Indoor cultivation of ginger is an alluring and fulfilling project for plant buffs and home vegetable gardeners. This complete guide will show you everything you need to know to grow this aromatic and versatile plant in the comfort of your own home. From choosing the appropriate ginger rhizome and establishing growing conditions to care and troubleshooting of common issues, you will find hands-on tips with deeper insights to ensure a thriving indoor ginger plant. Whether you’re an expert grower or a curious beginner, this guide will provide you with all the information you need to enjoy fresh ginger from your own home throughout the year.
Understanding Ginger as a Houseplant

Ginger is a tropical plant that grows indoors under the right care and conditions, making it an ideal addition to a rewarding and aromatic pursuit for home gardeners. These hardy plants must be grown in well-drained soils with warm temperatures and moderate humidity.
Key Requirements for Indoor Ginger:
- Bright filtered light (avoid direct sunlight)
- Consistent watering without overwatering
- Well-drained soil
- Regular fertilizing during growing season
- Warm temperatures and moderate humidity
What is Ginger?
Ginger is a flowering plant native to Southeast Asia, famous for its pungent, aromatic rhizomes that are used both as a spice and natural remedy. The plant belongs to the family Zingiberaceae, making it a cousin to turmeric and cardamom. Ginger is prized for its warm, slightly spicy flavor and is very common in cooking, baking, and beverages.
Benefits of Growing Ginger Indoors
The numerous benefits of cultivating ginger indoors make it a valuable addition to any home garden:
- Fresh Supply: Always have a fresh and ample supply of this flavorful ingredient
- Controlled Environment: Control temperature and humidity for optimal growing conditions
- Cost-Effective: A very economical way to get organically grown ginger
- Aesthetic Appeal: Lush green leaves add natural beauty to your home
- Reduced Pests: Indoor growing reduces pest and disease threats
Ideal Conditions for Ginger Growth
| Condition | Requirement | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 68-86°F (20-30°C) | Warm, stable temperatures are essential |
| Light | Bright, indirect | Avoid direct sunlight which can burn leaves |
| Soil pH | 5.5 to 6.5 | Slightly acidic, well-draining soil |
| Moisture | Consistently moist | Never waterlogged to prevent root rot |
| Fertilizer | Balanced organic | Regular feeding during growing season |
How to Grow Ginger Indoors

Planting ginger indoors begins with choosing a healthy ginger root and providing the proper growing environment. Follow these essential steps for successful indoor ginger cultivation.
Choosing the Right Ginger Root
What to Look For:
- Thick and firm root with smooth skin
- Several prominent buds (growth points)
- Fresh appearance without shriveled skin
- No mold or soft spots
- Organic when possible to avoid growth inhibitors
Preparing Your Planting Container
The right container setup is crucial for successful ginger growth:
- 1Choose a wide, shallow container – Ginger roots grow horizontally rather than deep
- 2Ensure good drainage holes – Prevent water accumulation and root rot
- 3Use rich, well-draining potting mix – Slightly sandy texture mimics natural conditions
- 4Mix in organic matter – Add compost or slow-release fertilizer for nutrients
Steps to Plant Your Ginger
Planting Process:
- Select a fresh ginger rhizome with visible growth buds or “eyes”
- Cut into smaller pieces, keeping at least one eye per piece
- Let pieces dry overnight to callus and prevent rotting
- Plant pieces 2-4 inches deep with buds facing upward
- Space pieces a few inches apart to allow for growth
- Water thoroughly but keep soil moist, never soggy
- Place in warm, partially-shaded spot with indirect sunlight
Care Tips for Growing Ginger Indoors

Proper care is essential for healthy ginger growth. Follow these comprehensive care guidelines to ensure your indoor ginger plant thrives.
Watering Requirements
Consistent watering is crucial for indoor ginger plants:
- Keep soil consistently moist but never waterlogged
- During growing season: Water when top 1 inch of soil feels dry
- Ensure proper drainage to prevent excess water accumulation
- Winter care: Reduce watering frequency as growth slows
- Humidity boost: Mist leaves regularly in dry environments
Light and Temperature Preferences
| Aspect | Requirement | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Light Type | Bright, indirect/filtered | Direct sunlight can scorch leaves |
| Temperature Range | 65°F to 75°F (18-24°C) | Optimal for tropical plant growth |
| Placement | Near bright window | Provides adequate light without direct exposure |
| Avoid | Drafts and temperature fluctuations | Sudden changes stress the plant |
Fertilizing Your Ginger Plant
Regular feeding during the growing season promotes healthy development:
Fertilizing Schedule:
- Frequency: Every 2 weeks during spring and summer
- Type: Balanced organic fertilizer
- Special focus: High phosphorus content for root development
- Alternatives: Compost or well-rotted manure
- Caution: Avoid over-fertilizing to prevent weak, leafy growth
Harvesting Ginger
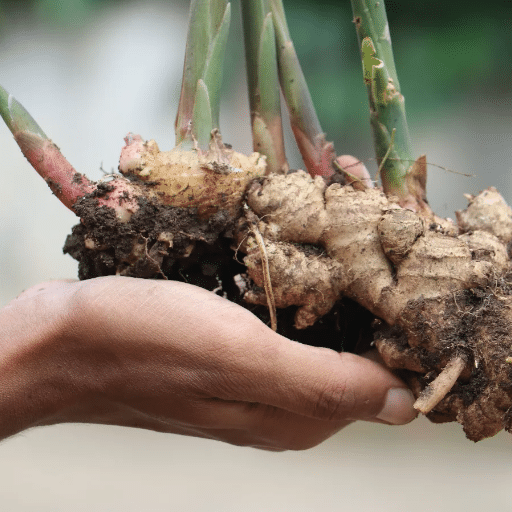

Harvesting ginger is an easy but completely rewarding process. The timing depends on your intended use and flavor preferences.
When to Harvest Your Ginger
| Harvest Type | Timing | Characteristics | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Young Ginger | 4-6 months | Mild flavor, thin skin | Fresh recipes, teas |
| Mature Ginger | 8-10 months | Strong flavor, thick skin | Storage, drying, cooking |
How to Harvest Ginger Properly
- 1Loosen the soil around the plant base with a garden fork
- 2Lift carefully to avoid damaging rhizomes
- 3Shake off loose dirt gently
- 4Partial harvest option: Cut section and replant remainder
- 5Full harvest: Remove all roots and rinse thoroughly
- 6Dry in shade for 1-2 days before storing
Storing and Using Your Harvested Ginger
Storage Options:
- Short-term (2 weeks): Paper bag in cool, dark, ventilated area
- Refrigerator: Store in crisper drawer for several weeks
- Freezer: Peel and slice before freezing for easy use
- Drying: Air dry or dehydrate for long-term storage
Usage Ideas:
- Fresh: Teas, smoothies, stir-fries, marinades
- Dried: Baking, seasoning blends
- Powdered: Convenient for cooking and baking
Common Issues When Growing Ginger Indoors
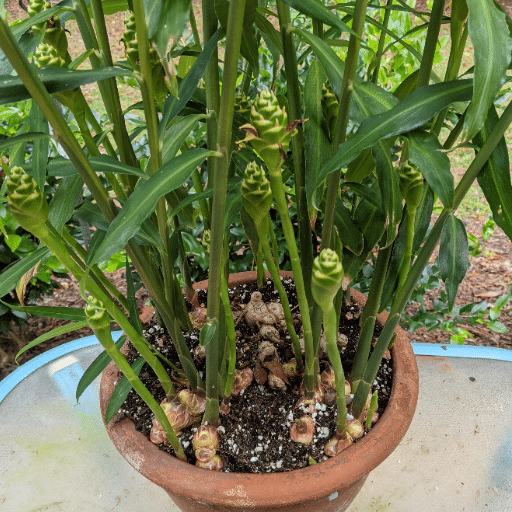
Growing ginger indoors can present several challenges. Here’s how to identify and solve common problems.
Pests and Diseases
| Problem | Signs | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spider Mites | Fine webbing, yellowing leaves | Neem oil treatment | Regular inspection, adequate humidity |
| Fungus Gnats | Small flying insects | Reduce watering, yellow sticky traps | Proper drainage, avoid overwatering |
| Root Rot | Soft, brown roots | Improve drainage, reduce watering | Well-draining soil, proper watering |
Signs of Stress in Your Ginger Plant
Common Stress Indicators:
- Yellow leaves: Often indicates overwatering or poor drainage
- Brown leaf tips: Usually signals low humidity
- Drooping leaves: May indicate dry soil conditions
- Stunted growth: Often related to nutrient deficiency
Solutions to Common Problems
Quick Fixes:
- Brown leaf tips: Increase humidity through misting or humidifier
- Drooping leaves: Check soil moisture and adjust watering
- Stunted growth: Apply balanced fertilizer for nutrition
- Poor drainage: Repot with better-draining soil mix
- Temperature stress: Maintain consistent 68-86°F range
References
-
Ginger Houseplant Care Tips: How to Grow Ginger Indoors – This guide explains the conditions needed to grow ginger indoors, such as filtered sunlight, warm and humid weather, and rich soil.
-
Grow Ginger As a Houseplant: 5 Steps – A step-by-step guide on planting and caring for ginger indoors.
-
How to Grow Ginger Indoors—as a Houseplant or to Harvest – A detailed guide from Martha Stewart on planting, maintaining, and harvesting ginger indoors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How to grow ginger indoors in a pot?
To grow ginger indoors in a pot, you should choose a shallow pot with good drainage holes. Start your ginger by soaking the green ginger rhizomes in water for a few hours before planting. Use potting soil that is rich in organic matter and mix in some peat moss to improve drainage. Plant the rhizomes about an inch deep, ensuring the nodes are facing upwards. Ginger prefers a warm climate, so keep the soil temperature around 68 degrees Fahrenheit. Throughout the growing season, make sure the soil remains moist but not waterlogged, and provide plenty of light to encourage healthy growth.
When is the best time to plant ginger indoors?
The best time to plant ginger indoors is in spring when the temperatures start to rise. This allows the plant to thrive during the short growing season. If you’re growing ginger at home, make sure to time your planting after the last frost date to avoid any temperature inhibitors. It’s also advisable to warm the soil before planting to promote quicker germination. By planting at the right time, you can ensure that your ginger grow well indoors and yield a healthy harvest.
How can I ensure my ginger grows well indoors?
To ensure your ginger grows well indoors, you should provide it with plenty of light, ideally near a sunny window or under grow lights. Make sure to use soil that drains well and is rich in organic matter. Regularly check the moisture levels, keeping the soil moist but not waterlogged. Applying a liquid fertilizer every few weeks can also help provide the nutrients your ginger needs throughout the growing season. If you notice slow growth, consider moving your ginger to a bigger pot to give the roots more space to expand. This will help promote a healthier plant that can thrive indoors.
How to harvest ginger grown indoors?
Harvesting ginger grown indoors can be done when the plant has matured, typically around 8 to 10 months after planting. Look for signs that the leaves are turning yellow and dying back, which indicates that your ginger is ready to be harvested. Carefully dig around the plant to avoid damaging the rhizomes. You can choose to harvest the whole plant or just a portion of the rhizomes, allowing the rest to continue growing. After harvesting, store any unused ginger in a cool, dry place or replant it to grow your own ginger again. Remember that ginger is also a beautiful plant, so you might want to keep some in your indoor garden for ornamental purposes.
Can I grow ginger in a shallow pot indoors?
Yes, you can grow ginger in a shallow pot indoors, but it’s essential to ensure that it has good drainage holes. A shallow pot allows you to manage the moisture levels more easily, which is crucial for ginger as it prefers soil that is moist but not waterlogged. When planting, make sure to use a high-quality potting soil rich in organic matter and consider mixing in some fresh compost. While a shallow pot can be effective, be mindful that ginger does develop extensive root systems, so if you notice stunted growth, it might be time to move your ginger to a bigger pot. With the right care, your ginger can thrive even in a shallow container.





