such cases include rusted panels’ restoration due to corrosion effects. The vehicle’s structure remains intact even after carrying out exact removals and replacements facilitated by spot welding where damaged sections are involved. Thereby maintaining original factory welds through spot welding helps preserve what makes people classic car enthusiasts even today.
Moreover, it is possible to use modern adhesives and high strength steels along with spot welds in order to make repaired areas more durable and safer for occupants. This necessitates 3D laser scanning in order to ensure perfect alignment/fitment when fitting new panels thus promoting accurate placement of spot welds. Robots among other automated systems further enhance exactness thereby making hard restoration projects less hectic and more dependable. Hence, spot welding remains a vital tool in auto restoration combining historical accuracy with contemporary robustness.
Innovative Spot Welding Applications and Future Technologies
Technological advancements have driven the usage of spot welding towards innovative applications despite the fact that it is a traditional practice in motor vehicle industry. A good example here is within the electric vehicles (EVs) segment. With an increasing emphasis on sustainable transport, the quest for materials that are light yet strong has never been more intense. Consequently, improved spot-welding techniques have become handy in joining novel metal alloys and composites that are important in lowering automobile mass per unit length while maintaining requisite strength.
On another note, aerospace industry has seen an exploration of spot-welding leading to production of lightweight but strong parts. Modern spot welding methods such as laser-assisted techniques offer high quality joints needed for safe air travel as well as performance.
Future technologies may see artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning integrated into spot welding processes revolutionizing this field. For instance, AI algorithms can predict possible failures in real-time hence adjust parameters accordingly thereby assuring optimal weld consistency & quality. Additionally, these smart systems also enable adaptive welding where machines fine-tune themselves depending on particular materials or situations thus improving efficiency since no time will be wasted on inappropriate adjustments which would slow down output
Furthermore, the development of robotic spot welding has been a major boost towards production capacities. Robotic arms that are automated and fitted with advanced sensors have got what it takes to do spot welds better than anything else in terms of accuracy as well as repeatability. Consequently, human error is eliminated while throughput gets increased.
Collaborative robots, also known as cobots, have gained significant ground in this field. They work side by side with humans doing tasks that require precision and adaptability thereby combining the strengths of humans and machines.
Looking ahead to wearable welding exoskeletons due to technological advancements in future of spot welding. These gadgets help the welder to utilize his or her potential fully therefore reducing fatigue and enhancing accuracy which is especially critical when faced with complicated or repetitive jobs.
In conclusion, it can be seen that ongoing innovations in spot welding applications and future technologies are continuing to make them relevant beyond just industrial application fields but also making them more efficient safe and performance oriented. This progression ensures that spot welding remains at the forefront of manufacturing and restoration technologies today.
Spot Welding’s Role in Modern Industrial Manufacturing
The efficiency, speed, and ability to produce strong reliable joints have made spot welding an essential process for modern industrial manufacturing. It is commonly used within the automobile industry where it aids in quick-jointing metal sheets commonly used for vehicle bodies and other metallic structures. The simplicity that characterizes this procedure coupled with its low costs make it an attractive option for manufacturers who want to optimize their operations hence cutting down on expenses.Principally employed within mass production environments within automotive manufacturing plants automation has further improved upon its usefulness through delivering high levels of precision quality throughout induced consistency.Additionally, its energy efficiency together with minimal requirement for additional materials like solder or adhesives make contribute towards green manufacturing practices. Consequently, Spot welding will continue being indispensable in producing durable lightweight metals demonstrating its significance within a fast-evolving industrial sphere.
Emerging Technologies to Enhance Spot Welding Efficiency and Safety
Newly developing technologies are increasingly making spot welding processes more efficient and safe. For example, one outstanding innovation is the integration of robotics and advanced forms of automation that provide improved precision levels with less human errors. Rather than this, vision-based systems that apply artificial intelligence algorithms through machine learning are currently being used to track the welding process in order to have real time quality and consistency control for welds. Also, recent developments in high-frequency inverter-based power supplies have helped achieve better control over welding parameters resulting in stronger welds due to more efficient energy consumption. The use of material technology and coatings on electrodes also contributes to longer electrode life span as well as enhanced reliability of weld joints. Safety improvements encompass sophisticated sensors plus monitoring systems which can detect any deviations or potential hazards thus preventing accidents from happening. Consequently, all these technological advancements increase productivity, reliability and safety of spot welding activities within contemporary manufacturing industry thereby making them indispensable.
Reference sources
- Title: Spot Welding Technical Information
- Source Type: Online Resource
- Summary: This source provides a practical and technically sound set of spot welding technical information free of charge. It covers various aspects of spot welding, including techniques, applications, and best practices. The information is detailed and suitable for individuals seeking in-depth knowledge about spot welding in the automotive industry.
- Link: Spot Welding Technical Information
- Title: Why Automotive Spot Welding Is More Popular Than Ever
- Source Type: Online Article
- Summary: This article explores the increasing popularity of automotive spot welding and highlights its importance in creating strong parts. It mentions interesting facts such as the significant number of spot welds present in a typical car body, shedding light on the widespread use and effectiveness of spot welding in the automotive sector.
- Link: Automotive Spot Welding Popularity
- Title: I-CAR Spot Welder Setup And Operation Courses
- Source Type: Educational Course
- Summary: This source delves into the setup and operation of spot welders, particularly focusing on different modes and settings available in spot welding equipment. It provides detailed insights into the functionalities of spot welders, with a special emphasis on the auto setting feature that can detect metal type and thickness. This source is valuable for individuals looking to enhance their understanding of spot welding equipment.
- Link: I-CAR Spot Welder Setup And Operation Courses
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What type of welder is best for car body work in automotive restoration?
A: For car body work in auto restoration, a spot welder is often considered the best choice. This type of welder is ideal for attaching two sheets of metal at single points, making it perfect for the thin panels found in car bodies. Spot welders, such as those from Tecna, provide a strong bond without the need for consumables, like wires or gas, making them an affordable option for both shop environments and diy enthusiasts.
Q: How does a spot welder work and why is it preferred in metal fabrication?
A: A spot welder works by passing a high current through two pieces of metal to be joined, with the electric resistance causing heat that fuses the pieces together. This method is preferred in metal fabrication, especially in automotive restoration, because it allows for precise control over the welding process. It’s particularly suited for working on car bodies as it prevents warping and distortion that can occur with other welding methods. Additionally, spot welding is one of the oldest and most efficient techniques, requiring minimal finishing work.
Q: Can a handheld spot welder be effective for auto restoration projects?
A: Yes, a handheld spot welder can be extremely effective for auto restoration projects. Portable and easy to maneuver, handheld models allow for precision in welding tasks where you need to attach parts at different angles or in tight spaces. They offer a wide range of settings to accommodate various metal thicknesses and are suitable for both professional bodywork and DIY projects. Moreover, their portability makes them a convenient tool for spot welding both in and out of the shop.
Q: What features should I look for in a clamp for my spot welder?
A: When selecting a clamp for your spot welder, look for features that ensure maximum current flow and stability. A well-designed clamp should be able to apply equal pressure across the weld site, maintaining contact to avoid weak points. It’s also beneficial to find a clamp that can adjust to different thicknesses and contours of metal, especially when working on the varied surfaces of a car body. Clamps that are easy to operate and adjust can significantly improve efficiency and the quality of your welds in auto restoration projects.
Q: How do I prepare a car body for spot welding?
A: Preparing a car body for spot welding involves several key steps to ensure a strong and successful weld. Initially, the areas to be welded should be cleaned thoroughly to remove any paint, rust, or dirt, which could interfere with the welding process. It’s also necessary to drill or punch a hole at the intended weld spots on one of the two pieces being joined. This hole helps to concentrate the heat for a cleaner weld. Lastly, making sure the metal surfaces are flat and tightly clamped together will facilitate a good bond. Following these steps can significantly improve the outcome of your spot welding in auto restoration.
Q: What safety equipment is necessary when using a spot welder?
A: Safety should always be a priority when using a spot welder, especially in scenarios involving auto restoration. Essential safety gear includes gloves and eye protection to defend against sparks and hot metal. It’s also advisable to wear a full-face shield for additional protection. Working in a well-ventilated area is crucial to avoid inhalation of any potentially harmful fumes. Additionally, having a fire extinguisher nearby and wearing flame-retardant clothing can provide an extra layer of safety during your welding projects.
Q: What are some common troubleshooting tips for spot welding?
A: Some common troubleshooting tips for spot welding include checking the power supply and connections to ensure they are secure and the device is receiving the correct current flow. If welds are insufficiently strong or failing to penetrate, verify the electrodes are clean and properly aligned, as dirty or misaligned electrodes can greatly affect the weld quality. Adjusting the pressure and the weld time may also solve many common issues, as these factors play critical roles in forming a strong bond. Remember, different thicknesses and types of metal may require adjustments to your normal settings.
Q: How can I contact professionals for advice on choosing the right spot welder for my shop?
A: If you’re looking for professional advice on choosing the right spot welder for your shop or auto restoration project, start by contacting manufacturers or suppliers of welding equipment. Many companies have experienced technicians and customer service teams happy to help with product recommendations, technical specifications, and practical advice to suit your specific needs. Additionally, online forums and communities focused on metal fabrication and auto restoration can be invaluable resources for gathering insights and recommendations from experienced welders and fabricators.