How is 3D Printing Used in the Aerospace Industry?

Image source: https://amfg.ai/
What Role Do 3D Printers Play in Aerospace Manufacturing?
Which Aerospace Components are Typically 3D Printed?
How Does Additive Manufacturing Improve the Aerospace Manufacturing Process?
What Are the Benefits of Using 3D Printing in Aircraft Manufacturing?
How Does 3D Printing Reduce Aircraft Part Production Time?
Are There Cost Advantages of 3D Printing for Aerospace Manufacturers?
How Does 3D Printing Enhance the Design Flexibility of Aircraft Components?
What Materials for 3D Printing are Best Suited for Aerospace Applications?
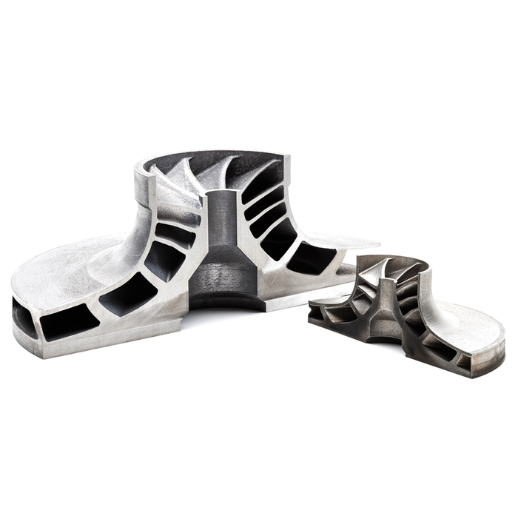

What Metals Are Commonly Used for 3D-Printed Aerospace Parts?
There are many metals that are typically used in making 3D printed aerospace parts because of their unique properties and performance at very high temperatures. The most common metal is titanium (specifically Ti6Al4V) with its outstanding strength-to-weight ratio, excellent resistance to corrosion and high temperature tolerance. Aluminum alloys such as AlSi10Mg are also commonly employed due to their lightness and strong mechanical properties. In addition, Inconel; a nickel-chromium superalloy, is highly regarded for its remarkable capacity to resist heat and oxidation which makes it suited for the engine components and other areas experiencing extreme conditions. This group of metals allows lightweight, long lasting & high performing aerospace parts using 3D printing.
Are There any Plastics That Are Suitable for Aircraft Interiors?
Yes, there are some plastics that can be used on aircraft interiors because they have special characteristics. Some major materials include polycarbonate (PC), known for its durability and shock resistance which makes it commonly employed in windows or seating. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is another type of plastic that is widely used as it has good toughness, ease of processing and cost effectiveness hence suitable for internal panels fittings among others. Moreover, Polyphenylsulfone (PPSU) exhibits exceptional flame retardancy, chemical stability and durability; therefore it is often utilized in applications subjected to strict safety standards requiring high performance levels. These materials give contemporary airline interiors both robustness as well as flexibility in their design requirements.
How is 3D Printing Transforming Aircraft Interior Design?
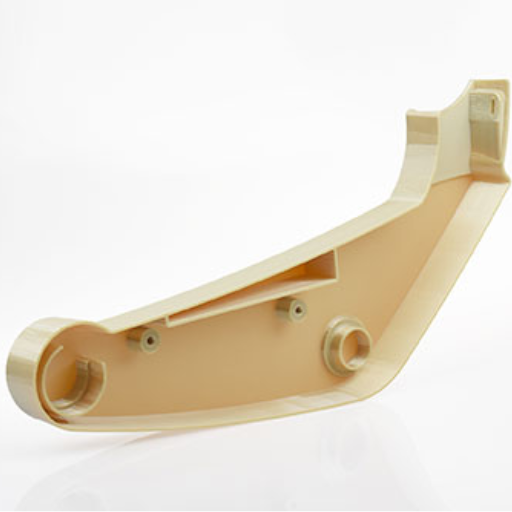

Which Aircraft Interior Parts Benefit from 3D Printing?
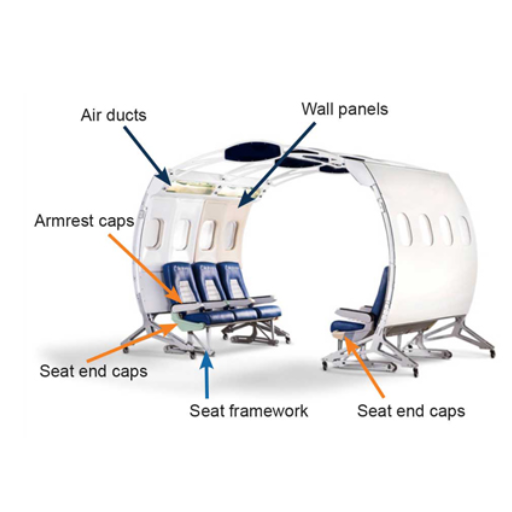
A number of aircraft interior parts derive immense benefits from 3D printing technology. The seat frames and armrests can be personalized in order to bring both comfort and reduce the weight, hence enhancing passenger experience and improving fuel efficiency. Similarly, the cabin dividers and overhead bin components are optimized by use of 3D printing which helps them to have better structural integrity as well as design flexibility. In addition, air ducts and ventilation systems built by 3D printers exhibit superior performance since they are elaborate, thus leading to better airflow and less noise. These advancements contribute collectively to lighter and more effective aircraft interiors that meet safety requirements as well as look good.
How Does 3D Printing Improve Passenger Comfort and Safety?
In this paper, there are a number of ways in which the comfort and safety of passengers has been improved through the aid of 3D printing. For instance, it allows for the production of ergonomically designed seats that fit each individual passenger thereby increasing passenger satisfaction during flights. Additionally, such seats may also feature zones with flexibility as well as cushioning tailored for long trips hence decreasing pressure points while promoting good posture. Moreover, personal air vents or other cabin amenities guarantee a tailor-made flying experience for the travelers.
What Are Key Challenges in 3D Printing for Aerospace?
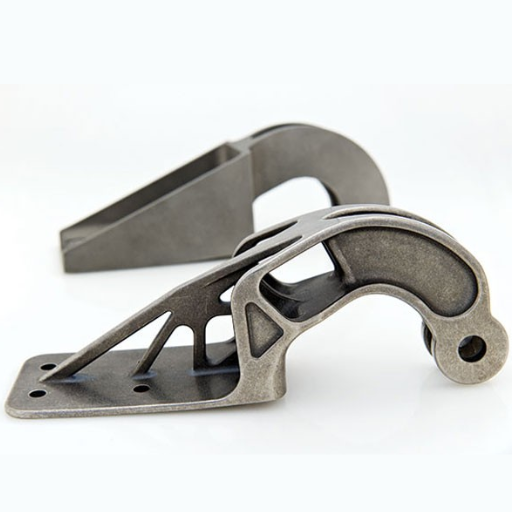

What Quality Control Measures Are Needed for 3D-Printed Aircraft Parts?
To ensure that parts meet rigorous safety and performance standards, quality control for 3D-printed aircraft parts calls for a multidimensional approach. First of all, demanding material selection procedures and testing protocols must be established to ensure that properties are consistent. This would entail pre-production tests to confirm the conformance of materials against required specifications and conformity checks in post –production.
Additionally, meticulous checking methods such as non-destructive testing (NDT) or in-situ monitoring should be used. NDT techniques like ultra-sonic testing, X-ray inspection, surface finish analysis are used to identify internal faults and surface flaws without causing any harm to the component. In-situ monitoring is used during the process of printing thus allowing fast detection and correction of any faults.
Furthermore, It is important to have an accurate calibration plan for 3D printers to continue producing high quality outputs. The regular maintenance along with machine validation helps avoid inconsistencies due to malfunctions in the equipment.
Finally, comprehensive documentation and traceability of each part’s production history are crucial towards this end. This includes detailed records on material batches, print parameters setting results from inspections made and then corrective actions taken thereof. Such documents not only enhance responsibility but will also guarantee compliance with regulatory frameworks as well as industry certifications.
How Do Aerospace Regulations Impact the Use of 3D Printing?
The utilization and adoption of 3D printing technology in the industry is greatly affected by aerospace regulations. Some regulatory bodies, for example, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) have several rules to guarantee safety and reliability of additive manufacturing parts used in aircrafts. Below are some areas these guidelines cover:
- Certification and Qualification: Stringent certification standards must be met before any part can be printed using a 3D printing machine to ensure it is safe and performs optimally. These include material qualifi¬cation, process validation as well as proving repeatability and always consistent production.
- Stringent Testing Requirements: The aerospace regulations need that all 3-D printed parts go through extensive testing both at the material level and structural evaluation levels. This ensures that the printed components can withstand operational stresses and environmental conditions they will encounter in service.
- Quality Control and Traceability: Aimed at ensuring quality control of final products is achieved alongside traceability, this plays a crucial role. All aspects including raw materials sourcing should be documented according to regulation requirements towards full accountability from initial contact with suppliers to last inspection.
- Continuous Monitoring and Compliance: Consequently, companies should also update their systems continually since regulatory frameworks call for continued adherence to evolving standards or best practices in relation to additive manufacturing technologies.
What is the Future of 3D Printing in Aerospace?

Which Emerging 3D Printing Technologies Will Impact Aerospace?
Emerging three-dimensional printing technologies are about to take off in the aerospace industry and revolutionize the same. These include:
- Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS): This method employs laser sintering of powdered metals thereby enabling the production of intricate metallic parts that are significant in aerospace. The application of DMLS leads to weight savings and performance improvement on airplanes, spacecrafts through it’s ability to fabricate very complex geometries not realizable by traditional manufacturing techniques.
- Electron Beam Melting (EBM): Like DMLS, EBM also works by melting and fusing metal powders layer by layer using an electron beam. The technology has a particular benefit of producing high strength-to-weight ratio titanium alloy components which are mandatory for strong aerospace applications. It is possible to have faster build times and handle larger parts compared to other laser based systems.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Additive manufacturing process which includes building products layer by layer through extrusion of thermoplastic materials. FDM finds application in designing lightweight but tough plastic components, prototyping, and tooling for aircraft construction purposes. Advances in high-performance thermoplastics extend their usage areas into such interior as well non-critical elements where there is need for reducing weight.
How Can 3D Printing Help Meet Increasing Aerospace Industry Demands?
Reference sources
-
Vaughn College – Advancements in 3D Printing are Revolutionizing the Aerospace Industry
- This article discusses how major aerospace companies like SpaceX, Boeing, and Lockheed Martin are leveraging 3D printing technology to produce components for next-generation aircraft. It highlights the significant advancements and practical applications of 3D printing in aerospace.
- Source: Vaughn College
-
Corrotherm – How 3D Printing is Revolutionising the Aerospace Industry
- Corrotherm explores the transformative impact of 3D printing in aerospace, focusing on the ability to create parts that are either impossible or incredibly difficult to manufacture using traditional methods. The article provides insights into the benefits and innovative uses of this technology.
- Source: Corrotherm
-
Xometry – 6 Main Advantages of 3D Printing in The Aircraft Industry
- Xometry outlines the key advantages of 3D printing in aviation, including weight reduction, cost savings, and improved part performance. The resource offers a detailed explanation of how additive manufacturing is being utilized to enhance various aspects of aircraft production.
- Source: Xometry
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are some innovative ways 3D printing is used in aerospace?
A: 3D printing is revolutionizing aerospace by allowing manufacturers like Airbus to create complex geometries, reduce aircraft weight, and produce end-use parts quickly and cost-effectively. This technology is widely adopted in the design and manufacturing of both interior components and structural parts of aircraft.
Q: How does aerospace 3d printing benefit the aviation industry?
A: Aerospace 3D printing provides numerous benefits including reduced lead times, cost savings, increased design flexibility, and the ability to produce lighter and more efficient parts for aircraft. It also allows for rapid prototyping and the manufacture of spare parts on demand, significantly improving maintenance operations.
Q: What is the printing process like for aerospace 3D printing?
A: The 3D printing process in the aerospace industry involves creating digital models of parts, slicing the model into layers, and then using 3D printing machines to build the part layer by layer. Techniques such as metal 3D printing are often used to create durable and high-strength parts required for aircraft.
Q: Which are the best materials for 3D printing used in aerospace?
A: The best materials for 3D printing in the aerospace industry include metals like titanium and aluminum, which offer high strength-to-weight ratios. Polymers such as PEEK and PEI are also used for their lightweight and heat-resistant properties. These materials contribute to producing reliable and high-performance parts for aircraft.
Q: How is 3D printing transforming the production of parts for aircraft?
A: 3D printing allows for the production of complex and lightweight parts that are difficult or impossible to make using traditional manufacturing methods. This technology is used to produce both functional prototypes and end-use parts, enabling aircraft manufacturers to innovate and improve their designs quickly.
Q: What are some challenges faced in the adoption of 3D printing in the aerospace industry?
A: Challenges in adopting 3D printing for the aerospace industry include ensuring the quality and reliability of 3D-printed parts, meeting stringent regulatory requirements, and the high initial costs of 3D printing machines and materials. Despite these challenges, ongoing advancements are helping to overcome these barriers.
Q: Can 3D printing be used to create multiple parts at once for an aircraft?
A: Yes, 3D printing can manufacture multiple parts in a single printing session. This capability is particularly beneficial for producing spare parts and small batches of components, allowing for efficient use of materials and time while reducing waste.
Q: How does 3D printing contribute to reducing aircraft weight?
A: 3D printing contributes to reducing aircraft weight by allowing for the creation of lightweight structures with complex geometries that are optimized for strength and weight. This capability leads to significant fuel savings and improved overall efficiency of the aircraft.
Q: What types of 3D printing machines are used in the aviation industry?
A: The aviation industry uses various types of 3D printing machines, including selective laser sintering (SLS), electron beam melting (EBM), and fused deposition modeling (FDM). These machines are capable of producing parts with high precision and quality, suitable for aerospace applications.
Q: How do aircraft manufacturers implement 3D printing into their production lines?
A: Aircraft manufacturers implement 3D printing by integrating it into their design and production workflows. This involves using 3D printing to create prototypes, tooling, and functional parts, utilizing printing materials that meet aerospace standards, and continuously optimizing the 3D printing process to enhance efficiency and quality.








