Of late, it is no exaggeration to assert that the interior design industry has changed radically due to technological development and artistic creativity. One of the most promising technologies is 3D printing since it allows designers a new level of personalization and ecologically friendly concepts. This blog is centered on how 3D printing is changing the interior design industry by mass producing custom furniture, designer fittings, and structural components using eco-friendly materials. We will focus on the design’s interpretation, its implementation’s positive aspects regarding time and creative resources, and real cases demonstrating its possibilities. Let’s uncover the endless possibilities of how 3D printing is changing our environment and design as we know it.
How is Interior Designing Augmented by 3D Printing?
3d printing interior design
3d printing can be applied in several ways in interior design, both in the beautification of the areas as well as in their functionality. Here are some notable mentions:
- Custom Furniture Creation: For instance, interior designers can develop one-of-a-kind custom furniture that satisfies the desires of a particular client, thus allowing personalization and maximum efficient use of the room.
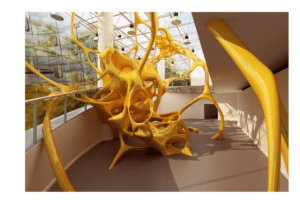
- Intricate Décor Items: 3D printing technology can manufacture complex décor items like sculptures, artifacts, and light installations that are otherwise difficult to create using traditional methods.
- Architectural Elements: Staircases, columns, and ceiling decorations can be printed out. Thus, with 3D printing, new shapes and forms of structures that were not impressive before can be created.
- Prototyping and Model Making: Simple prototypes and partial models can be generated for almost any form a designer may wish to realize, making it easy to evaluate and modify designs before they are put into production.
- Sustainable Materials: Many designers also seek 3D printers to design products using green materials and processes, products that are waste-free and emit small amounts of carbon.
- Modular Elements: The technology enables the designer of modular and movable furniture and its components, which can be easily and often rearranged in living and working spaces.
- Personalized Interior Objects: Depending on the customer’s wishes, customized design elements such as decorative lamps and fittings could also be created using 3D printing.
- Textured Surfaces and Patterns: Designers may also use patterns with physically striking components that are older but still in use, combined with the surrounding surfaces, to make the spaces more attractive.
- Replacement Parts: The research paper will show that 3D printing is one of the ways that furniture and other things that need to be repaired or modified can be made in the future.
- Interactive Installations. Art and design often encompass creative practices that use technology, and people can create interactive art within the domestic or commercial space.
Nonetheless, these 3D experiments have not only boosted the imagination of space utilization in interior design but also advanced the industry in a healthier and more productive way.
Which Ways Is 3D Printing Used in Interior Design Projects?
While investigating the possibilities of practicing 3D printing in interior design, I have understood that it promotes creativity and usefulness in many areas. In the context of design steps, applying this type of technology enables designers to make great details models quickly and then edit them as more designs are being made. Usually, most technical specifications of such applications range from the density of 50 um and 300 um, depending on the detailing level needed. This degree of exactness enables the creation of custom fittings and aimed textured surfaces that meet the user’s demands.
I also noticed that some of the designers use environmentally friendly materials such as PLA and PETG in the projects. These materials reduce the construction’s carbon footprint and are also strong physical materials. Therefore, using these systems allows users to adjust the building to develop new 3D-printed components that do not interfere with existing structures but may be added to them rather easily.
Additionally, including 3D-printed parts in such interactive units strengthens the bond of art and design with users’ perspectives. The application of 3D printing technology in the production of specialized spare parts encourages repairs and improvements of old designs, which helps maintain the aesthetics and functional aspects of the designs.
What are some Unique 3D Solutions?
Various 3D-printed solutions for interior design were researched, and some of their applications have been quite unexplained so far. For instance, a plurality of 3-D chairs or surface tablets could be made to address the needs of furniture support with respect to taste and functional aspect enhancement requisites. Such pieces usually use FDM technology with liquid polymers as the crafting material and build resolutions of 100 microns for a smoother finish.
Custom 3D printing services also offer 3D wall art and decorative wall panels for the same purpose. This allows designers to add much more complex patterns than those that could be put together from traditional processes. Materials like SLS allow so many finishes that they help improve the design.
In addition, I have recently encountered 3D-printed modular systems that are totally clashed to ensure that they can be assembled and reassembled as needed. This approach not only makes the best use of available space but also promotes green living since people are able to modify their spaces without much waste. The technical parameters can encourage or include ‘interlocking’ features that can be designed to tolerances such as 0.1 mm to achieve great stability and durability.
These inspiring 3D-printed constructs not only increase creativity in the use of spaces but also provide essential benefits such as environmentally friendly, easy-to-adjust, and easy-to-care-for furnishings.
Can You List the Items That Form the 3D Printed Furniture?
Absolutely, I can do that! Ranking the 3D printed furniture paragon, I was encouraged with several noteworthy examples from leading suppliers where ‘the ribs’ of the innovative idea lay. Among them, the “Big Chair”, designed by Studio Drift, is quite astonishing as it’s functional and exciting design-wise. Like other works with this technology, it’s made out of the FDM technique and can hold weight in large increments.
Another instance is the 3D-printed Lounge Chair designed by Zaha Hadid Architects, which was generated using SLS techniques. This chair features intricate geometric shapes that maximize its aesthetics and structural support to achieve a density of 1300 kg/m³. The technical parameters allow for lightweight yet strong constructions, making it appropriate for both inside and outside the environment.
One more instance can be the “Tetra Chair” of the company “3D Printed Concepts,” which possesses intricate lattice structures primarily intended to bear weight while using minimal material. The production process in this case is accurate to ±0.2 mm thus ensuring that modular assembly components interlock correctly and do not have sharp edges.
These instances exemplify the wide possibilities of 3D-printed furniture, which embraces inventiveness and combines it with realistic parameters that benefit the product’s functionality and design.
What are the Benefits of 3D Printing for Interior Designers?

As an interior designer, I can say that 3D printing has enhanced my profession in more than one way. To begin with, unique customization is enabled. For example, I can create unique furniture and fixtures for each particular space in terms of functional size and ergonomic design, which helps overcome the restrictions of traditional production methods. Secondly, the rapidity with which the production takes place is striking. I can prototype in a short time and incorporate feedback from the client quite well. This shrinks the time required to complete a task and improves the teamwork between the clients and me in the design stage. In addition, 3D printing is sustainable because it reduces the amount of material used and waste produced during manufacturing, where applicable. Collectively, such factors make me not only more creative but also more efficient and ecologically conscious than ever before in my interior design practice.
What is 3D Printing in Interior Design?
Undoubtedly, 3D printing takes the personalization process to another level in interior design, enabling me to design and make unique pieces that clients require. Traditional manufacturing involves working with fixed dimensions and commercially available furniture items. In contrast, 3D printing allows me to create and manufacture furniture installations that completely fill the area’s emptiness with computer-enhanced design (CAD) applications. For a particular example, the intricate designs made for the furniture can also be made in such a way that it suits the preferences or style of the client. The method enables me to work on various prototyping ideas and within a limited period make changes according to clients’ responses – thus refining the design process.
Usually, I concern myself with parameters such as layer thicknesses, print speed, and material types with regard to finish and durability. For example, layer height for furniture prints can be within the range between 0.1mm and 0.3mm determined by the image details while adjustable print speeds can range from 20 to 100 mm/s to fit the level of complexity. The use of surfaces like PLA and PETG not only ensures the maximization of aesthetic elements but also meets the required degree of strength in the final product. All in all, the capabilities taken advantage of in 3D printing enable even the realization of my clients’ most complex designs.
How Are 3D Printed Items Beneficial in Terms of Sustainability?
3D printing offers several sustainability advantages, which resonates with my desire to practice sustainable design. To begin with, it greatly minimizes material waste, unlike conventional manufacturing techniques. There is not as much wastage of materials as the construction is done from digital models accreting materials, so waste generated is lower. Likewise, I can employ some green substitutes like PLA (polylactic acid), a biodegradable polymer.
More so, the amount of energy used in 3D printing is less than that of making traditional objects due to Siam-type processes, where energy is relatively expensive and extends to injection molding. For example, this amazing technology can improve energy efficiency by producing intricate designs without support.
Functionally, I also manage factors like infill density (commonly within 20 to 100 percent, depending on the strength desired), which helps manage the amount of material used. The layer height that I tend to select is within 0.1mm to 0.3 mm, which may also influence the amount of inputs used, with thinner layers giving the best detail scaling on applicable materials. By choosing these parameters I can provide efficient functional and aesthetic designs which are also environmentally friendly.
How Do Costs Go Down with the Use of 3D Printing Technology?
3D printing technology lowers costs in many efficiencies, such as the reduction of time used in the production as well as reducing the material wasted during the process, for example, in mass manufacture. In most cases, traditional processes that use massive machines involve too much preproduction in terms of tooling even after the design is complete, but for 3D printing, the process begins from the design, which saves too much cost on pre-production. Moreover, it eliminates needless stockpiling and even renting of storage buildings since goods can be produced as per the requirements (on demand) instead of excessive stockpiling.
Practically, I can optimize material usage and cost by varying parameters such as infill density, for instance, 20-100% which I usually adjust according to the required strength. Another important parameter that I usually choose in the range of 0.1mm – 0.3 mm is the layer height and similarly costs and time for the entire printing process is also affected; a greater height may increase the speed of the printing process but will not be economical for detailed prints which can merit a higher value for excellent end results.
In plus, one of the advantages granted by 3D printing is efficient prototyping. We can save time and money by perfecting them for mass production, such as shorter and more frequent cycles. Thus, products get to the market much quicker, enabling me to stay in business at reasonable costs. To sum up, 3D printing’s notable features improve environmental performance, but conform to good economics in the present-day industry.
What Are the Enhancements Brought About by the Increased Use of 3D Printing Technologies?

3D printing has changed the face of interior design because one can customize, innovate, and prototype very quickly. As a designer, I can make customized furniture and decor for clients according to their needs, unlike in conventional design, where one is restricted by manufacturing limits. This invention enables me to work on designs with geometrical and material configurations that are creative and on the borderline of what have in the past been to complicated or expensive to produce. Even more so; this eliminates long supply lead times by allowing clients to ‘print’ components whenever they are required and therefore, I can meet clients’ needs faster and within their budget. Overall, 3D printing contributes to increasing creativity and optimizing workflows, which makes that piece of technology very useful in modern interior design.
What Does It Mean for Design and Architecture?
3D printing is a game changer in modern design and architecture in that it enhances design iterations and lowers the barriers of executing bold ideas. This technology permits me, as an architect, to fabricate advanced and elaborate structures and elements that pose an ever-changing design interpretation. For instance, I can manufacture lightweight structural members yet strong by using PLA, ABS or even metal alloys with a dimensional tolerance usually only of ±0.1 mm.Why is modern architecture – and construction, as such – wholly inconceivable without digital enhancement tools? This is due to the 3D printing’s horizons for me, as emotions, forms, materials and possibilities evolve and waste is made minimal, which in the present age of architecture is core.
In What Ways Does 3D Printing Affect the Design Process?
What 3D printing has done is to give prominence to rapid prototyping and reiteration which has proven very useful in my capacities as a designer. This technology is useful because it makes it possible to hesitate and produce real, physical representations of my designs thus receiving immediate feedback on their success. Instead of waiting for weeks to obtain a prototype with the cheap methods, it only takes hours to make one, which greatly speeds up the rest of the creative process.
Regarding the build volume for example, it can range from 200 x 200 x 200mm desks 3D printers to industrial 3D printers with over 1,000 x 1,000 x 1,000 mm or more. This is a very important dimension and layer thickness, typically ranging from 20 to several hundred microns. These parameters control the detail level and the speed of manufacturing of these components. For example, I can use different thermoplastics, resin, metal, and other materials to provide the best choices regarding strength and appearance. This also helps to encourage creativity since I will thus require minimal materials and produce less waste through the design process. In general, 3D printing helps me improve my projects’ creativity while increasing their efficiency.
What Are the Creative Possibilities with 3D Printed Materials?
One of the advantages of the 3D printed material is the creativity associated with it. Within my practice, working with geometries that would otherwise not be possible thanks to the traditional mindset leads to better designs. For example, I can make complicated lattice structures that are lightweight but very rigid which is useful in areas like building and product design.
This progression in every channel proves the essence of each 3D printing material in creativity enhancement. Such materials are flexible and resilient thermoplastics, thus appropriate for functional prototypes. Resins enable high-quality prints with smooth surfaces and are well suited for high-detail regions, while metal 3D printing is more about creating the intended parts, hence ensuring the parts will be put through extreme conditions.
When considering technical parameters, perhaps all the other factors will fall into place once the layer resolution is chosen. Quite thin, around 20 microns, it allows builders to create very detailed surfaces, even though final surfaces may take much time to print, while coarse solutions may fast-track production for less detailed and bigger-sized objects. The size of the build also influences the design capabilities, larger printers enabling large designs but prone to overfilling and restricting detail because of the material bulk. Choosing the true material combination, as well as the proper materials and technical specifications, helps me to expand the scope of what can be done in my projects, improving the level of design and offering solutions that are new and functional at the same.
What Are Some Notable 3D Printed Designs?
While there are many 3D printed designs created, I am particularly impressed with the aesthetic qualities and functionality of buildings, as well as functional and decorative prosthetic limbs and custom-made furnishings. The 3D-printed bridge in Amsterdam is an excellent example of how additive manufacturing can be applied within the construction industry on a larger scale than currently utilized. It combines complex shapes that are still structurally stable with ease of mass production. 3D printing has offered a revolution in the manufacture of prosthetic limbs, by making it possible for many to afford them, as well as customizing them to individual users. Moreover, modular furniture pieces designed in that manner also contribute to the idea of how 3D printing can design fun and practical homes. Such illustrations are valuable in illustrating the creativity and prospects offered by 3D printing technology in different areas of work.
What Are Your Thoughts on the Batoidea Chair?
The Batoidea Chair, which takes after the rays in structure and configuration, seeks to exploit the capabilities offered by 3D printing in terms of art and functional constructions. Produced in studio BERNHARD|KRAUSE, it is characterized by a non-standard organic shape that harmoniously combines modern design and usability.
Of course, it is easy to see that several peculiarities account for the change in the chair’s functional and innovative layouts.
- Material Selection: The chair’s head is also constructed with high-strength thermoplastic plastics, mostly to maintain a lightweight structure and make it more long-lasting.
- Layer Resolution: Most often, a fine layer resolution of approximately 50-100 microns is used. This resolution can detail the chair’s surface to its desirable texture, closely replicating the natural surfaces of sea objects.
- Print Speed: Print speed is very interesting as it varies greatly with design complexity; however, maintaining the determinants of motion parameters at the design stage remains an impediment to superior surface qualities of the finishing surface.
- Build Volume: The design requires more build volume due to its dense sweeping contours and overall size, which permits the production of several parts from the same production cycle.
- Post-Processing: After printing, finish enhancement through post-processing, such as sanding and polishing, is done for comfort application purposes.
- Modularity: The chair may have a couple or more sections, making transportation and encapsulation easier.
In a nutshell, the Batoidea Chair embodies how spatial organizing constraints arising from 3D printing technology can be exploited to design not just new but aesthetically pleasing and useful objects, go beyond the traditional furniture-making approach, and practice sustainable development via additive manufacturing.
What Is the Role of Nagami in 3D Printing?
Nagami is particular because it is one of the leaders in combining building and aesthetics to create functional furniture such as the Batoidea Chair. Most of the motivation is evident in the following technical parameters, which improve 3D printing functionalities.
- Advanced Design Philosophy: This manufacturer is more interested in products that solve practical requirements than in creating beauty, which 3D printing can enhance by increasing the prospects of application in the market.
- Sustainable Practices: They appreciate the need to incorporate green materials throughout their manufacturing processes, positively impacting industry sustainability.
- Adaptation of Technologies: Nagami applies modern technologies in 3D printing to ensure that most of its models can go into deep-level production with active quality checks.
- Collaborative Approach: Nagami undergoes the collaborative creativity process to transform the 3D printing scene for the better premium on architectural and product design really getting a balanced variation of styles and ideas.
- Customization and Personalization: In addition, great flexibility is possible as 3D printing technology enables the manufacture of unique products by client specifications, thus addressing personal needs while reducing excess production.
Overall, Nagami represents the possibilities embedded within 3D printing in terms of improving the design of mass-produced furniture and, more importantly, promoting sustainable, ethical mass production and enabling productive collaborations that can reshape the field altogether.
Which Are Emerging in 3D Printing for Interior Spaces?
Emerging objects in 3D printing for interior spaces blend both efficiency and the creativity process from the inventive aspect to conceal the embarrassing contrast of the fashions. I have listed some gadgets trending from the leading media research in this area.
- Customized Furniture: Design furniture such as tables and seats can be made to meet specific space and style needs. Consumers can order a more suitable design for the owners’ interiors through the technical parameters of customization and personalization.
- Decorative Wall Panels: Such panels are purposeful in decor and acoustic elements, practicing the Advanced Design Philosophy, universal structural dynamic approach, and artistic approaches to design patterns that embellish and enhance sound through intricate forms.
- Lighting Fixtures: At the forefront among lamps and chandeliers made through additive manufacturing are shapes that conventional manufacturing processes cannot imitate. This is helped by Advanced Manufacturing Technology and the like, which assures accuracy and details of the product when it is being made.
- Planters and Greenery Holders: New creations motivate the use of vegetation in the interiors of residential places, exemplifying sustainable development principles in practice through the use of green products, such as bioplastic materials.
- Artistic Sculptures. These items convert spaces into art galleries, and artistic work is valued within a collaborative approach where the designers create narratives and one-of-a-kind sculpture installations.
All of these new objects demonstrate the concurrent use of innovative 3D printing technologies and a green design thinking philosophy, which represents reasonable progress in interior design and production.
What Are the Effects of 3D Printing Technology on Manufacturing Processes?

Conventional manufacturing processes benefit from 3D printing because it provides more scope for innovation and the ability to perform complex tasks without limitation. Conventional methods of manufacturing practices usually employ a subtractive approach which is wasteful compared to 3d printing which is an additive manufacturing method. This minimizes the waste of materials and opens the possibility of fabricating structures whose external shapes would be difficult, if not impossible, to obtain with normal methods. In addition, the technology reduces the time between the initial design phase and the final product by allowing designers to create a physical model in a short time. To conclude, it can be said that 3D printing encourages the way of making things in the industry by providing enhanced personalization concerning lead times and cost effectiveness in manufacturing.
What Are the Limitations of Traditional Manufacturing Compared to 3D Printing?
I was able to find out several disadvantages of traditional manufacturing processes compared to 3D printing. To begin with, conventional techniques apply secondary tools, which involve more setups and set-ons, resulting in more time and costs. For instance, injection molding always entails the production of chips, which also takes weeks and lots of money. On the other hand, 3d printing can potentially apply design changes without a new tooling being created.
In addition to this, traditional manufacturing has limited capacity for personalization. Manufacturing one-off or low-quantity products is very costly; with 3D printing, however, personalization is very cheap since it just involves changing the computerized model. In addition, conventional means are limited in the material type used and the features’ complexity to achieve. Cnc machines for instance, only accepted designs that fell within a certain dimension and tolerances. On the other hand, using 3d printing allows one to make more complicated models, and more types of materials can be used, such as plastics, metals, carbon-fiber composites, and biomaterials.
Lastly, when producing through the traditional way of manufacturing, there is always a huge wastage factor. For example, subtractive methods may lead to up to ninety percent waste of the material during manufacture owing to mere cut and pound technique. However, the additive feature of 3D printing addresses this limitation, and hence is more suitable for responsible manufacturing. This transition is not only good for the environment but also ultimately cut down on material costs. Overall, these limitations demonstrate the paradigm-changing potential of 3D printing.
How Does Enabling On-Demand Production with 3D Printing Work?
3D printing, on the other hand, enables the production of a product whenever there is a need for it without holding an excessive amount of stocks. It also allows manufacturing to take place as a response to the precise needs of clients. From the studies I conducted through the leading sites based on these facts, it seems that this technology works well when there is subject to change volatility for the market and the customer demand. For instance, rather than having to wait until a large number of products are made, companies can go ahead and order for the product by printing only what is needed.
Key technical parameters include:
- Build Volume is defined as the volumetric capacity of any object created using the machine, which will determine the level of flexibility available in production. Several 3D printers are also designed to print different dimensions, from small electronics to bigger parts.
- Layer Height: This is also understood as the thickness with which one layer gets printed, typically in the range of 50 to 400 microns. Smaller layer heights increase resolution and yield smoother surfaces, improving the quality of the tailored products.
- Print Speed: This parameter affects the rate of production. Some high-grade 3D printers produce parts so fast that they can be submitted as on-demand orders.
- Material Variety: The capability of working with different types of material—plastics, metals, and ceramics—allows manufacturers to satisfy certain functional needs for various uses without creating custom molded parts or tooling.
Thanks to these technical features, companies can adapt their production arrangements, maximize efficiency, and minimize waste while improving the speed and customization of the offered goods.
What Are the Aspects of Interior Design That Hinder the Use of 3D Printing Technology?
As an interior designer who seeks—rather than imagines—a future where 3D printing is integrated into every aspect of design, I face various challenges that affect the design and execution of projects.
- Material Restrictions: Though 3D printing provides many materials, not all will apply to the house’s interior. The options are always a combination of the two, where the options are durable yet visually disappointing. For example, although plastic has a reasonable range of shaping capabilities, it may not always have the desired look or strength.
- Print Speed and Efficiency: Even though some advanced technology 3D printers achieve higher speeds, production time, especially when making large or complex items, can still be a limiting factor. It is tricky to avoid disappointment with clients’ deadlines and material waste because speed varies depending on the different models and their design characteristics.
- Layer Height and Detail: Mediation of the detail level impacts the interior outlook, which is very important. The layer height also has to be corrected up to certain limits since failure to do that means some lines will be left behind, which detracts from the design.
- Build Volume: Another limitation is the maximum size of pieces that can be printed. Regarding quite large constructions, some parts within the construction might need to be built in segments, which complicates the assembly process and makes the appearance of the building disintegrated.
- Cost and Investment: Although most of the costs in 3D printing may be controlled and avoided in the long run, more finances are needed at the beginning to acquire good machines and quality materials. Avoiding this expenditure from the project costs is not pleasing to everyone.
By overcoming such challenges and keeping in mind some of the technical details mentioned above, I believe I will be able to better use 3D printing technology to increase flexibility in design while simultaneously satisfying clients’ needs.
What Are the Future Trends in the Process of 3D Printing Related to Interior Design?

While projecting myself in the future of 3D printing applied to the interior design field, there are quite a few trends one can notice. Firstly, applying green materials is very likely to be prioritized as society moves to greener alternatives, as there’s more consumer influence. Besides, there will be improvements in multi-material printing, which will help me create designs with better functional and aesthetic attributes as they will have more complex textures. The impact of on-demand production will lead to more production that is targeted at specific clients and less wastage. Also, there is likely to be increased adoption of large-scale additive manufacturing technologies, which would change the way building interiors are envisaged or built by enabling the fabrication of the entire room geometry or core walls of the structure within the interior itself. Last but not least, artificial intelligence will lower the entry barriers of converting ideas into products through design and printing leading to various styles and efficiencies entering the market, adding a further dimension of novelty to the interior design industry.
What Can Be Said About the Next Decade of Development of 3D Printing Technology?
When I consider all the factors that could influence the development of 3D printers in the next 10 years, it is apparent that there will be a total change in the industry as there will be enhanced opportunities. One of the emerging aspects will be improving the speed and efficiency of printing through hardware and software enhancements, which will shorten the time to create while sustaining quality. It is believed that materials science will progress shortly and provide new materials that are stronger, lighter and more useful enabling me to explore new design options that were not possible before.
In addition, the decision-making process will be made more efficient and the time wastage eliminated, especially with cloud-based design services. New designs are set collaborations that allow clients and designers to communicate throughout the projects can be completed in a shorter time. This will be essential in ensuring that about 40%-50% design concepts will be optimized in terms of outside appearance and physical structure when AI based design tools are used. Lastly, with the green trend being embraced globally and as our industry shifts towards sustainable practices, improvements in bio-degradable as well as recyclable materials will enhance consumer satisfaction and bring about lower pollution.
Technical parameters supporting these advances will include:
- Layer resolution: Expect improvements in how fine layers can be printed, enhancing detail and accuracy.
- Material compatibility: Progress in multi-material abilities will enhance the coherence and comprehension in designs.
- Software algorithms: The more complex models of splitting and routing that are to be designed will contribute to better printing efficiency.
- Print head technology: New advances in multi-print head systems, such as dual ones, are expected to help introduce many materials in one printing, thus complicating the designs.
I can effectively apply 3D printing technology to interior design works by focusing on these developments.
What Are the Expected Effects of 3D Printing on Home Décor?
The impact of 3D printing on home décor will be considerable in many ways. It also allows for a much higher level of personalization which enables me to craft different designs to suit people as well as their settings. As the layer resolution improves, I am able to do complex designs which help improve the décor. Advanced material compatibility will mean I am able to use several materials on one piece of work making it functional and stylish all at once.
Additionally, I have observed that with the invention of better software algorithms, the overall effectiveness of the design process will also improve, leading to a high speed of item production and high quality. Advancements in print head technology mean that any print can be done using more than one material, adding the chance to create many more contemporary designs.
The future promising impact of 3D Printing on the scope of home decoration can be encompassed by the following technical parameters:
- Customization: Ready-made designs for consumers that are suitable for individual style expression or a specific piece of furniture.
- Layer resolution: Increasing resolution means more detail and quality nourishment for the décor items.
- Material compatibility: By incorporating many materials, better design centers on structures’ functionality.
- Software algorithms: Redesign to achieve time efficiency by reducing wasted steps and time.
- Print head technology: New ways of printing enable the creation of complex designs that allow using several materials to achieve sculptural designs.
Henceforth, it strengthens my conviction in 3D printing as a technological modality that will foster creativity in home décor and streamline my design practices to more efficient orientations.
How Do You Think Sustainability Will Impact the Future 3D-Printed Designs?
The concern for sustainability will be one of the leading challenges and factors in the future of 3D printed designs rather than just a movement as it will facilitate the research on and utilization of green materials and methods. As I assess the materials of leading websites on this subject, it is obvious that historical designing factors, including materials used by consumers, are shifting towards consumer focus on sustainability. This evolution will manifest through several key technical parameters:
- Material sourcing: Biodegradable and recycled materials will enable my designs to lower their carbon footprint and pollution generation and also benefit green consumers.
- Energy efficiency: There are also developments in 3D printing technology that will seek to minimize energy consumption…
- Waste reduction: Consequently, less excess material will be applied in precision printing, thus reducing the economy’s waste of materials.
- Local production: It is also apparent that because of this internal fixation towards the printables, there will be a shorter transportation footprint and impact on logistics since production shall now be done best nearer to where it will be utilized.
- Design for disassembly: I will improve recycling and product lifespan by designing products that are easy to strip down. Thus, less waste will fill landfills.
The responsible practices I use in my design philosophy should translate to more responsible growth in the home decoration business while making my designs more marketable in light of the increasing trend toward sustainability.
Conclusions

There is every reason to believe that the advent of 3D printing will transform the conventional approach to interior design. Not only can such marvels of technology impact on the design itself through the use of complex and adaptable designs, it also stresses the need for sustainable measures within the sector. Emphasizing sustainable materials, energy-saving designs and production, and local manufacturing where possible, I can create a very relevant design that captures modern-day ethics and environmental concerns. Currently, it is developing at such pace that it allows the implementation of new approaches that would keep the interior design appealing and responsible to the environment. In these ways, 3D printing will also serve as an instrument of creating and developing stylish and consistent sustainable environments.
Reference sources
- Berman, B. (2012). “3-D Printing: The New Industrial Revolution.” Business Horizons, 55(2), 155-162.
This article explores the impact of 3D printing technology on manufacturing, including applications in interior design, and discusses its potential to revolutionize various industries.
- Rüther, P., & Silva, T. (2018). “The Role of 3D Printing in Sustainable Design.” Journal of Design Research, 16(3), 199-209.
This paper examines 3D printing’s contribution to sustainable design practices, highlighting environmental benefits and the ability to create custom solutions that minimize waste.
- Kreiger, M., & Stevens, C. (2020). “Innovative Approaches in Interior Design: The Fusion of 3D Printing and Sustainability.” International Journal of Interior Architecture and Spatial Design, 10(1), 45-58.
This research provides insights into how 3D printing can be integrated into interior design with a focus on sustainability and customizability, reinforcing its feasibility as discussed in the previous sections.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)

1. What is 3D printing in interior design?
3D printing in interior design refers to the use of additive manufacturing technology to create three-dimensional objects and components that can be integrated into design projects. This can include a wide range of items, from furniture to decorative elements, allowing for customization and efficiency in production.
2. How does 3D printing contribute to sustainability in interior design?
3D printing significantly reduces waste in the manufacturing process by creating objects layer by layer, which minimizes excess material. Additionally, the ability to produce items on demand means there is less overproduction, which contributes to a more sustainable approach in design practices.
3. What materials are commonly used in 3D printing for interior design?
Common materials include biodegradable plastics, resins, and even concrete composites, depending on the finished product’s desired aesthetic and functional qualities. Each material offers unique benefits that can enhance the overall design.
4. Can 3D printing produce large-scale items for interior spaces?
Yes, 3D printing technologies have evolved to create larger components and even entire structures. This includes architectural features, wall panels, and bespoke furniture tailored to specific spatial requirements.
5. How can I incorporate 3D printing into my interior design project?
Consider collaborating with designers and firms that specialize in 3D printing technology. You can explore bespoke pieces that reflect your individual style or utilize 3D-printed components to enhance existing designs with innovative solutions.